Polarization of light II
... This fact can be used to get a polarised beam of light from an unpolarised beam. An unpolarised beam is made to incident at an interface at Brewster angle. The reflected beam will contain the s component only. In this experiment , you will study the variation of intensity as a function of angle of ...
... This fact can be used to get a polarised beam of light from an unpolarised beam. An unpolarised beam is made to incident at an interface at Brewster angle. The reflected beam will contain the s component only. In this experiment , you will study the variation of intensity as a function of angle of ...
Plane Mirrors
... Incident Ray: The ray of light that travels ____________ the mirror. Reflected Ray: The ray of light that travels ________________ the mirror. Normal to: _____________________. Image: An optically formed duplicate, counterpart, or other representative reproduction of an object, especially an optical ...
... Incident Ray: The ray of light that travels ____________ the mirror. Reflected Ray: The ray of light that travels ________________ the mirror. Normal to: _____________________. Image: An optically formed duplicate, counterpart, or other representative reproduction of an object, especially an optical ...
setting up of a total internal reflection fluorescent microscope
... The green curve in Fig. 6b indicates the spectrum of Dichromatic beamsplitter (dichroic mirror) which is a specialized filter designed to efficiently reflect excitation wavelengths and pass emission wavelengths. These filters are always the interference type. Dichroic mirror is positioned in the lig ...
... The green curve in Fig. 6b indicates the spectrum of Dichromatic beamsplitter (dichroic mirror) which is a specialized filter designed to efficiently reflect excitation wavelengths and pass emission wavelengths. These filters are always the interference type. Dichroic mirror is positioned in the lig ...
Historical burdens on physics 54 Coherence of waves
... that does not mean that coherence or incoherence is a property of the source. 2. Coherence is a local property of the light. That means that a given light distribution can be more coherent at one place than at another. So the spacial coherence of the light that is emitted by a star is minimum at the ...
... that does not mean that coherence or incoherence is a property of the source. 2. Coherence is a local property of the light. That means that a given light distribution can be more coherent at one place than at another. So the spacial coherence of the light that is emitted by a star is minimum at the ...
Parhelic-like Circle and Chaotic Light Scattering
... 4 The Parlaseric Circle Besides these phenomena, we also observed the formation of some caustics. One of these caustics is the light pattern involving the parlaseric circle [2], explained by the Theory of Geometrical Diffraction [3]. The parlaseric circle is a luminous ring generated by light scatte ...
... 4 The Parlaseric Circle Besides these phenomena, we also observed the formation of some caustics. One of these caustics is the light pattern involving the parlaseric circle [2], explained by the Theory of Geometrical Diffraction [3]. The parlaseric circle is a luminous ring generated by light scatte ...
10-GHz Bandwidth RF Spectral Analyzer With MHz Resolution
... gigahertz of bandwidth in battle field environment or (sub)millimeter astronomy shows the growing need in developing processing techniques able to analyze such signals. For instance, radio-frequency (RF) analyzers must have the capability to Fourier analyze multigigahertz (multi-GHz) signals (10 GHz ...
... gigahertz of bandwidth in battle field environment or (sub)millimeter astronomy shows the growing need in developing processing techniques able to analyze such signals. For instance, radio-frequency (RF) analyzers must have the capability to Fourier analyze multigigahertz (multi-GHz) signals (10 GHz ...
Laser Refraction and Diffraction
... As shown in Fig. 5, we extended the slit interference concept and considered a great amount of slits that were extremely narrow. When multiple-slit apparatus is illuminated by a ray, the resulting interference can be considered to be produced by numerous light point sources. Constructive interferenc ...
... As shown in Fig. 5, we extended the slit interference concept and considered a great amount of slits that were extremely narrow. When multiple-slit apparatus is illuminated by a ray, the resulting interference can be considered to be produced by numerous light point sources. Constructive interferenc ...
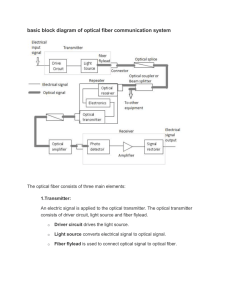
optical-fiber-communication-system
... It consists of a cable that provides mechanical and environmental protection to the optical fibers contained inside. Each optical fiber acts as an individual channel. o ...
... It consists of a cable that provides mechanical and environmental protection to the optical fibers contained inside. Each optical fiber acts as an individual channel. o ...
Interferometry
Interferometry is a family of techniques in which waves, usually electromagnetic, are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, remote sensing, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, and velocimetry.Interferometers are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of small displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In analytical science, interferometers are used in continuous wave Fourier transform spectroscopy to analyze light containing features of absorption or emission associated with a substance or mixture. An astronomical interferometer consists of two or more separate telescopes that combine their signals, offering a resolution equivalent to that of a telescope of diameter equal to the largest separation between its individual elements.