Zero loss magnetic metamaterials using powered
... frequencies exhibiting loss (µr00 < 0) and others gain (µr00 > 0). As Vb increases, the real permeability exhibits a bandwidth of strong negative response and the character of the imaginary permeability changes as well. To demonstrate the specific ways in which the magnetic response of this particle ...
... frequencies exhibiting loss (µr00 < 0) and others gain (µr00 > 0). As Vb increases, the real permeability exhibits a bandwidth of strong negative response and the character of the imaginary permeability changes as well. To demonstrate the specific ways in which the magnetic response of this particle ...
Depth Estimation and Focus Recovery
... important kernels as Fresnel transform and fractional Fourier transform and so on. In words, LCT (defined as (3.1) (3.2) (3.3) (3.4)) is a representation of matrix which contains 4 parameters is formed from 3 freedoms as in (3.5). Commutative character does not hold in Matrix properties and so as t ...
... important kernels as Fresnel transform and fractional Fourier transform and so on. In words, LCT (defined as (3.1) (3.2) (3.3) (3.4)) is a representation of matrix which contains 4 parameters is formed from 3 freedoms as in (3.5). Commutative character does not hold in Matrix properties and so as t ...
Diffraction is…
... moving the screen changes size but not shape of diffraction pattern Next week: Fresnel (near-field) diffraction ...
... moving the screen changes size but not shape of diffraction pattern Next week: Fresnel (near-field) diffraction ...
"Contrast Enhancement in Light Microscopy". In: Current Protocols in
... specimen is conjugated to the field diaphragm and imaged by the objective into the real intermediate image plane, then projected by the eyepiece into infinity and reimaged by the detector’s objective (eye lens or camera lens) onto the final sensor (retina, film, or camera). There are several advanta ...
... specimen is conjugated to the field diaphragm and imaged by the objective into the real intermediate image plane, then projected by the eyepiece into infinity and reimaged by the detector’s objective (eye lens or camera lens) onto the final sensor (retina, film, or camera). There are several advanta ...
Fourier Optics
... given by xx/(f) where is the wavelength of the laser and f is the focal length of the Fourier transform lens. Because these distances are usually small, we will use a lens to magnify the Fourier transform. The relationship between the frequency and the distance is then given by ...
... given by xx/(f) where is the wavelength of the laser and f is the focal length of the Fourier transform lens. Because these distances are usually small, we will use a lens to magnify the Fourier transform. The relationship between the frequency and the distance is then given by ...
fourier optics - The Institute of Optics
... the thinking, creation, design, and understanding of novel or modern optical systems that one consider the input electric field E(r,t) and its intensity, proportional to E • E, and its progress through the complete system. The complete system includes of course the optical front-end, an array-type o ...
... the thinking, creation, design, and understanding of novel or modern optical systems that one consider the input electric field E(r,t) and its intensity, proportional to E • E, and its progress through the complete system. The complete system includes of course the optical front-end, an array-type o ...
Improving fluorescence detection in lab on chip devices
... the sample is illuminated with light of twice the wavelength that best excites the fluorophore, so that excitation only occurs when the fluorophore absorbs two photons simultaneously.26 Since the crosssection for two-photon absorption depends on the square of the illumination intensity, this technique ...
... the sample is illuminated with light of twice the wavelength that best excites the fluorophore, so that excitation only occurs when the fluorophore absorbs two photons simultaneously.26 Since the crosssection for two-photon absorption depends on the square of the illumination intensity, this technique ...
ray optics and optical instruments
... In order to explain the phenomena of refraction, Newton postulated that the speed of the corpuscles was greater in water or glass than in air. However, later on it was discovered that the speed of light is less in water or glass than in air. In the field of optics, Newton – the experimenter, was gre ...
... In order to explain the phenomena of refraction, Newton postulated that the speed of the corpuscles was greater in water or glass than in air. However, later on it was discovered that the speed of light is less in water or glass than in air. In the field of optics, Newton – the experimenter, was gre ...
CHAPTER 3 Optical Components of Spectrometers
... • It arises when the two orthogonal waves are 90° out of phase. • In such a case a circularly polarized light is obtained because the resultant traces out a circle. • When the resultant vector (when the x component lags the y component by 90°) rotates clockwise, the resultant wave is said to be righ ...
... • It arises when the two orthogonal waves are 90° out of phase. • In such a case a circularly polarized light is obtained because the resultant traces out a circle. • When the resultant vector (when the x component lags the y component by 90°) rotates clockwise, the resultant wave is said to be righ ...
Sun et al., Nature 493, 195 (2013).
... radar, broadcasting and astronomy1. The ability to generate arbitrary radiation patterns with large-scale phased arrays has long been pursued. Although it is extremely expensive and cumbersome to deploy large-scale radiofrequency phased arrays2, optical phased arrays have a unique advantage in that ...
... radar, broadcasting and astronomy1. The ability to generate arbitrary radiation patterns with large-scale phased arrays has long been pursued. Although it is extremely expensive and cumbersome to deploy large-scale radiofrequency phased arrays2, optical phased arrays have a unique advantage in that ...
© NCERT not to be republished
... For the determination of the index correction, bring a mounted pin close to the concave lens L2. Adjust the index needle (a sharpedged knitting needle would also serve the purpose) horizontally such that its one end touches one of the curved surfaces of the lens and the other end touches the tip of ...
... For the determination of the index correction, bring a mounted pin close to the concave lens L2. Adjust the index needle (a sharpedged knitting needle would also serve the purpose) horizontally such that its one end touches one of the curved surfaces of the lens and the other end touches the tip of ...
Lecture_22
... light under water. We said that color depends on wavelength. For example, for an object emitting 650 nm light in air, we see red. But this is true only in air. If we observe this same object when under water, it still looks red. But the wavelength in water λn is 650 nm/1.33 = 489 nm. Light with wave ...
... light under water. We said that color depends on wavelength. For example, for an object emitting 650 nm light in air, we see red. But this is true only in air. If we observe this same object when under water, it still looks red. But the wavelength in water λn is 650 nm/1.33 = 489 nm. Light with wave ...
Exam 4-WWP
... length. When is the focal length of the eye’s lens the largest? a. when the object is far away b. when the object is near c. when the eye is out of focus d. none of these 15. When two waves are offset by one-half of a wavelength, they experience ____________. a. total constructive interference b. to ...
... length. When is the focal length of the eye’s lens the largest? a. when the object is far away b. when the object is near c. when the eye is out of focus d. none of these 15. When two waves are offset by one-half of a wavelength, they experience ____________. a. total constructive interference b. to ...
Observation of near-field correlations in spontaneous parametric
... Figure 1 shows the experimental setup used to observe the near-field structure in the two-photon field. In our experimental implementation we use a magnified 共instead of a 1:1兲 imaging system. Entangled photon pairs of equal polarization are generated by mildly focusing 共w p = 157 m兲 a laser beam 共 ...
... Figure 1 shows the experimental setup used to observe the near-field structure in the two-photon field. In our experimental implementation we use a magnified 共instead of a 1:1兲 imaging system. Entangled photon pairs of equal polarization are generated by mildly focusing 共w p = 157 m兲 a laser beam 共 ...
Theory of confocal fluorescence imaging in the
... multiple apertures for the simultaneous illumination and detection of a large number of points. However, since the spacing between the pinholes must be large to maintain the confocal effect, much of the illumination light is rejected by the disc ($ 97%; Fewer et al., 1997). This problem can be circu ...
... multiple apertures for the simultaneous illumination and detection of a large number of points. However, since the spacing between the pinholes must be large to maintain the confocal effect, much of the illumination light is rejected by the disc ($ 97%; Fewer et al., 1997). This problem can be circu ...
Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors
... the distances by a factor of one-half. Using this scaling, the object distance you should draw is 8 cm from the lens drawn on the data sheet. The object height drawn on the page should also be divided in half. Each person in your lab group should construct a ray diagram. 3. Measure to scale the imag ...
... the distances by a factor of one-half. Using this scaling, the object distance you should draw is 8 cm from the lens drawn on the data sheet. The object height drawn on the page should also be divided in half. Each person in your lab group should construct a ray diagram. 3. Measure to scale the imag ...
Introduction to Inverse Problems
... • The object is a “continuous” function (amplitude or intensity) assuming quantum mechanical effects are at sub-nanometer scales, i.e. much smaller than the scales of interest (100nm or more) – i.e. the object dimension is uncountably infinite • The measurement is “discrete,” therefore countable and ...
... • The object is a “continuous” function (amplitude or intensity) assuming quantum mechanical effects are at sub-nanometer scales, i.e. much smaller than the scales of interest (100nm or more) – i.e. the object dimension is uncountably infinite • The measurement is “discrete,” therefore countable and ...
Chapter 34 Geometric Optics
... the wavelength of light, we can treat light as a bundle of light rays. Each light ray is a straight line in a uniform medium (i.e., when the index of refraction n is a constant.) The light rays change direction only when reflection and refraction are encountered. (1b) Each extended object can be tho ...
... the wavelength of light, we can treat light as a bundle of light rays. Each light ray is a straight line in a uniform medium (i.e., when the index of refraction n is a constant.) The light rays change direction only when reflection and refraction are encountered. (1b) Each extended object can be tho ...
Wave Optics Theory and 3-D Deconvolution for the Light Field
... volume is accomplished by characterizing the microscope’s point spread function (PSF) and using it to perform 3-D deconvolution. In the appendix of [1], it is shown that for light field microscopy of a relatively transparent sample, 3-D deconvolution is equivalent to solving a limited-angle tomograp ...
... volume is accomplished by characterizing the microscope’s point spread function (PSF) and using it to perform 3-D deconvolution. In the appendix of [1], it is shown that for light field microscopy of a relatively transparent sample, 3-D deconvolution is equivalent to solving a limited-angle tomograp ...
FRAUNHOFER and FRESNEL DIFFRACTION
... (1) Choose one of the single slits in the diffraction plate, whose width is no more than a few tenths of a millimeter. Estimate the value of r that will satisfy the Fraunhofer condition when the slit is illuminated by parallel light from a HeNe laser (i.e., ρ → ∞ for the incident plane wave). (2) Fo ...
... (1) Choose one of the single slits in the diffraction plate, whose width is no more than a few tenths of a millimeter. Estimate the value of r that will satisfy the Fraunhofer condition when the slit is illuminated by parallel light from a HeNe laser (i.e., ρ → ∞ for the incident plane wave). (2) Fo ...
ABSTRACT Dissertation: STUDIES OF
... atomic-force microscopes (AFM), near-field scanning optical microscopes (NSOM) and tunneling-electronic microscopes (TEM), science research has entered a tiny world on a nanometer scale. How small is this? Comparing 10 nm to 1 m is the same as comparing 10 cm to the earth’s diameter. In the past, op ...
... atomic-force microscopes (AFM), near-field scanning optical microscopes (NSOM) and tunneling-electronic microscopes (TEM), science research has entered a tiny world on a nanometer scale. How small is this? Comparing 10 nm to 1 m is the same as comparing 10 cm to the earth’s diameter. In the past, op ...
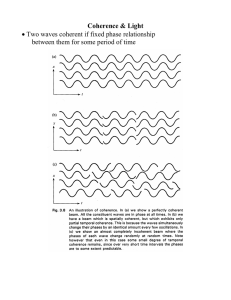
Week 9 Wed. (Lesson 15) Coherence and Optical Tomography
... • Two waves coherent if fixed phase relationship between them for some period of time ...
... • Two waves coherent if fixed phase relationship between them for some period of time ...
Wave optics theory and 3-D deconvolution
... reconstructed volume is accomplished by characterizing the microscope’s point spread function (PSF) and using it to perform 3-D deconvolution. In the appendix of [1] it is shown that, for light field microscopy of a relatively transparent sample, 3-D deconvolution is equivalent to solving a limited- ...
... reconstructed volume is accomplished by characterizing the microscope’s point spread function (PSF) and using it to perform 3-D deconvolution. In the appendix of [1] it is shown that, for light field microscopy of a relatively transparent sample, 3-D deconvolution is equivalent to solving a limited- ...
MICROSCOPY I: BRIGHT
... 1. Choose an objective to start, e.g. 10x. (Again, note that this will need to be repeated for each objective under which you wish to measure an object.) 2. Place a slide with the stage micrometer on the microscope stage and focus on the ruler. 3. Make ocular micrometer parallel with the stage micro ...
... 1. Choose an objective to start, e.g. 10x. (Again, note that this will need to be repeated for each objective under which you wish to measure an object.) 2. Place a slide with the stage micrometer on the microscope stage and focus on the ruler. 3. Make ocular micrometer parallel with the stage micro ...
Full Text - Journal of The Royal Society Interface
... photonic structures in plants are much more rare and many of them have been described only very recently. These include a variety of flowers [6–9], leaves [10] and fruits [11,12]. The biological functions of these photonic structures are only starting to be unveiled: the ability of a flower to produ ...
... photonic structures in plants are much more rare and many of them have been described only very recently. These include a variety of flowers [6–9], leaves [10] and fruits [11,12]. The biological functions of these photonic structures are only starting to be unveiled: the ability of a flower to produ ...
Superlens

A practical superlens, or super lens, is a lens which uses metamaterials to go beyond the diffraction limit. The diffraction limit is a feature of conventional lenses and microscopes that limits the fineness of their resolution. Many lens designs have been proposed that go beyond the diffraction limit in some way, but there are constraints and obstacles involved in realizing each of them.