Extended depth-of-field iris recognition system for a
... requirement was partially met by optimizing the Wavefront Coded element with an iris recognition algorithm inside the optimization loop [9]. This is particularly important in order to take into account the non-linear steps required for feature extraction and identification. Nevertheless, correct iri ...
... requirement was partially met by optimizing the Wavefront Coded element with an iris recognition algorithm inside the optimization loop [9]. This is particularly important in order to take into account the non-linear steps required for feature extraction and identification. Nevertheless, correct iri ...
Time-of-flight optical ranging system based on time
... Our time-of-flight ranging system uses standard TCSPC techniques and is shown in simplified schematic form in Fig. 1. A fraction ~;2%! of the laser output is split off and provides a timing signal that starts a time-to-amplitude converter ~TAC!. The remaining laser signal is directed toward the targ ...
... Our time-of-flight ranging system uses standard TCSPC techniques and is shown in simplified schematic form in Fig. 1. A fraction ~;2%! of the laser output is split off and provides a timing signal that starts a time-to-amplitude converter ~TAC!. The remaining laser signal is directed toward the targ ...
Two-Photon Excited Fluorescence Microscopy - Spectra
... powers due to high peak intensity. It can be shown that in order to induce the same fluorescence signal, the power of a CW laser has to be (τp fp)-1/2 higher than the average power of a pulsed laser where τp and fp are the pulse width and the repetition rate respectively. For example the fluorescenc ...
... powers due to high peak intensity. It can be shown that in order to induce the same fluorescence signal, the power of a CW laser has to be (τp fp)-1/2 higher than the average power of a pulsed laser where τp and fp are the pulse width and the repetition rate respectively. For example the fluorescenc ...
Direct Imaging of Transient Interference in a Optical Microscopy
... To analyze the interference phenomenon in a proof-of-concept configuration without the underlying detector array, NSOM is used to directly measure the evanescent field on the upper surface of the waveguide. The NSOM technique has been frequently used for optical waveguide characterization in light p ...
... To analyze the interference phenomenon in a proof-of-concept configuration without the underlying detector array, NSOM is used to directly measure the evanescent field on the upper surface of the waveguide. The NSOM technique has been frequently used for optical waveguide characterization in light p ...
Fibre Optics Material Choice?
... Transverse dimensions must not be much larger then wavelength. ...
... Transverse dimensions must not be much larger then wavelength. ...
Chapter 3 Fiber Optics and Integrated Optics
... e. Secure to interception f. Low power lost g. enormous capacity of transmission: WDM/ DWDM(Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing), Higher data rates over longer distances-- more “bandwidth” for internet traffic ...
... e. Secure to interception f. Low power lost g. enormous capacity of transmission: WDM/ DWDM(Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing), Higher data rates over longer distances-- more “bandwidth” for internet traffic ...
5 - www2
... biological samples is the optical coherence tomography. Images from different layers of a microorganism (e.g. cell) can be obtained with μm spatial resolution utilizing the coherence (and monochromaticity) of the laser in an arrangement similar to a Michelson interferometer (Fig. 5.7). The echoes of ...
... biological samples is the optical coherence tomography. Images from different layers of a microorganism (e.g. cell) can be obtained with μm spatial resolution utilizing the coherence (and monochromaticity) of the laser in an arrangement similar to a Michelson interferometer (Fig. 5.7). The echoes of ...
Optics in Confocal Microscopy
... NA and resolution For lenses in air NA = 1 / 2F, where F = the F number of the lens. (i.e. an objective of NA 0.5 has an F number of one). Ernst Abbe introduced this term because he realised that it is proportional to the (lateral) resolving power of the lens, according to the famous equation r = 0. ...
... NA and resolution For lenses in air NA = 1 / 2F, where F = the F number of the lens. (i.e. an objective of NA 0.5 has an F number of one). Ernst Abbe introduced this term because he realised that it is proportional to the (lateral) resolving power of the lens, according to the famous equation r = 0. ...
Lab Writeup Michelson(New)
... The image of M1 appears in line with M2 and may be either in front of or behind M2 (see Fig. 2). The complete theory, which must take into account the fact that the source is an extended source, shows that when M2, and the image of M1 are parallel, then monochromatic light produces an interference p ...
... The image of M1 appears in line with M2 and may be either in front of or behind M2 (see Fig. 2). The complete theory, which must take into account the fact that the source is an extended source, shows that when M2, and the image of M1 are parallel, then monochromatic light produces an interference p ...
MINIATURIZED FLUORESCENCE EXCITATION PLATFORM WITH OPTICAL FIBER FOR BIO-DETECTION CHIPS
... without Al coating and with Al coating as shown in Table 1. Samples 1 to 3 without Al coating were measured to average 31% reflectivity. Samples 4 to 6 with Al coating (100 nm thick) showed average 70% reflectivity. The visual optical shapes of the excitation light captured by the detector are shown ...
... without Al coating and with Al coating as shown in Table 1. Samples 1 to 3 without Al coating were measured to average 31% reflectivity. Samples 4 to 6 with Al coating (100 nm thick) showed average 70% reflectivity. The visual optical shapes of the excitation light captured by the detector are shown ...
The Michelson Interferometer
... In this experiment, the mercury source is used with a green filter so that we have a given wavelength, 0 546nm , incident on the beam-splitter. There is a cell of air placed along that arm of the interferometer which does not have the compensating plate. This cell is initially evacuated, and air ...
... In this experiment, the mercury source is used with a green filter so that we have a given wavelength, 0 546nm , incident on the beam-splitter. There is a cell of air placed along that arm of the interferometer which does not have the compensating plate. This cell is initially evacuated, and air ...
2011 Research Poster
... diffracts the laser beam and slightly increases the laser frequency. This slight increase in frequency between the two counterpropagating beams produces a standing wave that moves through, and extracts a fraction of atoms from the condensate. ...
... diffracts the laser beam and slightly increases the laser frequency. This slight increase in frequency between the two counterpropagating beams produces a standing wave that moves through, and extracts a fraction of atoms from the condensate. ...
Microwaves and Fiber Optics Summer 2013
... use a variety of techniques to optimize power flow or minimize reflections in transmission line systems and in particular become comfortable with the applications of the Smith Chart, ...
... use a variety of techniques to optimize power flow or minimize reflections in transmission line systems and in particular become comfortable with the applications of the Smith Chart, ...
Super-resolution Microscopy
... can be broadly categorized into two main approaches [1]. In the first approach, called “targeted switching and readout”, the illumination volume in a fluorescent sample is confined to a small region, which is much smaller than the diffraction-limited spot size. Stimulated emission depletion (STED) m ...
... can be broadly categorized into two main approaches [1]. In the first approach, called “targeted switching and readout”, the illumination volume in a fluorescent sample is confined to a small region, which is much smaller than the diffraction-limited spot size. Stimulated emission depletion (STED) m ...
1958: The divergence of the light field in optical media
... The most general relation for the divergence of the light vector is derived from the equation of transfer for an arbitrary optical medium, and is shown to yield a direct means of determining the volume absorption function in natural aerosols and hydrosols. It is also shown that a correct special •. ...
... The most general relation for the divergence of the light vector is derived from the equation of transfer for an arbitrary optical medium, and is shown to yield a direct means of determining the volume absorption function in natural aerosols and hydrosols. It is also shown that a correct special •. ...
PHYS 242 BLOCK 11 NOTES Sections 33.1 to 33.7 Geometrical
... bends toward the normal when it slows down (when υ decreases, n increases so θ decreases, Fig. 33.8a) and light bends away from the normal when it speeds up (when υ increases, n decreases so θ increases, Fig. 33.8b). (The right-angle symbols in Fig. 33.8c do not mean θa and θb are 90˚—rather, the in ...
... bends toward the normal when it slows down (when υ decreases, n increases so θ decreases, Fig. 33.8a) and light bends away from the normal when it speeds up (when υ increases, n decreases so θ increases, Fig. 33.8b). (The right-angle symbols in Fig. 33.8c do not mean θa and θb are 90˚—rather, the in ...
Fabry-Perot Interferometer FABRYPEROT.TEX KB 20020122
... K LAUS B ETZLER1 , FACHBEREICH P HYSIK , U NIVERSIT ÄT O SNABR ÜCK This short lecture note recalls some of the properties of Fabry-Perot interferometers. As an addition to textbooks, it may present some help to students working with such instruments. It is neither intended as a substitute for text ...
... K LAUS B ETZLER1 , FACHBEREICH P HYSIK , U NIVERSIT ÄT O SNABR ÜCK This short lecture note recalls some of the properties of Fabry-Perot interferometers. As an addition to textbooks, it may present some help to students working with such instruments. It is neither intended as a substitute for text ...
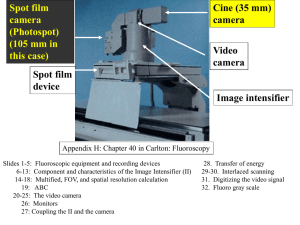
No Slide Title
... Question: How is a conventional fluoroscopic, analog imaging chain converted to digital? Answer: Measure the impulses from the camera with an analog to digital converter (ADC) and store the results in a computer. If the monitor is analog a digital to analog converter (DAC) must restore the analog s ...
... Question: How is a conventional fluoroscopic, analog imaging chain converted to digital? Answer: Measure the impulses from the camera with an analog to digital converter (ADC) and store the results in a computer. If the monitor is analog a digital to analog converter (DAC) must restore the analog s ...
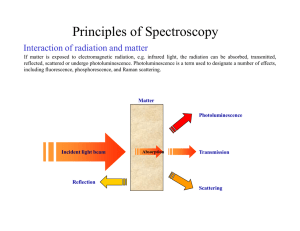
Principles of Spectroscopy
... 3) In grating spectrometers the spectrum S(ν) is measured directly by recording the intensity at successive, narrow, wavelength ranges. In FT-IR spectrometers all wavelengths from the IR source impinge simultaneously on the detector. This leads to the multiplex, or FELLGETT’S, advantage. The combina ...
... 3) In grating spectrometers the spectrum S(ν) is measured directly by recording the intensity at successive, narrow, wavelength ranges. In FT-IR spectrometers all wavelengths from the IR source impinge simultaneously on the detector. This leads to the multiplex, or FELLGETT’S, advantage. The combina ...
test - Lyle School of Engineering
... ANALYTICALLY) to determine what the spectral resolution of your optical system. Choose the cheapest lens (lowest performing) that will accomplish your goals. You may elect to “stop down” an aperture on a larger lens of lower quality if you only need the central portion of it. Note if you get stuck o ...
... ANALYTICALLY) to determine what the spectral resolution of your optical system. Choose the cheapest lens (lowest performing) that will accomplish your goals. You may elect to “stop down” an aperture on a larger lens of lower quality if you only need the central portion of it. Note if you get stuck o ...
Optical diffraction tomography for high resolution live cell imaging
... The quantitative refractive index maps thus obtained can be used to quantify molecular concentrations without adding fluorescence agents [23]. They also provide a means of studying the light scattering of single cells [24], which may lead to develop in-vivo light scattering instruments for disease d ...
... The quantitative refractive index maps thus obtained can be used to quantify molecular concentrations without adding fluorescence agents [23]. They also provide a means of studying the light scattering of single cells [24], which may lead to develop in-vivo light scattering instruments for disease d ...
Acknowledgments
... many cases these non-intrusive optical devices have significant advantages over physical probes that perturb the system that is being studied. Lasers are finding increasing use as machining and manufacturing devices. All types of lasers from continuous-wave lasers to lasers with femtosecond pulse le ...
... many cases these non-intrusive optical devices have significant advantages over physical probes that perturb the system that is being studied. Lasers are finding increasing use as machining and manufacturing devices. All types of lasers from continuous-wave lasers to lasers with femtosecond pulse le ...
Tristate and Gate Using Photonic Crystal
... Now a day’s photonics is a new research field and innovative domain till now most of the people don’t have the awareness about the emerging field. Photonics is the science of generating and harnessing light and other forms of radiant energy whose quantum unit is photon[1]. The science that includes ...
... Now a day’s photonics is a new research field and innovative domain till now most of the people don’t have the awareness about the emerging field. Photonics is the science of generating and harnessing light and other forms of radiant energy whose quantum unit is photon[1]. The science that includes ...
Chapter 19 Reading Quiz
... the focal length of the eyepiece is increased. the distance between the objective lens and eyepiece is decreased. ...
... the focal length of the eyepiece is increased. the distance between the objective lens and eyepiece is decreased. ...
Optical coherence tomography

Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an established medical imaging technique that uses light to capture micrometer-resolution, three-dimensional images from within optical scattering media (e.g., biological tissue). Optical coherence tomography is based on low-coherence interferometry, typically employing near-infrared light. The use of relatively long wavelength light allows it to penetrate into the scattering medium. Confocal microscopy, another optical technique, typically penetrates less deeply into the sample but with higher resolution.Depending on the properties of the light source (superluminescent diodes, ultrashort pulsed lasers, and supercontinuum lasers have been employed), optical coherence tomography has achieved sub- micrometer resolution (with very wide-spectrum sources emitting over a ~100 nm wavelength range).Optical coherence tomography is one of a class of optical tomographic techniques. A relatively recent implementation of optical coherence tomography, frequency-domain optical coherence tomography, provides advantages in signal-to-noise ratio, permitting faster signal acquisition. Commercially available optical coherence tomography systems are employed in diverse applications, including art conservation and diagnostic medicine, notably in ophthalmology and optometry where it can be used to obtain detailed images from within the retina. Recently it has also begun to be used in interventional cardiology to help diagnose coronary artery disease. It has also shown promise in dermatology to improve the diagnostic process.