Lab #9: Ecology (Day 1)
... individuals of the ith species or taxon. The summation symbol (∑) means to do the calculation following the ∑ for each of the species or taxa and then add up the results of all the calculations. D ranges from 1, for a community made up of one species (or other taxon), to infinity, for a community ma ...
... individuals of the ith species or taxon. The summation symbol (∑) means to do the calculation following the ∑ for each of the species or taxa and then add up the results of all the calculations. D ranges from 1, for a community made up of one species (or other taxon), to infinity, for a community ma ...
Soil - drakepond8thgradescience
... to take up as nutrients. This decayed material is called humus. Humus is mostly insoluble, so it remains in these upper layers of soil. It is very dark, nearly black in color. Human created humus is called compost! ...
... to take up as nutrients. This decayed material is called humus. Humus is mostly insoluble, so it remains in these upper layers of soil. It is very dark, nearly black in color. Human created humus is called compost! ...
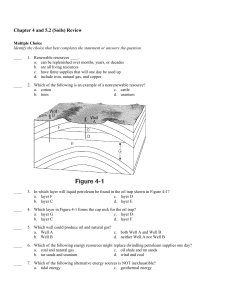
Chapter 4 and 5.2 Review
... ____ 32. Compost helps preserve the health of soil because it ____. a. is a natural fertilizer b. contains pesticides that kill insects c. breaks rock down into additional soil d. adds artificial fertilizers that help plants grow ____ 33. The factor that has the greatest effect on soil formation is ...
... ____ 32. Compost helps preserve the health of soil because it ____. a. is a natural fertilizer b. contains pesticides that kill insects c. breaks rock down into additional soil d. adds artificial fertilizers that help plants grow ____ 33. The factor that has the greatest effect on soil formation is ...
COST 634 "On- and Off-site Environmental
... land management remains very limited • Large gaps exist between knowledge and application at different scales from farm to small regions • Main drivers include socio-economy and policies • soil protection strategies suitable for implementation in practice requires mutual co-operation of scientific e ...
... land management remains very limited • Large gaps exist between knowledge and application at different scales from farm to small regions • Main drivers include socio-economy and policies • soil protection strategies suitable for implementation in practice requires mutual co-operation of scientific e ...
printable mushroom worksheet
... Like animals, they get their food secondhand, so they are not plants. But they are not animals either. So scientists decided to put them in a new kingdom named fungi. Mushrooms are among thousands of different kinds of fungi. (One is called a fungus.) The mushroom is the fruiting stage. Most of the ...
... Like animals, they get their food secondhand, so they are not plants. But they are not animals either. So scientists decided to put them in a new kingdom named fungi. Mushrooms are among thousands of different kinds of fungi. (One is called a fungus.) The mushroom is the fruiting stage. Most of the ...
TDR (Time Domain Reflectometers)
... • The TDR technique is relatively insensitive to salinity as long as the salinity level is low enough that a useful wave form is returned • As salinity levels increase, the signal reflection from the ends of the rods in the TDR probe is lost (amplitude is less). • This occurs because of conduction o ...
... • The TDR technique is relatively insensitive to salinity as long as the salinity level is low enough that a useful wave form is returned • As salinity levels increase, the signal reflection from the ends of the rods in the TDR probe is lost (amplitude is less). • This occurs because of conduction o ...
Weathering and Soil Formation - PAMS-Doyle
... and the amount of time • More surface area means more weathering • Fractured and jointed rock weathers faster • Climate that has extreme seasons allows the greatest rate of weathering. Hot dry climates allow the least amount of weathering • Higher elevations and steeper topography allow for faster w ...
... and the amount of time • More surface area means more weathering • Fractured and jointed rock weathers faster • Climate that has extreme seasons allows the greatest rate of weathering. Hot dry climates allow the least amount of weathering • Higher elevations and steeper topography allow for faster w ...
Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem
... humans have on these cycles? • Can you provide any examples of human activities that result in the alteration of the water or nutrient cycles? ...
... humans have on these cycles? • Can you provide any examples of human activities that result in the alteration of the water or nutrient cycles? ...
11.4 Limiting Factors
... ___________________ 7. A biome that has hot-to-moderate temperatures and very little rainfall is the tropical rain forest biome. ___________________ 8. Large herds of animals often are found grazing in deserts. ...
... ___________________ 7. A biome that has hot-to-moderate temperatures and very little rainfall is the tropical rain forest biome. ___________________ 8. Large herds of animals often are found grazing in deserts. ...
The Group of Plant Nutrition and the Laboratory of
... The Group of Plant Nutrition and the Laboratory of Inorganic Chemistry at ETH Zürich invite applications for a PhD position in soil organic matter/phosphorus biogeochemistry Soil organic matter is one of the most important components regulating the transfer of nutrients in terrestrial ecosystems. An ...
... The Group of Plant Nutrition and the Laboratory of Inorganic Chemistry at ETH Zürich invite applications for a PhD position in soil organic matter/phosphorus biogeochemistry Soil organic matter is one of the most important components regulating the transfer of nutrients in terrestrial ecosystems. An ...
technology for tomato production in bhutan
... type of tomatoes. For bush-type of tomatoes, do fruit thinning to get better size and quality fruits. • For stacking type of tomatoes, remove all suckers on the lower 50 cm of the stem, then let the plant bush out with branches tied to a stake to achieve early and quality fruit production and to avo ...
... type of tomatoes. For bush-type of tomatoes, do fruit thinning to get better size and quality fruits. • For stacking type of tomatoes, remove all suckers on the lower 50 cm of the stem, then let the plant bush out with branches tied to a stake to achieve early and quality fruit production and to avo ...
Feeding and Digestion
... a. Symbionts are the organisms involved in a symbiosis b. Parasitic Symbionts - Parasites live within or on a host organism, where they feed on tissues or on blood and other body fluids. c. Mutualistic Symbionts - relationships in which both participants benefit; example: Reef-building corals depend ...
... a. Symbionts are the organisms involved in a symbiosis b. Parasitic Symbionts - Parasites live within or on a host organism, where they feed on tissues or on blood and other body fluids. c. Mutualistic Symbionts - relationships in which both participants benefit; example: Reef-building corals depend ...
Landscape position effects on water deficit, corn growth, and gene
... At V12: at 10 summit and 5 toeslope locations: 4 newly emerged leaf tips sampled for RNA ...
... At V12: at 10 summit and 5 toeslope locations: 4 newly emerged leaf tips sampled for RNA ...
Part I - Nutrition. I. How to obtain food: This is descriptive
... example is nitrogenous compounds - can’t fix nitrogen, so animals need to get this from diet. Important for amino acids (see below). v) essential nutrients: These are compounds the animal can not manufacture, but are needed for survival. A good example is Vitamins. Note the following: - not all anim ...
... example is nitrogenous compounds - can’t fix nitrogen, so animals need to get this from diet. Important for amino acids (see below). v) essential nutrients: These are compounds the animal can not manufacture, but are needed for survival. A good example is Vitamins. Note the following: - not all anim ...
Soil - Weebly
... • Composition refers to the components that make up soil. • The basic components include minerals, organic matter, water, and air. • Typical soil consists of 45% mineral, 5% organic matter, 20-30% water, and 20-30% air. • These numbers vary greatly, depending on conditions in that specific location. ...
... • Composition refers to the components that make up soil. • The basic components include minerals, organic matter, water, and air. • Typical soil consists of 45% mineral, 5% organic matter, 20-30% water, and 20-30% air. • These numbers vary greatly, depending on conditions in that specific location. ...
CHAPTER 3
... concentration of elements in the plant cell sap can be much higher than in the external solution ...
... concentration of elements in the plant cell sap can be much higher than in the external solution ...
Soil Horizons Questions
... resource. Soil is a thin layer in which plants can grow. Soil is not all the same. It has different layers. The layer on top is made of humus (HYOO-muss). Humus is dark brown or black. It is made of the remains of plants and animals that were once alive. As leaves and other remains rot, they become ...
... resource. Soil is a thin layer in which plants can grow. Soil is not all the same. It has different layers. The layer on top is made of humus (HYOO-muss). Humus is dark brown or black. It is made of the remains of plants and animals that were once alive. As leaves and other remains rot, they become ...
Environmental Consequences of Mining
... process recovered ore. The result is the resulting mine effluent is typically a stew of hazardous acidgenerating sulphides, toxic heavy metals, waste rock impoundments and water—and it is often deposited nearby in large free-draining piles where it can pollute land and water supplies for decades to ...
... process recovered ore. The result is the resulting mine effluent is typically a stew of hazardous acidgenerating sulphides, toxic heavy metals, waste rock impoundments and water—and it is often deposited nearby in large free-draining piles where it can pollute land and water supplies for decades to ...
Lesson 2 overhead page 1 Reducing Sedimentation-A
... Soil with lots of organic matter is often less dense than water so it floats 9. Which soil do you think had most organic matter? Clay, sand or loam? The answer depends on your source of soils, but loam is usually darker and with more organic material. ...
... Soil with lots of organic matter is often less dense than water so it floats 9. Which soil do you think had most organic matter? Clay, sand or loam? The answer depends on your source of soils, but loam is usually darker and with more organic material. ...
Interactive comment on “Seasonal and vertical variations in soil CO2
... evidence. L67: “All these variables”- not exactly clear what you are referring to L70: Different time scales are mentioned here but they are not well defined. As best as I can tell I think you mean seasons as opposed to hourly or diurnal variations. If the hysteresis and eddy covariance evaluations ...
... evidence. L67: “All these variables”- not exactly clear what you are referring to L70: Different time scales are mentioned here but they are not well defined. As best as I can tell I think you mean seasons as opposed to hourly or diurnal variations. If the hysteresis and eddy covariance evaluations ...
LIST OF SOIL TESTING LABS THAT SERVE MICHIGAN and
... Science Society of America and the Soil and Plant Analysis Council. Hence, I discontinued my sample exchange program. The national program is called the North American Proficiency Testing (NAPT) program. There are about 160 labs participating. In this NAPT program five soil samples are sent to parti ...
... Science Society of America and the Soil and Plant Analysis Council. Hence, I discontinued my sample exchange program. The national program is called the North American Proficiency Testing (NAPT) program. There are about 160 labs participating. In this NAPT program five soil samples are sent to parti ...
Soil food web

The soil food web is the community of organisms living all or part of their lives in the soil. It describes a complex living system in the soil and how it interacts with the environment, plants, and animals. Food webs describe the transfer of energy between species in an ecosystem. While a food chain examines one, linear, energy pathway through an ecosystem, a food web is more complex and illustrates all of the potential pathways. Much of this transferred energy comes from the sun. Plants use the sun’s energy to convert inorganic compounds into energy-rich, organic compounds, turning carbon dioxide and minerals into plant material by photosynthesis. Plants are called autotrophs because they make their own energy; they are also called producers because they produce energy available for other organisms to eat. Heterotrophs are consumers that cannot make their own food. In order to obtain energy they eat plants or other heterotrophs.