UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
... We have learned many things about elementary particles in the history of science. But by discovering new features about nature also new puzzles emerged. This is how science works: answers create puzzles which need to be answered again. Today, several big puzzles remain to be solved. Two puzzles will ...
... We have learned many things about elementary particles in the history of science. But by discovering new features about nature also new puzzles emerged. This is how science works: answers create puzzles which need to be answered again. Today, several big puzzles remain to be solved. Two puzzles will ...
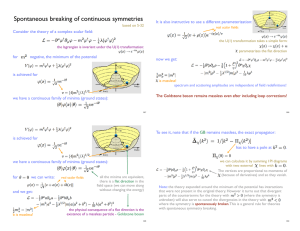
Spontaneous breaking of continuous symmetries
... (because of derivatives) and so they vanish. Note: the theory expanded around the minimum of the potential has interactions that were not present in the original theory. However it turns out that divergent parts of the counterterms for the theory with (where the symmetry is unbroken) will also serve ...
... (because of derivatives) and so they vanish. Note: the theory expanded around the minimum of the potential has interactions that were not present in the original theory. However it turns out that divergent parts of the counterterms for the theory with (where the symmetry is unbroken) will also serve ...
Ch - cmpascience
... 1. Explain Dalton’s atomic theory, and describe why it was more successful than Democritus’s theory. 2. State the charge, mass, and location of each part of an atom according to the modern model of the atom. 3. Compare and contrast Bohr’s model with the modern model of an atom. Dalton’s Theory 1. Ev ...
... 1. Explain Dalton’s atomic theory, and describe why it was more successful than Democritus’s theory. 2. State the charge, mass, and location of each part of an atom according to the modern model of the atom. 3. Compare and contrast Bohr’s model with the modern model of an atom. Dalton’s Theory 1. Ev ...
File 3
... The atomic nucleus In addition to the “discovery” of the nucleus and of the proton, Rutherford also noted the need of a “neutral” particle in the atomic nucleus, due to the disagreement between the atomic number of an atom (number of positive charges) and its mass computed in atomic mass units. In ...
... The atomic nucleus In addition to the “discovery” of the nucleus and of the proton, Rutherford also noted the need of a “neutral” particle in the atomic nucleus, due to the disagreement between the atomic number of an atom (number of positive charges) and its mass computed in atomic mass units. In ...
L1-The Atom
... Atoms in compounds combine, separate, or rearrange in normal chemical reactions to form new compounds. Atoms of an element are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions. ...
... Atoms in compounds combine, separate, or rearrange in normal chemical reactions to form new compounds. Atoms of an element are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions. ...
Untitled
... of electric or gravitational origin, although in many respects they are similar to the electro-magnetic interaction. In particular they act through some kind of charges, of which there are however three types, instead of one as in the electromagnetic case. To distinguish them these charges are repre ...
... of electric or gravitational origin, although in many respects they are similar to the electro-magnetic interaction. In particular they act through some kind of charges, of which there are however three types, instead of one as in the electromagnetic case. To distinguish them these charges are repre ...
The Differential Geometry and Physical Basis for the Application of
... Aharonov-Bohm effect, gauge theory, Yang Mills Theory, Feynman diagrams The design of a commemorative stamp tells a wonderful story. The Feynman diagrams on it show how Feynman’s work, originally applicable to QED, for which he won the Nobel Prize, was then later used to elucidate the electroweak fo ...
... Aharonov-Bohm effect, gauge theory, Yang Mills Theory, Feynman diagrams The design of a commemorative stamp tells a wonderful story. The Feynman diagrams on it show how Feynman’s work, originally applicable to QED, for which he won the Nobel Prize, was then later used to elucidate the electroweak fo ...
Spinless Fermions with Repulsive Interactions
... to deal with it. The Fermi arcs seen in angular-resolved photoemession (ARPES) measurements and the quantum oscillations seen under extremely high magnetic field also lacks a coherent theoretical framework. Moreover, we have yet to have a theory (excluding holographic dual from gravity) which predic ...
... to deal with it. The Fermi arcs seen in angular-resolved photoemession (ARPES) measurements and the quantum oscillations seen under extremely high magnetic field also lacks a coherent theoretical framework. Moreover, we have yet to have a theory (excluding holographic dual from gravity) which predic ...
Document
... Symmetry makes some d.o.f. redundant: A0,r¢A are c-numbers. Gauge fixing necessary to quantize theory. Symmetry dictates form of allowed interactions. Gauge fields selfinteract, hence single universal coupling for each group –g Ja Aa Symmetry permits the renormalization of gauge theory Symmetry fo ...
... Symmetry makes some d.o.f. redundant: A0,r¢A are c-numbers. Gauge fixing necessary to quantize theory. Symmetry dictates form of allowed interactions. Gauge fields selfinteract, hence single universal coupling for each group –g Ja Aa Symmetry permits the renormalization of gauge theory Symmetry fo ...