Lecture 12: Fraunhofer diffraction by a single slit
... Problem: A propagating wave encounters an obstacle (i.e. a distortion of the wave-front occurs). How will the distortion influence the propagation of the wave? Fraunhofer diffraction: the resultant wave is measured very far away from the place where the wave-front was distorted (R>>size of the obsta ...
... Problem: A propagating wave encounters an obstacle (i.e. a distortion of the wave-front occurs). How will the distortion influence the propagation of the wave? Fraunhofer diffraction: the resultant wave is measured very far away from the place where the wave-front was distorted (R>>size of the obsta ...
Nonconfocal Differential Interferometry Sensing Scheme for
... fluctuating signals were produced that were impractical and possibly obstructed the sample. This limitation is due to the fact that the two reflection planes are not rigidly connected, subsequently inducing vibration between them. The only position that the reference beam can point to is the cantileve ...
... fluctuating signals were produced that were impractical and possibly obstructed the sample. This limitation is due to the fact that the two reflection planes are not rigidly connected, subsequently inducing vibration between them. The only position that the reference beam can point to is the cantileve ...
Experiment Guide - Industrial Fiber Optics
... stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise) without prior written permission from Industrial Fiber Optics. ...
... stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise) without prior written permission from Industrial Fiber Optics. ...
Laser Beam Profile, Spot size and Beam Divergence
... The laser that we are working with is a rectangular one. So, any measurement done should has two primary orientation taken into consideration and the results should be given for both the orientations separately. The setup is very simple. We have a laser and a detector(for measuring the intensity) se ...
... The laser that we are working with is a rectangular one. So, any measurement done should has two primary orientation taken into consideration and the results should be given for both the orientations separately. The setup is very simple. We have a laser and a detector(for measuring the intensity) se ...
FTIR Instrumentation
... Dispersive spectrophotometers, which use a monochromator to produce an infrared spectrum one resolution element at a time. Michelson interferometers, which use a moving mirror to create an interference pattern, or interferogram, from which all resolution elements are determined simultaneously. ...
... Dispersive spectrophotometers, which use a monochromator to produce an infrared spectrum one resolution element at a time. Michelson interferometers, which use a moving mirror to create an interference pattern, or interferogram, from which all resolution elements are determined simultaneously. ...
Zeeman Effect - UCI Physics and Astronomy
... a problem in the Zeeman experiment because the shifts are not large and the lines can be followed as the field is gradually increased. Finally, how can you estimate how much wavelength resolution to expect from the F-P? The intensity maximums that are described by Eqs. (1) and (2) are not infinitely ...
... a problem in the Zeeman experiment because the shifts are not large and the lines can be followed as the field is gradually increased. Finally, how can you estimate how much wavelength resolution to expect from the F-P? The intensity maximums that are described by Eqs. (1) and (2) are not infinitely ...
PDF
... collimated beam. The grating strength was modified along the antenna in order to create a constant intensity across the array length. Phase shifting was achieved using the thermo-optic effect in silicon. The use of an S-shaped waveguide allowed both a longer phase-shifter length in a small space and ...
... collimated beam. The grating strength was modified along the antenna in order to create a constant intensity across the array length. Phase shifting was achieved using the thermo-optic effect in silicon. The use of an S-shaped waveguide allowed both a longer phase-shifter length in a small space and ...
Direct Patterning of Three-Dimensional Periodic
... of 3 µm. A thin layer of OmniCoat (MicroChem) was applied between the resist and the mask to improve adhesion. The photoresist was then exposed to UV light for 3 min through the mask using a UV aligner (HTG, 365 nm). After exposure, the samples were developed in SU-8 developer for an hour and then ...
... of 3 µm. A thin layer of OmniCoat (MicroChem) was applied between the resist and the mask to improve adhesion. The photoresist was then exposed to UV light for 3 min through the mask using a UV aligner (HTG, 365 nm). After exposure, the samples were developed in SU-8 developer for an hour and then ...
\ A/58
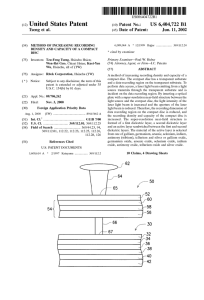
... are used to control the thermal conductivity of the recording layer 16. The upper and loWer dielectric layers 18 and 14 thus include materials such as silicon nitride, silicon oxide, Zinc sul?de-silicon dioxide, titanium oxide or carbide. The compact disc is shone With a laser light beam 26 from a l ...
... are used to control the thermal conductivity of the recording layer 16. The upper and loWer dielectric layers 18 and 14 thus include materials such as silicon nitride, silicon oxide, Zinc sul?de-silicon dioxide, titanium oxide or carbide. The compact disc is shone With a laser light beam 26 from a l ...
Optical Computers (Erin Raphael, 2006)
... The information is then sent through different fiber optic cables depending on it’s final location. Some information will be sent to the holographic memory, where it will then be saved. After information is saved and the program would like to use it, the program sends a command to the processor, whi ...
... The information is then sent through different fiber optic cables depending on it’s final location. Some information will be sent to the holographic memory, where it will then be saved. After information is saved and the program would like to use it, the program sends a command to the processor, whi ...
5. Reflection, refraction and polarization
... undeviated. (Remember the light bends on entering a new medium, so this enables the device to accept light from a wider field of view.) Polarization extinctions on the order of 104 to 105 are achieved with high transmission. Most vendors use a glue that matches the index of refraction between the tw ...
... undeviated. (Remember the light bends on entering a new medium, so this enables the device to accept light from a wider field of view.) Polarization extinctions on the order of 104 to 105 are achieved with high transmission. Most vendors use a glue that matches the index of refraction between the tw ...
Tabletop nanometer extreme ultraviolet imaging in an
... need for a large number of scan positions. This also results in fewer necessary scan positions when imaging a large field of view. Third, reflection ptychography produces surface images containing quantitative amplitude and phase information about the sample that are in excellent agreement with atom ...
... need for a large number of scan positions. This also results in fewer necessary scan positions when imaging a large field of view. Third, reflection ptychography produces surface images containing quantitative amplitude and phase information about the sample that are in excellent agreement with atom ...
Holography

Holography is the science and practice of making holograms. Typically, a hologram is a photographic recording of a light field, rather than of an image formed by a lens, and it is used to display a fully three-dimensional image of the holographed subject, which is seen without the aid of special glasses or other intermediate optics. The hologram itself is not an image and it is usually unintelligible when viewed under diffuse ambient light. It is an encoding of the light field as an interference pattern of seemingly random variations in the opacity, density, or surface profile of the photographic medium. When suitably lit, the interference pattern diffracts the light into a reproduction of the original light field and the objects that were in it appear to still be there, exhibiting visual depth cues such as parallax and perspective that change realistically with any change in the relative position of the observer.In its pure form, holography requires the use of laser light for illuminating the subject and for viewing the finished hologram. In a side-by-side comparison under optimal conditions, a holographic image is visually indistinguishable from the actual subject, if the hologram and the subject are lit just as they were at the time of recording. A microscopic level of detail throughout the recorded volume of space can be reproduced. In common practice, however, major image quality compromises are made to eliminate the need for laser illumination when viewing the hologram, and sometimes, to the extent possible, also when making it. Holographic portraiture often resorts to a non-holographic intermediate imaging procedure, to avoid the hazardous high-powered pulsed lasers otherwise needed to optically ""freeze"" living subjects as perfectly as the extremely motion-intolerant holographic recording process requires. Holograms can now also be entirely computer-generated and show objects or scenes that never existed.Holography should not be confused with lenticular and other earlier autostereoscopic 3D display technologies, which can produce superficially similar results but are based on conventional lens imaging. Stage illusions such as Pepper's Ghost and other unusual, baffling, or seemingly magical images are also often incorrectly called holograms.