Geometric Optics - Mr. Gabrielse's Physics
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (θi, the incidence angle) as it reflects off the mirror (θr, the reflection angle). ...
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (θi, the incidence angle) as it reflects off the mirror (θr, the reflection angle). ...
Geometric Optics
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (θi, the incidence angle) as it reflects off the mirror (θr, the reflection angle). ...
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (θi, the incidence angle) as it reflects off the mirror (θr, the reflection angle). ...
AcuityXR Technology Significantly Enhances Lateral Resolution of
... limited lateral resolution of optical systems.3,4 However, such methods have only been commercially successful in improving resolution when it is camera-pixel limited, such as is generally the case for satellite imagery or for reconstruction of scenes taken with a video camera. For improving diffrac ...
... limited lateral resolution of optical systems.3,4 However, such methods have only been commercially successful in improving resolution when it is camera-pixel limited, such as is generally the case for satellite imagery or for reconstruction of scenes taken with a video camera. For improving diffrac ...
Experimental demonstration of near-infrared
... epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) metamaterials have been studied to realize anomalous electromagnetic properties in microwave and optical frequency ranges. ENZ metamaterials can be used to squeeze and tunnel electromagnetic energy through narrow channels due to the extremely large wavelength they support [3 ...
... epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) metamaterials have been studied to realize anomalous electromagnetic properties in microwave and optical frequency ranges. ENZ metamaterials can be used to squeeze and tunnel electromagnetic energy through narrow channels due to the extremely large wavelength they support [3 ...
Asphere Metrology
... An asphere can be tested in the same way as a sphere if the departure from spherical is mild enough that the fringes formed by the interferometer do not violate the Nyquist condition, which states each fringe must cover two or more pixels for the pattern to be accurately resolvable by the sensor. A ...
... An asphere can be tested in the same way as a sphere if the departure from spherical is mild enough that the fringes formed by the interferometer do not violate the Nyquist condition, which states each fringe must cover two or more pixels for the pattern to be accurately resolvable by the sensor. A ...
[pdf]
... waves (DPDW) within the diffusion approximation. The new equation, which is developed for bounded turbid media does not explicitly contain any terms involving gradients of the light diffusion coefficient. We then use this integro-differential equation and develop a theoretical inverse scattering alg ...
... waves (DPDW) within the diffusion approximation. The new equation, which is developed for bounded turbid media does not explicitly contain any terms involving gradients of the light diffusion coefficient. We then use this integro-differential equation and develop a theoretical inverse scattering alg ...
Extended depth-of-field iris recognition system for a
... Figure 5 shows the experimentally-determined MTF of our iris recognition system without Wavefront Coded optics for various object positions. For the purpose of this discussion, we refer to our iris recognition system without Wavefront Coded optics as the traditional imaging system. The various curve ...
... Figure 5 shows the experimentally-determined MTF of our iris recognition system without Wavefront Coded optics for various object positions. For the purpose of this discussion, we refer to our iris recognition system without Wavefront Coded optics as the traditional imaging system. The various curve ...
Fundamental Limit to Linear One-Dimensional Slow Light Structures
... unity, and again we can conclude our limit exceeds that of Tucker et al. [7] in this case also. Despite having used none of the simplifying assumptions of Tucker et al. [7] (e.g., idealized linear dispersion, periodic structures of resonators, validity of group velocity concepts), we have derived a ...
... unity, and again we can conclude our limit exceeds that of Tucker et al. [7] in this case also. Despite having used none of the simplifying assumptions of Tucker et al. [7] (e.g., idealized linear dispersion, periodic structures of resonators, validity of group velocity concepts), we have derived a ...
Microscopy corrected
... 10. Now that you have focused on the cells using the 10X objective (100X total magnification = 10X ocular lens x 10X objective lens) rotate the set of lenses so that 40X or 45X objective, depending on your microscope, is over the slide. Now the magnification is 400X or 450X. The cells will still be ...
... 10. Now that you have focused on the cells using the 10X objective (100X total magnification = 10X ocular lens x 10X objective lens) rotate the set of lenses so that 40X or 45X objective, depending on your microscope, is over the slide. Now the magnification is 400X or 450X. The cells will still be ...
Light sheet-based fluorescence microscopy: more dimensions, more
... fluorescence microscopy, the illumination light excites fluorophores along the entire thickness of the specimen. In confocal fluorescence microscopy, the out-of-focus light is discriminated by the pinhole in front of the detector. So, most of the light is not detected but its damaging effects (in pa ...
... fluorescence microscopy, the illumination light excites fluorophores along the entire thickness of the specimen. In confocal fluorescence microscopy, the out-of-focus light is discriminated by the pinhole in front of the detector. So, most of the light is not detected but its damaging effects (in pa ...
4Pi Microscopy
... properties of the dye to break the diffraction barrier. Using two lenses for STED, the axial resolution was improved down to 30 to 50 nm (Dyba and Hell, 2002; Dyba et al., 2003). However, as STED is still in its infancy and, unlike I5M and 4Pi microscopy, relies on the specific properties of the dye ...
... properties of the dye to break the diffraction barrier. Using two lenses for STED, the axial resolution was improved down to 30 to 50 nm (Dyba and Hell, 2002; Dyba et al., 2003). However, as STED is still in its infancy and, unlike I5M and 4Pi microscopy, relies on the specific properties of the dye ...
biology 163 laboratory use of the compound light microscope
... being studied. Total magnification is the product of the magnifying power of the objective lens times the magnifying power of the ocular lens. Typical microscopes have four objective lenses (4X, 10X, 40X, and 100X) that can be rotated into position. Combined with a 10X ocular lens (standard on our m ...
... being studied. Total magnification is the product of the magnifying power of the objective lens times the magnifying power of the ocular lens. Typical microscopes have four objective lenses (4X, 10X, 40X, and 100X) that can be rotated into position. Combined with a 10X ocular lens (standard on our m ...
Lecture 10: Surface Plasmon Excitation
... Notes: Light intensity reflected from the back surface depends on the film thickness There exists a film thickness for perfect coupling (destructive interference between two refl. beams) When light coupled in perfectly, all the EM energy dissipated in the film) ...
... Notes: Light intensity reflected from the back surface depends on the film thickness There exists a film thickness for perfect coupling (destructive interference between two refl. beams) When light coupled in perfectly, all the EM energy dissipated in the film) ...
Amplitude and Phase of Tightly Focused Laser Beams in Turbid Media
... the focal spot along both lateral and axial dimensions [5]. Current formulations of diffraction theory, being limited to homogeneous media, cannot describe these important changes to the focal volume. Monte Carlo methods can be used to solve the radiative transport equation by simulating light propa ...
... the focal spot along both lateral and axial dimensions [5]. Current formulations of diffraction theory, being limited to homogeneous media, cannot describe these important changes to the focal volume. Monte Carlo methods can be used to solve the radiative transport equation by simulating light propa ...
Bright Field Microscopy
... frequently observed on large, extended objects such as extended or flattened cells, flattened nuclei, and planar slabs of materials, for example, mica or glass. • Center and the edges of an object diffract light differently. • In central regions, the amount of diffraction and the angle of scattering ...
... frequently observed on large, extended objects such as extended or flattened cells, flattened nuclei, and planar slabs of materials, for example, mica or glass. • Center and the edges of an object diffract light differently. • In central regions, the amount of diffraction and the angle of scattering ...
A1990DA63800001
... must typically be explored to find the singularity. Thom realized that his classification described optical caustics (via Fermat’s principle, according to which a family of light rays is a gradient map generated by the travel time function). In catastrophe theory an important idea is that the causti ...
... must typically be explored to find the singularity. Thom realized that his classification described optical caustics (via Fermat’s principle, according to which a family of light rays is a gradient map generated by the travel time function). In catastrophe theory an important idea is that the causti ...
Ultrahigh-resolution full-field optical coherence microscopy using
... reference reflector. Images from within the tissue are typically reconstructed by arithmetic combination of the resulting interference patterns at different reference arm path lengths [1]. The advantages of FFOCM compared with other reflectance-based optical sectioning techniques, including parallel ...
... reference reflector. Images from within the tissue are typically reconstructed by arithmetic combination of the resulting interference patterns at different reference arm path lengths [1]. The advantages of FFOCM compared with other reflectance-based optical sectioning techniques, including parallel ...
Chromatic and Monochromatic Aberrations
... (reference material: Keating 20.9-20.11, 20.15,20.16) Everything you have learned about object and image formation is an approximation. When light is refracted by spherical surfaces the rays do not all converge to a point, even if they are of one wavelength. Monochromatic aberrations can arise from ...
... (reference material: Keating 20.9-20.11, 20.15,20.16) Everything you have learned about object and image formation is an approximation. When light is refracted by spherical surfaces the rays do not all converge to a point, even if they are of one wavelength. Monochromatic aberrations can arise from ...
Sir Anthony James Leggett - International School of Photonics CUSAT
... one another in such a way as to perfectly cancel each other out. The discovery could pave the way for a number of novel technologies with applications in everything from optical computing to radiology. Conventional lasers, which were first invented in 1960, use a so-called "gain medium," to produce ...
... one another in such a way as to perfectly cancel each other out. The discovery could pave the way for a number of novel technologies with applications in everything from optical computing to radiology. Conventional lasers, which were first invented in 1960, use a so-called "gain medium," to produce ...
Immersion microscopy based on photonic crystal materials
... from Fig.1(e), which is also confirmed by the cross section through the image shown in Fig.1(f). This simple numerical example demonstrates that a far-field optical microscope with resolution beyond the λ/2 diffraction limit of usual optics can be built using photonic crystal materials. However, in ...
... from Fig.1(e), which is also confirmed by the cross section through the image shown in Fig.1(f). This simple numerical example demonstrates that a far-field optical microscope with resolution beyond the λ/2 diffraction limit of usual optics can be built using photonic crystal materials. However, in ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... Abstract: This paper presents an optical diffraction tomography technique based on digital holographic microscopy. Quantitative 2-dimensional phase images are acquired for regularly-spaced angular positions of the specimen covering a total angle of π, allowing to built 3-dimensional quantitative ref ...
... Abstract: This paper presents an optical diffraction tomography technique based on digital holographic microscopy. Quantitative 2-dimensional phase images are acquired for regularly-spaced angular positions of the specimen covering a total angle of π, allowing to built 3-dimensional quantitative ref ...
INDIAN SCHOOL DARSAIT
... State reason and also draw a ray diagram in support of your answer. Image with magnification -1 means image is inverted and of the same size. Therefore, object is at 2F and the image is also at 2F on the other side of the lens. Therefore, distance between the object and its image is 4f = 60 cm f = ...
... State reason and also draw a ray diagram in support of your answer. Image with magnification -1 means image is inverted and of the same size. Therefore, object is at 2F and the image is also at 2F on the other side of the lens. Therefore, distance between the object and its image is 4f = 60 cm f = ...
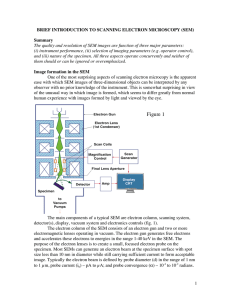
Introduction to Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
... The electron beam interacts with the specimen to a depth approximately 1 µm. Complex interactions of the beam electrons with the atoms of the specimen produce wide variety of radiation. The need of understanding of the process of image formation for reliable interpretation of images arises in specia ...
... The electron beam interacts with the specimen to a depth approximately 1 µm. Complex interactions of the beam electrons with the atoms of the specimen produce wide variety of radiation. The need of understanding of the process of image formation for reliable interpretation of images arises in specia ...
Noniterative Exact Solution to the Phase Problem in Optical Imaging Implemented with Scanning Probe Microscope.
... As is well-known, the basis for obtaining superresolution is multiple images.20 This of course can be obtained in a cumbersome way by moving the sample, which would require the accurate verification of the exact sample movement. This could be done in our method by the presence of an online AFM. Howev ...
... As is well-known, the basis for obtaining superresolution is multiple images.20 This of course can be obtained in a cumbersome way by moving the sample, which would require the accurate verification of the exact sample movement. This could be done in our method by the presence of an online AFM. Howev ...
Superlens

A practical superlens, or super lens, is a lens which uses metamaterials to go beyond the diffraction limit. The diffraction limit is a feature of conventional lenses and microscopes that limits the fineness of their resolution. Many lens designs have been proposed that go beyond the diffraction limit in some way, but there are constraints and obstacles involved in realizing each of them.



![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008852277_1-2045a3551aa6b77e10f6e1bfc991b19e-300x300.png)