Supercomputing in High Energy Physics
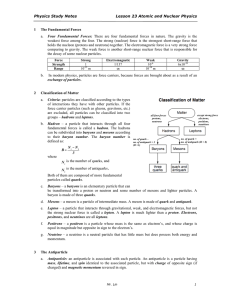
... • the patterns of fermion masses hint at deeper structures ...
... • the patterns of fermion masses hint at deeper structures ...
Reader Overview Table
... the order of their atomic weight, a periodic repetition of atomic weight ...
... the order of their atomic weight, a periodic repetition of atomic weight ...
Chapter 1 Section 1
... • Early scientists theorized that eventually you would not be able to cut it in half any more. o Only one particle would be left. o They named these particles ‘Atoms’ • Atoms means ‘cannot be divided’ • Scientists could not study this because they lacked the tools to see things this small. ...
... • Early scientists theorized that eventually you would not be able to cut it in half any more. o Only one particle would be left. o They named these particles ‘Atoms’ • Atoms means ‘cannot be divided’ • Scientists could not study this because they lacked the tools to see things this small. ...
atomic structure
... 1. atoms can gain or lose electrons 2. when they do they are now charged and thus cannot be called an atom: why ? 3. same # protons as original element/atom 4. different # electrons 5. mass ? 6. + (positive) = cation: gain or lose e-? Na+1, how many electrons? 7. - (negative) = anion: gain or lose e ...
... 1. atoms can gain or lose electrons 2. when they do they are now charged and thus cannot be called an atom: why ? 3. same # protons as original element/atom 4. different # electrons 5. mass ? 6. + (positive) = cation: gain or lose e-? Na+1, how many electrons? 7. - (negative) = anion: gain or lose e ...
Ch3 Video 2 pdf file
... Daughter nuclide is a different, lighter element (mass# decreases by 4) ...
... Daughter nuclide is a different, lighter element (mass# decreases by 4) ...
Study Notes Lesson 23 Atomic and Nuclear Physics
... € composed of antiparticles. Antimatter: The antimatter is a material consisting of atoms that are ...
... € composed of antiparticles. Antimatter: The antimatter is a material consisting of atoms that are ...
Parts of an Atom Power Point
... fixed path. Electrons are found in the Electron Cloud – the space in an atom outside the nucleus. Electrons are arranged in Energy Levels. An Energy Level is the most likely location in the Electron Cloud in which an electron can be found. ...
... fixed path. Electrons are found in the Electron Cloud – the space in an atom outside the nucleus. Electrons are arranged in Energy Levels. An Energy Level is the most likely location in the Electron Cloud in which an electron can be found. ...
6.6
... Unlike a free neutron, a free proton cannot decay into a neutron since the rest energy of a neutron is larger than that of a proton. ...
... Unlike a free neutron, a free proton cannot decay into a neutron since the rest energy of a neutron is larger than that of a proton. ...
Document
... Like photons and electrons, protons, neutrons, atoms, and even molecules have wave properties ...
... Like photons and electrons, protons, neutrons, atoms, and even molecules have wave properties ...
Oct 6
... “What is that evidence? Tracks of particles in a bubble chamber. In the Fermilab accelerator, the “debris” from a collision between a proton and an antiproton is captured by a 3 story, 60 million dollar detector. … “Here, the “evidence” – the “seeing” – is tens of thousands of sensors that develop a ...
... “What is that evidence? Tracks of particles in a bubble chamber. In the Fermilab accelerator, the “debris” from a collision between a proton and an antiproton is captured by a 3 story, 60 million dollar detector. … “Here, the “evidence” – the “seeing” – is tens of thousands of sensors that develop a ...
alice - STEM
... millionths of a second after the Big Bang. At ALICE it will last for less than 10-30 seconds before expanding and cooling into many particles. ...
... millionths of a second after the Big Bang. At ALICE it will last for less than 10-30 seconds before expanding and cooling into many particles. ...
ConceptQ35_Solutions
... A) 1 B) 1/1000 C) 1000 D) 1/2000 E) 2000 This time we are told the momentum is the same. Remember that p=mv, so if mv is the same and qB are the same, the radii are the same. A strong magnetic field points in the same direction as a beam of electrons. The electrons will be: A) Deflected up, B) Defle ...
... A) 1 B) 1/1000 C) 1000 D) 1/2000 E) 2000 This time we are told the momentum is the same. Remember that p=mv, so if mv is the same and qB are the same, the radii are the same. A strong magnetic field points in the same direction as a beam of electrons. The electrons will be: A) Deflected up, B) Defle ...
Section III: A World of Particles
... The atom is composed of even smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons. The protons and neutrons are located in the dense nucleus of the atom. The electrons surround the nucleus. Protons are positively charged, neutrons have no charge, and electrons are negatively charged. Science is ...
... The atom is composed of even smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons. The protons and neutrons are located in the dense nucleus of the atom. The electrons surround the nucleus. Protons are positively charged, neutrons have no charge, and electrons are negatively charged. Science is ...
What do the numbers 238, 235 written against the name of the
... manages to escape from the nucleus. When the particle is originally very localised in space, the level of uncertainty in its position is so small that it follows that the uncertainty of its velocity becomes very large, possibly much greater than one would have expected, and sufficient even to escape ...
... manages to escape from the nucleus. When the particle is originally very localised in space, the level of uncertainty in its position is so small that it follows that the uncertainty of its velocity becomes very large, possibly much greater than one would have expected, and sufficient even to escape ...
What is the dark matter?
... even if they do not “shine” as stars (nuclear fusion in the early universe would drastically overproduce Helium) ...
... even if they do not “shine” as stars (nuclear fusion in the early universe would drastically overproduce Helium) ...