2-6 Solving Literal Equations for a Variable
... Check It Out! Example 1 Solve the formula d = rt for t. Find the time in hours that it would take Van Dyk to travel 26.2 ...
... Check It Out! Example 1 Solve the formula d = rt for t. Find the time in hours that it would take Van Dyk to travel 26.2 ...
Electromagnetic waves in vacuum.
... Polarization of EM waves The two classes of solutions (Ex,By) and (Ey,Bx) are independent: they represent the two polarization modes of EM radiation. As the E and B fields lie on a plane, these modes correspond to linear polarizations. A generic (unpolarized) EM wave is a superposition of the two m ...
... Polarization of EM waves The two classes of solutions (Ex,By) and (Ey,Bx) are independent: they represent the two polarization modes of EM radiation. As the E and B fields lie on a plane, these modes correspond to linear polarizations. A generic (unpolarized) EM wave is a superposition of the two m ...
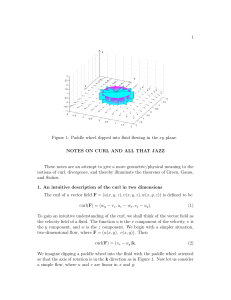
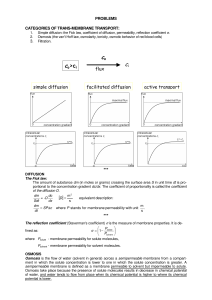
Flow Measurement
... substantial obstruction into the flow path to measure the flow. For this reason, these devices are used only when an obstruction does not cause any unwanted reaction on the flow system ...
... substantial obstruction into the flow path to measure the flow. For this reason, these devices are used only when an obstruction does not cause any unwanted reaction on the flow system ...
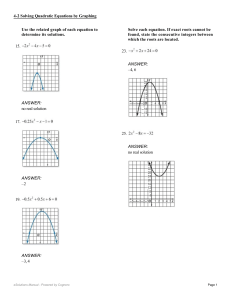
Solve the equation.
... To find solutions, perform inverse operations until you have isolated the variable. A variable is isolated when it appears by itself on one side of an equation, and not at all on the other side. Inverse Operations ...
... To find solutions, perform inverse operations until you have isolated the variable. A variable is isolated when it appears by itself on one side of an equation, and not at all on the other side. Inverse Operations ...