Revised Experiment 4
... Diffraction and interference experiments provide evidence that light may behave as a wave in some cases. They do not, however, indicate whether the waves are longitudinal or transverse. Polarization experiments demonstrate that light waves are transverse waves. In this experiment, you will produce a ...
... Diffraction and interference experiments provide evidence that light may behave as a wave in some cases. They do not, however, indicate whether the waves are longitudinal or transverse. Polarization experiments demonstrate that light waves are transverse waves. In this experiment, you will produce a ...
Real Beam Propagation
... parameter was developed in the early 1970s to meet this need, based on the fact that, for any given laser beam (even those not operating in the TEM00 mode) the product of the beam waist radius (w0) and the far-field divergence (θ) are constant as the beam propagates through an optical system, and th ...
... parameter was developed in the early 1970s to meet this need, based on the fact that, for any given laser beam (even those not operating in the TEM00 mode) the product of the beam waist radius (w0) and the far-field divergence (θ) are constant as the beam propagates through an optical system, and th ...
Excited State Processes and Application to Lasers The technology
... 3.0 The population inversion Gain represents the increase in photons emitted from the sample compared to a Boltzmann distribution. The Boltzmann distribution will never allow for more population in an excited state than in the ground state. Therefore, gain represents a non-Boltzmann distribution in ...
... 3.0 The population inversion Gain represents the increase in photons emitted from the sample compared to a Boltzmann distribution. The Boltzmann distribution will never allow for more population in an excited state than in the ground state. Therefore, gain represents a non-Boltzmann distribution in ...
Optical image recognition of three-dimensional objects
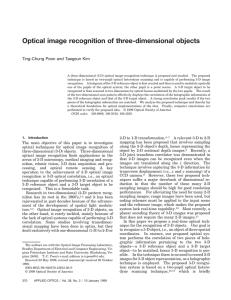
... Among the temporal frequency-modulation techniques, the use of active optical heterodyne scanning has been studied extensively by Poon and Korpel,12 Poon,13 and Indebetouw and Poon.15 In the optical heterodyne scanning system two laser beams of different temporal frequency that carry the information ...
... Among the temporal frequency-modulation techniques, the use of active optical heterodyne scanning has been studied extensively by Poon and Korpel,12 Poon,13 and Indebetouw and Poon.15 In the optical heterodyne scanning system two laser beams of different temporal frequency that carry the information ...
OSA journals template (MSWORD)
... copper vapour lasers at 578 nm and dye lasers operating at 585 nm and 595 nm. These lasers are both bulky and inefficient and it would be attractive to develop a solid-state alternative to these lasers. One path that has been followed for the generation of yellow light is second harmonic generation ...
... copper vapour lasers at 578 nm and dye lasers operating at 585 nm and 595 nm. These lasers are both bulky and inefficient and it would be attractive to develop a solid-state alternative to these lasers. One path that has been followed for the generation of yellow light is second harmonic generation ...
Chapter 6: Speed of Light
... oscilloscope is shifted by Δt. The speed of light can be determined from the slope of the line Δs = fΔt) by recording multiple value pairs. To measure the absolute time t that a light pulse requires to travel path s, a reference signal U0 for the zero point is required in addition to the time signal ...
... oscilloscope is shifted by Δt. The speed of light can be determined from the slope of the line Δs = fΔt) by recording multiple value pairs. To measure the absolute time t that a light pulse requires to travel path s, a reference signal U0 for the zero point is required in addition to the time signal ...
plane-polarized
... When the light beam enters the piece of material, it slows down because the refracting index of the material is greater than 1.0. Its ν does not change, therefore its λ decreases (the product of the frequency and the wavelength should be equal to c). In these animations, we used a refraction index n ...
... When the light beam enters the piece of material, it slows down because the refracting index of the material is greater than 1.0. Its ν does not change, therefore its λ decreases (the product of the frequency and the wavelength should be equal to c). In these animations, we used a refraction index n ...
1.9 W yellow, CW, high-brightness light from a high efficiency
... For applications such as flow cytometry , photocoagulation2, imaging3,4 and cancer treatment5, yellow lasers have started to attract a lot of attention in recent years. Indeed, higher signal-to-noise ratios can be achieved for some important fluorophores when excited with light at 562 nm compared to ...
... For applications such as flow cytometry , photocoagulation2, imaging3,4 and cancer treatment5, yellow lasers have started to attract a lot of attention in recent years. Indeed, higher signal-to-noise ratios can be achieved for some important fluorophores when excited with light at 562 nm compared to ...
Observation of subluminal twisted light in vacuum
... Here we investigate the exotic group velocities exhibited by Laguerre-Gauss (LG) modes in vacuum. In particular, we observe and explain subluminal effects that arise due to the twisted nature of the optical phase front. We use an experimental setup that employs nonlinear intensity autocorrelation to ...
... Here we investigate the exotic group velocities exhibited by Laguerre-Gauss (LG) modes in vacuum. In particular, we observe and explain subluminal effects that arise due to the twisted nature of the optical phase front. We use an experimental setup that employs nonlinear intensity autocorrelation to ...
Generation of a dark hollow beam by a four
... effective intensity from z=0 to z=-16cm is 6.66mK and 5.65mK, respectively. The two DHBODTs showed in Fig.3 all can be used to trap cold atoms, in which the ratio wo/f is not very small has the characteristic of large intensity and small volume. When illuminated by 1000mW laser, the effective intens ...
... effective intensity from z=0 to z=-16cm is 6.66mK and 5.65mK, respectively. The two DHBODTs showed in Fig.3 all can be used to trap cold atoms, in which the ratio wo/f is not very small has the characteristic of large intensity and small volume. When illuminated by 1000mW laser, the effective intens ...
Laser Systems for Inverse Compton Scattering Gamma
... photofission in SNM, resulting in prompt fission gammarays and/or neutrons. What is needed most is a convenient gamma-ray source that can be used to induce photofission. Electron accelerators, which are a very mature technology, can be used to produce gamma-rays via bremsstrahlung. Unfortunately, ga ...
... photofission in SNM, resulting in prompt fission gammarays and/or neutrons. What is needed most is a convenient gamma-ray source that can be used to induce photofission. Electron accelerators, which are a very mature technology, can be used to produce gamma-rays via bremsstrahlung. Unfortunately, ga ...
b1.2. generation and propagation of higher order gaussian beams
... a confocal microscope leads to lots of spatial and temporal changes to the beam. Hence, it needs to be understood while using such higher order Gaussian beams. It has been thought that Gaussian beam propagating through an ideal thin lens or a mirror with small curvature undergoes a change in paramet ...
... a confocal microscope leads to lots of spatial and temporal changes to the beam. Hence, it needs to be understood while using such higher order Gaussian beams. It has been thought that Gaussian beam propagating through an ideal thin lens or a mirror with small curvature undergoes a change in paramet ...
Experiment VI Polarized Light
... In an unpolarized beam of light, such as that from an ordinary light bulb, the electric field points in random directions (of course all of these directions are always perpendicular to the direction in which the light is traveling). For linearly polarized light, the electric field points along one p ...
... In an unpolarized beam of light, such as that from an ordinary light bulb, the electric field points in random directions (of course all of these directions are always perpendicular to the direction in which the light is traveling). For linearly polarized light, the electric field points along one p ...
The Setup, Design, and Implementation of a Photoluminescence Experiment on Quantum Wells
... functional and optimized by aligning its cavity, to create an experimental setup designed for completing photoluminescence experiments, to integrate the Ti:Sapphire laser into the setup, and to begin running exp ...
... functional and optimized by aligning its cavity, to create an experimental setup designed for completing photoluminescence experiments, to integrate the Ti:Sapphire laser into the setup, and to begin running exp ...
Chapter 12: Light
... radiation to visible light Lasers - produce light waves that have the same wavelength To create a laser a number of identical atoms are given a certain amount of energy. Once each atom has received that energy the energy is released as a light wave. Each light wave is identical to the other light ...
... radiation to visible light Lasers - produce light waves that have the same wavelength To create a laser a number of identical atoms are given a certain amount of energy. Once each atom has received that energy the energy is released as a light wave. Each light wave is identical to the other light ...
Three models of light
... the image is called real. • If a screen is put at the real image, the rays will scatter in all directions and an image can be seen on the screen, just as if it were a ...
... the image is called real. • If a screen is put at the real image, the rays will scatter in all directions and an image can be seen on the screen, just as if it were a ...
Holography

Holography is the science and practice of making holograms. Typically, a hologram is a photographic recording of a light field, rather than of an image formed by a lens, and it is used to display a fully three-dimensional image of the holographed subject, which is seen without the aid of special glasses or other intermediate optics. The hologram itself is not an image and it is usually unintelligible when viewed under diffuse ambient light. It is an encoding of the light field as an interference pattern of seemingly random variations in the opacity, density, or surface profile of the photographic medium. When suitably lit, the interference pattern diffracts the light into a reproduction of the original light field and the objects that were in it appear to still be there, exhibiting visual depth cues such as parallax and perspective that change realistically with any change in the relative position of the observer.In its pure form, holography requires the use of laser light for illuminating the subject and for viewing the finished hologram. In a side-by-side comparison under optimal conditions, a holographic image is visually indistinguishable from the actual subject, if the hologram and the subject are lit just as they were at the time of recording. A microscopic level of detail throughout the recorded volume of space can be reproduced. In common practice, however, major image quality compromises are made to eliminate the need for laser illumination when viewing the hologram, and sometimes, to the extent possible, also when making it. Holographic portraiture often resorts to a non-holographic intermediate imaging procedure, to avoid the hazardous high-powered pulsed lasers otherwise needed to optically ""freeze"" living subjects as perfectly as the extremely motion-intolerant holographic recording process requires. Holograms can now also be entirely computer-generated and show objects or scenes that never existed.Holography should not be confused with lenticular and other earlier autostereoscopic 3D display technologies, which can produce superficially similar results but are based on conventional lens imaging. Stage illusions such as Pepper's Ghost and other unusual, baffling, or seemingly magical images are also often incorrectly called holograms.