Soil Contamination #11 - Compost Education Centre
... Unlike chemical contaminants, heavy metals cannot be broken down and can continue to build up in soils. However, their characteristics may change so that they can be more or less easily taken up by plants or animals. Many of the practices that gardeners already use in their gardens (such as mulching ...
... Unlike chemical contaminants, heavy metals cannot be broken down and can continue to build up in soils. However, their characteristics may change so that they can be more or less easily taken up by plants or animals. Many of the practices that gardeners already use in their gardens (such as mulching ...
Implementing Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation in Tennessee SP 765-B
... planting can help to ensure that any of these byproducts are flushed from the planting zone. Some evidence suggests that longer treatment periods (up to six weeks) may be beneficial in cooler soils (less than 60 F), where decomposition proceeds more slowly. As mentioned previously, the use of soil a ...
... planting can help to ensure that any of these byproducts are flushed from the planting zone. Some evidence suggests that longer treatment periods (up to six weeks) may be beneficial in cooler soils (less than 60 F), where decomposition proceeds more slowly. As mentioned previously, the use of soil a ...
Colorado Agri-science Curriculum Section: Plant & Soil
... Then they are replaced by others that are thermophilic, or heat-loving. ...
... Then they are replaced by others that are thermophilic, or heat-loving. ...
Open Education Resource Study of soil formation and physical
... 2. Laterites and Lateritic soil: These soils are red to reddish yellow in colour and low in N, R, K, lime and magnesia. These soils are formed in situ under conditions of high rainfall with alternation dry and wet periods. On account of heavy rainfall there is an excessive leaching of soil colloids ...
... 2. Laterites and Lateritic soil: These soils are red to reddish yellow in colour and low in N, R, K, lime and magnesia. These soils are formed in situ under conditions of high rainfall with alternation dry and wet periods. On account of heavy rainfall there is an excessive leaching of soil colloids ...
VIC - University of Washington
... hydrology scheme for use in the NCAR Community Land Model (CLM) is proposed. The new scheme incorporates the fundamental principles and concepts of the three-layer Variable Infiltration Capacity (VIC) soil moisture generation scheme, as well as its surface runoff and base flow schemes. The modified ...
... hydrology scheme for use in the NCAR Community Land Model (CLM) is proposed. The new scheme incorporates the fundamental principles and concepts of the three-layer Variable Infiltration Capacity (VIC) soil moisture generation scheme, as well as its surface runoff and base flow schemes. The modified ...
SKE2 Students will describe the physical attributes of rocks and soils
... SKE2 Students will describe the physical attributes of rocks and soils. a. Use senses to observe and group rocks by physical attributes such as large/small, heavy/light, smooth/ rough, dark/light, etc. b. Use senses to observe soils by physical attributes such as smell, texture, color, particle/grai ...
... SKE2 Students will describe the physical attributes of rocks and soils. a. Use senses to observe and group rocks by physical attributes such as large/small, heavy/light, smooth/ rough, dark/light, etc. b. Use senses to observe soils by physical attributes such as smell, texture, color, particle/grai ...
soil as a resource
... 11. Dust storms have greatly increased worldwide over the past two centuries primarily because of a. worldwide drought. b. deforestation and increasing cultivation. c. increasing urbanization. d. intense winds. 12. All of the following can be used to reduce wind erosion on farmland except a. plantin ...
... 11. Dust storms have greatly increased worldwide over the past two centuries primarily because of a. worldwide drought. b. deforestation and increasing cultivation. c. increasing urbanization. d. intense winds. 12. All of the following can be used to reduce wind erosion on farmland except a. plantin ...
Summary 10 done
... testing a tube without any soil in it? Explain that there is no organic matter in Tube C because there is no soil in it. Because this is known, this provides a basis of color comparison for the other tubes, confirming that the test worked as intended. Review the term control. Explain that this is pa ...
... testing a tube without any soil in it? Explain that there is no organic matter in Tube C because there is no soil in it. Because this is known, this provides a basis of color comparison for the other tubes, confirming that the test worked as intended. Review the term control. Explain that this is pa ...
Development of Soil-Student Info
... The Parent Material may be directly below the soil, or great distances away (wind, water or glaciers have transported the soil) The soil formation process is termed 'pedogenesis'. Climatic conditions are important factors affecting both the form and rate of physical and chemical weathering of ...
... The Parent Material may be directly below the soil, or great distances away (wind, water or glaciers have transported the soil) The soil formation process is termed 'pedogenesis'. Climatic conditions are important factors affecting both the form and rate of physical and chemical weathering of ...
GCSE activity on active transport in waterlogged soil
... To describe and explain why waterlogged soils prevent active transport through the displacement of soil oxygen To describe and explain why waterlogged soils cause denitrification to take place due to anaerobic bacteria To describe and explain the process of ion leaching ...
... To describe and explain why waterlogged soils prevent active transport through the displacement of soil oxygen To describe and explain why waterlogged soils cause denitrification to take place due to anaerobic bacteria To describe and explain the process of ion leaching ...
English PDF, 50 kB
... that the glucose produced from this process, is then converted into a variety of forms. It is the speed at which the process of photosynthesis is carried out which ensures that what is produced in this entire mechanism is useful not only for the plants themselves but for the entire earth. This is t ...
... that the glucose produced from this process, is then converted into a variety of forms. It is the speed at which the process of photosynthesis is carried out which ensures that what is produced in this entire mechanism is useful not only for the plants themselves but for the entire earth. This is t ...
Soils 2 - Coastalzone
... Soil texture is the relative proportions of sand, silt and clay in a soil. Soil separates are the size groups of mineral particles less than 2 millimeters (mm). See the chart on page 23, Table 3.1). See Textural Triangle on pg 25. Sand is the 2.0 to .05 millimeter fraction. Under the USDA system it ...
... Soil texture is the relative proportions of sand, silt and clay in a soil. Soil separates are the size groups of mineral particles less than 2 millimeters (mm). See the chart on page 23, Table 3.1). See Textural Triangle on pg 25. Sand is the 2.0 to .05 millimeter fraction. Under the USDA system it ...
animal nutrition propia
... Like other vertebrates, ruminant (including deer, cows...) cannot digest cellulose/fiber. Digestion in ruminants occurs in a four-chambered stomach. Plant material is initially taken into the Rumen, where it is exposed to bacteria than can break down cellulose. The Reticulum allows the animal to reg ...
... Like other vertebrates, ruminant (including deer, cows...) cannot digest cellulose/fiber. Digestion in ruminants occurs in a four-chambered stomach. Plant material is initially taken into the Rumen, where it is exposed to bacteria than can break down cellulose. The Reticulum allows the animal to reg ...
Biology 12 Human Biology - Respiratory System Vocabulary alveoli
... Under what pH conditions is hemoglobin fully saturated? ______pH = 7.4__________ Under what temperature conditions is hemoglobin fully saturated? ____37○C_______ Where are these conditions found, in the lung capillaries or in the tissue capillaries? _______Tissue pH is slightly less than 7.4 and tem ...
... Under what pH conditions is hemoglobin fully saturated? ______pH = 7.4__________ Under what temperature conditions is hemoglobin fully saturated? ____37○C_______ Where are these conditions found, in the lung capillaries or in the tissue capillaries? _______Tissue pH is slightly less than 7.4 and tem ...
Effects of Phosphorus on Nitrogen Fixation
... a low oxygen environment within the nodule Phosphorus Increases Yield and which allows Rhizobium bacteria to live and to Nitrogen Content in Legumes fix N2. Phosphorus becomes involved as an Other studies reveal that P applied to low energy source when 16 molecules of adeno- P soils can increase the ...
... a low oxygen environment within the nodule Phosphorus Increases Yield and which allows Rhizobium bacteria to live and to Nitrogen Content in Legumes fix N2. Phosphorus becomes involved as an Other studies reveal that P applied to low energy source when 16 molecules of adeno- P soils can increase the ...
Lactic acid - Crestwood Science
... The muscles ache and the body experiences cramp, which forces the body to stop what it is doing and rest. Why can anaerobic respiration only be carried out for short periods of time? 7 of 36 ...
... The muscles ache and the body experiences cramp, which forces the body to stop what it is doing and rest. Why can anaerobic respiration only be carried out for short periods of time? 7 of 36 ...
Chapter 5 web
... 5.2 Soil Characteristics of Soil Soil Texture • Texture refers to the proportions of different particle sizes. - Sand (large size) - Silt - Clay (small size) • Loam (a mixture of all three sizes) is best suited for plant life. ...
... 5.2 Soil Characteristics of Soil Soil Texture • Texture refers to the proportions of different particle sizes. - Sand (large size) - Silt - Clay (small size) • Loam (a mixture of all three sizes) is best suited for plant life. ...
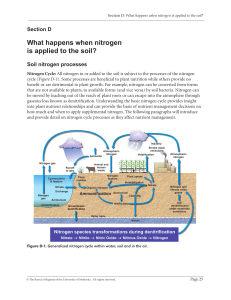
What happens when nitrogen is applied to the soil?
... Mineralization: Mineralization is the process by which organic nitrogen (N) is converted to inorganic, or plant available N (Figure D-2). Specifically, mineralization is the conversion of organic N to NH4+(ammonium). This process is very important for plant growth as organic N is not available for p ...
... Mineralization: Mineralization is the process by which organic nitrogen (N) is converted to inorganic, or plant available N (Figure D-2). Specifically, mineralization is the conversion of organic N to NH4+(ammonium). This process is very important for plant growth as organic N is not available for p ...
objectives
... nitrogen and carbon. Calcite, dolomite, and lime are examples of compounds. These substances consist of several elements bound together (e.g. CaCO3 or CaMg(CO3)2. Most minerals are compounds containing specific elements. The 16 elements required by plants are obtained from the soil, water and air. T ...
... nitrogen and carbon. Calcite, dolomite, and lime are examples of compounds. These substances consist of several elements bound together (e.g. CaCO3 or CaMg(CO3)2. Most minerals are compounds containing specific elements. The 16 elements required by plants are obtained from the soil, water and air. T ...
Rocks and Soils - PES Science Staff Development
... What are the physical characteristics of rocks? Color: The color of the rock. Texture: The way that a rock feels. Luster: The way a rock reflects light. (Is it shiny or dull?) Size: How large or small a rock is. What are some words that might describe my rock’s color? For this part of your AKS, the ...
... What are the physical characteristics of rocks? Color: The color of the rock. Texture: The way that a rock feels. Luster: The way a rock reflects light. (Is it shiny or dull?) Size: How large or small a rock is. What are some words that might describe my rock’s color? For this part of your AKS, the ...
CHAPTER 11CSOIL AS A RESOURCE
... b. overgrazing. c. industrialization. d. agricultural activities. 10. The Dust Bowl of the 1930s resulted from a. clearing and/or close grazing of natural vegetation. b. sustained drought. c. poor farming practices. d. All of the above choices are correct. 11. Dust storms have greatly increased worl ...
... b. overgrazing. c. industrialization. d. agricultural activities. 10. The Dust Bowl of the 1930s resulted from a. clearing and/or close grazing of natural vegetation. b. sustained drought. c. poor farming practices. d. All of the above choices are correct. 11. Dust storms have greatly increased worl ...
Mismatched models: how farmers and scientists see soils
... not only apply different criteria; they arrive at soil categories in different ways. The scientific system starts with a detailed description of the various chemical and physical properties, and sums these up into a single unit called a soil type. Farmers start the other way round. They arrive at a ...
... not only apply different criteria; they arrive at soil categories in different ways. The scientific system starts with a detailed description of the various chemical and physical properties, and sums these up into a single unit called a soil type. Farmers start the other way round. They arrive at a ...
Why Do Septic Systems Fail?
... in disease-causing organisms. This effluent is treated and absorbed in a soil absorption (or leach) field. No matter what the cause, septic system failure is a nuisance and a health hazard that should be corrected promptly. Failures can result in the spread of serious disease and pollution of wells, ...
... in disease-causing organisms. This effluent is treated and absorbed in a soil absorption (or leach) field. No matter what the cause, septic system failure is a nuisance and a health hazard that should be corrected promptly. Failures can result in the spread of serious disease and pollution of wells, ...
teacher guide - National Agriculture in the Classroom
... therefore affects plant growth. 2. Climate: The higher the precipitation and temperature, the greater the weathering. 3. Living organisms: the number of organisms in the soil depends upon the climate. Soils in warmer, moister climates have more microbes. The organisms break down the humus in the soi ...
... therefore affects plant growth. 2. Climate: The higher the precipitation and temperature, the greater the weathering. 3. Living organisms: the number of organisms in the soil depends upon the climate. Soils in warmer, moister climates have more microbes. The organisms break down the humus in the soi ...
Soil respiration

Soil respiration refers to the production of carbon dioxide when soil organisms respire. This includes respiration of plant roots, the rhizosphere, microbes and fauna.Soil respiration is a key ecosystem process that releases carbon from the soil in the form of CO2. CO2 is acquired from the atmosphere and converted into organic compounds in the process of photosynthesis. Plants use these organic compounds to build structural components or respire them to release energy. When plant respiration occurs below-ground in the roots, it adds to soil respiration. Over time, plant structural components are consumed by heterotrophs. This heterotrophic consumption releases CO2 and when this CO2 is released by below-ground organisms, it is considered soil respiration.The amount of soil respiration that occurs in an ecosystem is controlled by several factors. The temperature, moisture, nutrient content and level of oxygen in the soil can produce extremely disparate rates of respiration. These rates of respiration can be measured in a variety of methods. Other methods can be used to separate the source components, in this case the type of photosynthetic pathway (C3/C4), of the respired plant structures.Soil respiration rates can be largely affected by human activity. This is because humans have the ability to and have been changing the various controlling factors of soil respiration for numerous years. Global climate change is composed of numerous changing factors including rising atmospheric CO2, increasing temperature and shifting precipitation patterns. All of these factors can affect the rate of global soil respiration. Increased nitrogen fertilization by humans also has the potential to effect rates over the entire Earth.Soil respiration and its rate across ecosystems is extremely important to understand. This is because soil respiration plays a large role in global carbon cycling as well as other nutrient cycles. The respiration of plant structures releases not only CO2 but also other nutrients in those structures, such as nitrogen. Soil respiration is also associated with positive feedbacks with global climate change. Positive feedbacks are when a change in a system produces response in the same direction of the change. Therefore, soil respiration rates can be effected by climate change and then respond by enhancing climate change.