Fiber Optic Cable Beam Delivery Systems
... Conventional beam delivery techniques involve a combination of reflective and refractive optics (mirrors and lenses), and must rely on a straight, uninterrupted line of sight between each optical element. In some cases, especially those involving delivery over significant distances, this may prove t ...
... Conventional beam delivery techniques involve a combination of reflective and refractive optics (mirrors and lenses), and must rely on a straight, uninterrupted line of sight between each optical element. In some cases, especially those involving delivery over significant distances, this may prove t ...
- vjs.ac.vn
... For simplicity, we assume that the radius (a) of the particle is much smaller than the wavelength of the laser (i.e., a ), in this case we can treat the dielectric particle as a point dipole. We also assume that the refractive index of the dielectric particle is n1 and n1 n2 . This is the ne ...
... For simplicity, we assume that the radius (a) of the particle is much smaller than the wavelength of the laser (i.e., a ), in this case we can treat the dielectric particle as a point dipole. We also assume that the refractive index of the dielectric particle is n1 and n1 n2 . This is the ne ...
Theory of relativistic optical harmonic generation
... fundamental laser beam [14]. Let us recall why traditional models [15] predict the vanishing of THG under excitation with circularly polarized radiation and see why this argument breaks down under relativistic conditions. Nonlinear optical interactions are often described in terms of a nonlinear opt ...
... fundamental laser beam [14]. Let us recall why traditional models [15] predict the vanishing of THG under excitation with circularly polarized radiation and see why this argument breaks down under relativistic conditions. Nonlinear optical interactions are often described in terms of a nonlinear opt ...
en_20160128_lzh_pm_hymnos_final
... coaxially flowing fluid pairs using wave-optical light propagation in fluid-dynamically and thermally superimposed refractive index distributions”, the beam guidance in flowing liquids will be simulated. The scientists in the Production and Systems Department want to predict light propagation in flu ...
... coaxially flowing fluid pairs using wave-optical light propagation in fluid-dynamically and thermally superimposed refractive index distributions”, the beam guidance in flowing liquids will be simulated. The scientists in the Production and Systems Department want to predict light propagation in flu ...
Research Article Influence of Thickness on the Holographic Parameters of H-PDLC Materials
... conditions (or visible light at a wavelength where the dye does not absorb) and then sandwiched between two conductive ITO glass plates separated using glass microspheres. In order to obtain samples of the same physical thickness, a weight of 1 kg was placed over the layer for 5 minutes. As a result ...
... conditions (or visible light at a wavelength where the dye does not absorb) and then sandwiched between two conductive ITO glass plates separated using glass microspheres. In order to obtain samples of the same physical thickness, a weight of 1 kg was placed over the layer for 5 minutes. As a result ...
laser optical disk set
... the convex side faces the incoming light and position it as shown in Diagram 5.8. Mark two points on each of the reflected rays, then remove the mirror and project the lines joining the exit rays backwards to their meeting point, the focal Diagram 5.8 point. Measure the focal length, f. Note tha ...
... the convex side faces the incoming light and position it as shown in Diagram 5.8. Mark two points on each of the reflected rays, then remove the mirror and project the lines joining the exit rays backwards to their meeting point, the focal Diagram 5.8 point. Measure the focal length, f. Note tha ...
Electroholographic tunable volume grating in the g44
... is the grating vector (K 储 x, 兩K 兩 = 2 / ⌳, and ⌳ is the grating period). A plane wave with wavelength o propagating in the 共x , z兲 plane is incident on the crystal at an angle . Because of Snell’s law of refraction, the direction of the incident beam is shifted as it enters the crystal so that i ...
... is the grating vector (K 储 x, 兩K 兩 = 2 / ⌳, and ⌳ is the grating period). A plane wave with wavelength o propagating in the 共x , z兲 plane is incident on the crystal at an angle . Because of Snell’s law of refraction, the direction of the incident beam is shifted as it enters the crystal so that i ...
Plasmonic Airy beams with dynamically controlled trajectories Peng Zhang, Sheng Wang,
... generation and dynamic control of plasmonic Airy beams (PABs). By directly coupling 1D Airy beams from free space to SPPs on a metal surface through a grating coupler, we show that the excited PABs can propagate along parabolic trajectories while maintaining the nondiffracting nature. Furthermore, w ...
... generation and dynamic control of plasmonic Airy beams (PABs). By directly coupling 1D Airy beams from free space to SPPs on a metal surface through a grating coupler, we show that the excited PABs can propagate along parabolic trajectories while maintaining the nondiffracting nature. Furthermore, w ...
Plasmonic Airy beams with dynamically controlled trajectories Peng Zhang, Sheng Wang,
... generation and dynamic control of plasmonic Airy beams (PABs). By directly coupling 1D Airy beams from free space to SPPs on a metal surface through a grating coupler, we show that the excited PABs can propagate along parabolic trajectories while maintaining the nondiffracting nature. Furthermore, w ...
... generation and dynamic control of plasmonic Airy beams (PABs). By directly coupling 1D Airy beams from free space to SPPs on a metal surface through a grating coupler, we show that the excited PABs can propagate along parabolic trajectories while maintaining the nondiffracting nature. Furthermore, w ...
Interferometer design for writing Bragg gratings in optical fibers
... interference of two mutually coherent, high-intensity UV beams in the doped region induces the refractive index modulation during manufacture. The projected pattern is thus typically a set of parallel fringes having a sinusoidal intensity profile. In its simplest form a Bragg grating writer consists ...
... interference of two mutually coherent, high-intensity UV beams in the doped region induces the refractive index modulation during manufacture. The projected pattern is thus typically a set of parallel fringes having a sinusoidal intensity profile. In its simplest form a Bragg grating writer consists ...
Rapid fabrication of 3D terahertz split ring resonator arrays by novel
... utilizing 780 nm light from a Coherent RegA Ti:Sapphire oscillator laser system utilizing an 80 MHz rep rate with 160 fs pulses. Continuous wave 532 nm exposure was performed with a Coherent Verdi-V5 laser. Power was controlled by a neutral density filter and measured with a power meter (Newport 81 ...
... utilizing 780 nm light from a Coherent RegA Ti:Sapphire oscillator laser system utilizing an 80 MHz rep rate with 160 fs pulses. Continuous wave 532 nm exposure was performed with a Coherent Verdi-V5 laser. Power was controlled by a neutral density filter and measured with a power meter (Newport 81 ...
Diode Laser Characteristics
... A lens in front of the laser collimates the output into a nearly nondiverging elliptical beam. After the lens, the beam strikes a diffraction grating, which is a holographic (no blaze) grating with 2400 lines/mm. Most of the light is directly reflected by the grating (m=0 grating order), but roughly 2 ...
... A lens in front of the laser collimates the output into a nearly nondiverging elliptical beam. After the lens, the beam strikes a diffraction grating, which is a holographic (no blaze) grating with 2400 lines/mm. Most of the light is directly reflected by the grating (m=0 grating order), but roughly 2 ...
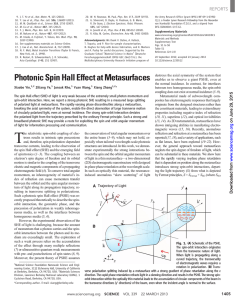
... conducted for three samples with different phase gradients of 3.6, 4.0, and 4.4 rad/mm. The measured refraction angles agree well with the theoretical predictions (solid curves). The angles are the same for both the left and right circularly polarized light. (Inset) Schematic depiction of the light ...
Holography

Holography is the science and practice of making holograms. Typically, a hologram is a photographic recording of a light field, rather than of an image formed by a lens, and it is used to display a fully three-dimensional image of the holographed subject, which is seen without the aid of special glasses or other intermediate optics. The hologram itself is not an image and it is usually unintelligible when viewed under diffuse ambient light. It is an encoding of the light field as an interference pattern of seemingly random variations in the opacity, density, or surface profile of the photographic medium. When suitably lit, the interference pattern diffracts the light into a reproduction of the original light field and the objects that were in it appear to still be there, exhibiting visual depth cues such as parallax and perspective that change realistically with any change in the relative position of the observer.In its pure form, holography requires the use of laser light for illuminating the subject and for viewing the finished hologram. In a side-by-side comparison under optimal conditions, a holographic image is visually indistinguishable from the actual subject, if the hologram and the subject are lit just as they were at the time of recording. A microscopic level of detail throughout the recorded volume of space can be reproduced. In common practice, however, major image quality compromises are made to eliminate the need for laser illumination when viewing the hologram, and sometimes, to the extent possible, also when making it. Holographic portraiture often resorts to a non-holographic intermediate imaging procedure, to avoid the hazardous high-powered pulsed lasers otherwise needed to optically ""freeze"" living subjects as perfectly as the extremely motion-intolerant holographic recording process requires. Holograms can now also be entirely computer-generated and show objects or scenes that never existed.Holography should not be confused with lenticular and other earlier autostereoscopic 3D display technologies, which can produce superficially similar results but are based on conventional lens imaging. Stage illusions such as Pepper's Ghost and other unusual, baffling, or seemingly magical images are also often incorrectly called holograms.