Article cod in the North Sea
... covers over two thirds of our planet. Not only that, phytoplankton provide us with just over 50% of the oxygen we breathe on a day-to-day basis through the process of photosynthesis. Much of the plankton production each year is transferred to the ocean floor, either by dead plankton falling directly ...
... covers over two thirds of our planet. Not only that, phytoplankton provide us with just over 50% of the oxygen we breathe on a day-to-day basis through the process of photosynthesis. Much of the plankton production each year is transferred to the ocean floor, either by dead plankton falling directly ...
The Growth of Marine Labs
... Hydrolab – The most famous and widely used habitat based in the Bahamas and Caribbean from 1972 to 1985. Aquarius – Based in the Florida Keys. It is currently the world’s only underwater marine science lab. ...
... Hydrolab – The most famous and widely used habitat based in the Bahamas and Caribbean from 1972 to 1985. Aquarius – Based in the Florida Keys. It is currently the world’s only underwater marine science lab. ...
Mapping the Ocean Floor
... rift valley, a deep V-shaped notch. From this valley, new oceanic crust is constantly being extruded from Earth's mantle by processes not yet fully understood. In the case of the Mid-Atlantic rift valley, one sheet flows east and the other west, each moving at about half an inch per year. This cause ...
... rift valley, a deep V-shaped notch. From this valley, new oceanic crust is constantly being extruded from Earth's mantle by processes not yet fully understood. In the case of the Mid-Atlantic rift valley, one sheet flows east and the other west, each moving at about half an inch per year. This cause ...
Lowest Elevation - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... apart. The East Rift Valley runs through most of Africa, but it starts north of the Dead Sea and runs south along the eastern side of the continent. The Sea is located right along the Rift Valley where the earth's crust is being stretched thin. To get an idea of how this "crustal spreading" thing wo ...
... apart. The East Rift Valley runs through most of Africa, but it starts north of the Dead Sea and runs south along the eastern side of the continent. The Sea is located right along the Rift Valley where the earth's crust is being stretched thin. To get an idea of how this "crustal spreading" thing wo ...
Ocean Floor
... • Seal pups emerge just when ice is melting - earlier melt means they are exposed before ready to thrive • Caribou need ice to island-hop; they are falling through as ice thins • Polar bears hunt on ice in winter, retreat to land in summer. Less ice forces them onto land earlier ...
... • Seal pups emerge just when ice is melting - earlier melt means they are exposed before ready to thrive • Caribou need ice to island-hop; they are falling through as ice thins • Polar bears hunt on ice in winter, retreat to land in summer. Less ice forces them onto land earlier ...
Lowest Elevation
... forming where two crustal plates are spreading apart. The East Rift Valley runs through most of Africa, but it starts north of the Dead Sea and runs south along the eastern side of the continent. The Sea is located right along the Rift Valley where the earth's crust is being stretched thin. To get a ...
... forming where two crustal plates are spreading apart. The East Rift Valley runs through most of Africa, but it starts north of the Dead Sea and runs south along the eastern side of the continent. The Sea is located right along the Rift Valley where the earth's crust is being stretched thin. To get a ...
Quiz 4 - Study Guidelines Study Outline
... 7. The aging process of water masses may be monitored by measuring the amount of dissolved oxygen in deep waters (below 4000 meters). Where are the highest concentrations of dissolved oxygen found? (This identifies the youngest deep waters.) 8. What processes are responsible for the decrease in diss ...
... 7. The aging process of water masses may be monitored by measuring the amount of dissolved oxygen in deep waters (below 4000 meters). Where are the highest concentrations of dissolved oxygen found? (This identifies the youngest deep waters.) 8. What processes are responsible for the decrease in diss ...
Ocean Movements
... Incoming crests catch up to slower crests ahead Smaller crest-crest wavelength Waves become higher, steeper, and unstable The crests collapse forward ...
... Incoming crests catch up to slower crests ahead Smaller crest-crest wavelength Waves become higher, steeper, and unstable The crests collapse forward ...
Waves and Tides
... When the trough of a wave gets close to land, it starts to drag while the crest moves on, getting higher and higher until it tumbles over. ...
... When the trough of a wave gets close to land, it starts to drag while the crest moves on, getting higher and higher until it tumbles over. ...
GEM-PPP-30-RISING SEA LEVELS
... sea level would rise by about 80 meters, or more than 260 feet. This scenario could be thousands of years in the future, but it would render many of the world's best-loved coastal cities unrecognizable. ...
... sea level would rise by about 80 meters, or more than 260 feet. This scenario could be thousands of years in the future, but it would render many of the world's best-loved coastal cities unrecognizable. ...
Script - FOG - City College of San Francisco
... This rotatable sphere shows how this world ocean is distributed across the globe. The largest basin within the world ocean, representing 50% of it, is the Pacific Ocean, which sits between Asia, Australia, and the Americas. 25% of the world ocean is the Atlantic Ocean, which sits between the America ...
... This rotatable sphere shows how this world ocean is distributed across the globe. The largest basin within the world ocean, representing 50% of it, is the Pacific Ocean, which sits between Asia, Australia, and the Americas. 25% of the world ocean is the Atlantic Ocean, which sits between the America ...
1 - National Oceanography Centre
... What are the limits of ecosystem resilience to warming, acidification, de-‐oxygenation ? What will be the impact of a new summer sea-‐ice free Arctic Ocean ? What is the role of viruses in ...
... What are the limits of ecosystem resilience to warming, acidification, de-‐oxygenation ? What will be the impact of a new summer sea-‐ice free Arctic Ocean ? What is the role of viruses in ...
Unit 7 Chapter 23 Powerpoint
... Sound signals are sent through the water to the sea floor. By tracking how long it takes for them to bounce back, the depth can be determined. ...
... Sound signals are sent through the water to the sea floor. By tracking how long it takes for them to bounce back, the depth can be determined. ...
Geological and Physical Factors of the Marine
... vii. Rifts – cracks that are found generally by the ridges c. Mid Ocean Ridges – formed when material rising from below the mantle pushes up on the oceanic crust i. Central Rift Valley – a great gap or depression caused by the plates pulling apart at the center of the ridge ii. Hydrothermal Vents – ...
... vii. Rifts – cracks that are found generally by the ridges c. Mid Ocean Ridges – formed when material rising from below the mantle pushes up on the oceanic crust i. Central Rift Valley – a great gap or depression caused by the plates pulling apart at the center of the ridge ii. Hydrothermal Vents – ...
Currents and Climate
... water. The warm water transported to high latitudes in the North Atlantic is very salty since it comes from the warm regions near the equator where evaporation removes much water vapor. The very cold, salty water is dense so it sinks and flows slowly (over the course of about 1000 years) at depth ar ...
... water. The warm water transported to high latitudes in the North Atlantic is very salty since it comes from the warm regions near the equator where evaporation removes much water vapor. The very cold, salty water is dense so it sinks and flows slowly (over the course of about 1000 years) at depth ar ...
On the Origin of the Mediterranean Sea and its Surrounding
... As stated already last year during this conference, it is a fact that tidal forces of the Earth – Moon double system act w e s t w a r d on Earth (i.e. within the Earth’s hydrosphere a n d lithosphere) whereas the off-centre rotation of the Earth – Moon double system ultimately results in an e a s t ...
... As stated already last year during this conference, it is a fact that tidal forces of the Earth – Moon double system act w e s t w a r d on Earth (i.e. within the Earth’s hydrosphere a n d lithosphere) whereas the off-centre rotation of the Earth – Moon double system ultimately results in an e a s t ...
Crinoids- Sea Lily
... Crinoids are known as "Sea Lilies" but are not plants at all. They are, in fact, small plankton-gathering animals that possess feathery structures on their arms to filter the plankton from seawater. They were anchored to the seabed or rocky substrate by a stalk that allowed them to sway back and for ...
... Crinoids are known as "Sea Lilies" but are not plants at all. They are, in fact, small plankton-gathering animals that possess feathery structures on their arms to filter the plankton from seawater. They were anchored to the seabed or rocky substrate by a stalk that allowed them to sway back and for ...
Outline
... • Turbidity currents carve submarine canyons into the slope and shelf • Debris from turbidity currents creates graded bedding deposits and deep-sea fans • Deep flat areas formed by suspension settling • Volcanic peaks poke through the sediment – Abyssal hills (seaknolls) – Seamounts – Tablemounts (g ...
... • Turbidity currents carve submarine canyons into the slope and shelf • Debris from turbidity currents creates graded bedding deposits and deep-sea fans • Deep flat areas formed by suspension settling • Volcanic peaks poke through the sediment – Abyssal hills (seaknolls) – Seamounts – Tablemounts (g ...
The Floors of the Oceans
... Examples: Scotia Arc in South Atlantic, West Indies near Barbados Explains why there is little oceanic crust more than 200 my ...
... Examples: Scotia Arc in South Atlantic, West Indies near Barbados Explains why there is little oceanic crust more than 200 my ...
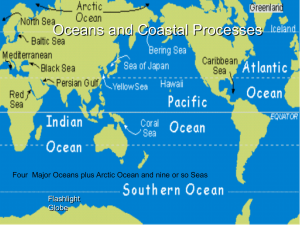
Lecture 14 Oceans and Coastal Processes u
... • Currents started by prevailing winds • Currents deflected by continent positions and Earth’s rotation • Climates caused by current and wind circulation ...
... • Currents started by prevailing winds • Currents deflected by continent positions and Earth’s rotation • Climates caused by current and wind circulation ...
Geological Components of the ocean
... The size of the shelf varies though. In some areas it can be virtually non-existent but else were it can extend for several hundred miles. The continental shells average distance is about 64 kilometers. The shelf ends at a depth of about two hundred meters (660 ft), giving way to the continental s ...
... The size of the shelf varies though. In some areas it can be virtually non-existent but else were it can extend for several hundred miles. The continental shells average distance is about 64 kilometers. The shelf ends at a depth of about two hundred meters (660 ft), giving way to the continental s ...
Sea

A sea is a large body of salt water that is surrounded in whole or in part by land. More broadly, the sea (with the definite article) is the interconnected system of Earth's salty, oceanic waters—considered as one global ocean or as several principal oceanic divisions. The sea moderates Earth's climate and has important roles in the water cycle, carbon cycle, and nitrogen cycle. Although the sea has been travelled and explored since prehistory, the modern scientific study of the sea—oceanography—dates broadly to the British Challenger expedition of the 1870s. The sea is conventionally divided into up to five large oceanic sections—including the IHO's four named oceans (the Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, and Arctic) and the Southern Ocean; smaller, second-order sections, such as the Mediterranean, are known as seas.Owing to the present state of continental drift, the Northern Hemisphere is now fairly equally divided between land and sea (a ratio of about 2:3) but the South is overwhelmingly oceanic (1:4.7). Salinity in the open ocean is generally in a narrow band around 3.5% by mass, although this can vary in more landlocked waters, near the mouths of large rivers, or at great depths. About 85% of the solids in the open sea are sodium chloride. Deep-sea currents are produced by differences in salinity and temperature. Surface currents are formed by the friction of waves produced by the wind and by tides, the changes in local sea level produced by the gravity of the Moon and Sun. The direction of all of these is governed by surface and submarine land masses and by the rotation of the Earth (the Coriolis effect).Former changes in the sea levels have left continental shelves, shallow areas in the sea close to land. These nutrient-rich waters teem with life, which provide humans with substantial supplies of food—mainly fish, but also shellfish, mammals, and seaweed—which are both harvested in the wild and farmed. The most diverse areas surround great tropical coral reefs. Whaling in the deep sea was once common but whales' dwindling numbers prompted international conservation efforts and finally a moratorium on most commercial hunting. Oceanography has established that not all life is restricted to the sunlit surface waters: even under enormous depths and pressures, nutrients streaming from hydrothermal vents support their own unique ecosystem. Life may have started there and aquatic microbial mats are generally credited with the oxygenation of Earth's atmosphere; both plants and animals first evolved in the sea.The sea is an essential aspect of human trade, travel, mineral extraction, and power generation. This has also made it essential to warfare and left major cities exposed to earthquakes and volcanoes from nearby faults; powerful tsunami waves; and hurricanes, typhoons, and cyclones produced in the tropics. This importance and duality has affected human culture, from early sea gods to the epic poetry of Homer to the changes induced by the Columbian Exchange, from Viking funerals to Basho's haikus to hyperrealist marine art, and inspiring music ranging from the shanties in The Complaynt of Scotland to Rimsky-Korsakov's ""The Sea and Sinbad's Ship"" to A-mei's ""Listen to the Sea"". It is the scene of leisure activities including swimming, diving, surfing, and sailing. However, population growth, industrialization, and intensive farming have all contributed to present-day marine pollution. Atmospheric carbon dioxide is being absorbed in increasing amounts, lowering its pH in a process known as ocean acidification. The shared nature of the sea has made overfishing an increasing problem.