Galileoscope Optics Guide - Teaching with Telescopes
... You will notice that a converging lens has a curved surface and is thick in the middle and thin at the edges. Light rays that pass through the center of the lens will not change direction. Light rays that hit away from the center of the lens have a different angle of incidence. Therefore, they are r ...
... You will notice that a converging lens has a curved surface and is thick in the middle and thin at the edges. Light rays that pass through the center of the lens will not change direction. Light rays that hit away from the center of the lens have a different angle of incidence. Therefore, they are r ...
Determination of Absolute Values of Refractive Index of Liquids
... would simply be meaningless if the temperature of the sample was not known with high accuracy. As the temperature coefficients of most liquid samples are of the order of ∂n/∂T ≈ 10−4 K−1 a measured index with 6 significant digits is only meaningful if the temperature is declared with precision of th ...
... would simply be meaningless if the temperature of the sample was not known with high accuracy. As the temperature coefficients of most liquid samples are of the order of ∂n/∂T ≈ 10−4 K−1 a measured index with 6 significant digits is only meaningful if the temperature is declared with precision of th ...
The Michelson Interferometer
... The Michelson interferometer is the best known example of a class of interferometers that are known as amplitude-splitting interferometers, that is they produce interference by means of division of the amplitude of incident light by means of arrangements of mirrors and beamsplitters. Michelson devel ...
... The Michelson interferometer is the best known example of a class of interferometers that are known as amplitude-splitting interferometers, that is they produce interference by means of division of the amplitude of incident light by means of arrangements of mirrors and beamsplitters. Michelson devel ...
Progess 11-4-13.pdf
... The mouse phenomenon that makes it so useful is due to several factors; the flat mousing surface, the fact that you are in a gravity field that holds the mouse onto the surface, sufficient friction for the mouse not to be moved by small disturbances, and the user knowing where the mouse is at all ti ...
... The mouse phenomenon that makes it so useful is due to several factors; the flat mousing surface, the fact that you are in a gravity field that holds the mouse onto the surface, sufficient friction for the mouse not to be moved by small disturbances, and the user knowing where the mouse is at all ti ...
measurement of three-dimensional temperature fields
... sequentially in time on a single hologram. In the experiments described in this paper. C,, is an optical wavefront which has passed through an isothermal fluid, and C;: is an initially identical wavefront which has passed through the same fluid after steady natural convection has been established. T ...
... sequentially in time on a single hologram. In the experiments described in this paper. C,, is an optical wavefront which has passed through an isothermal fluid, and C;: is an initially identical wavefront which has passed through the same fluid after steady natural convection has been established. T ...
Manual - Brown University Wiki
... a reference, and adjust the longitudinal position of the lens until the rays are parallel. ...
... a reference, and adjust the longitudinal position of the lens until the rays are parallel. ...
Automated Mode-Matching of Gaussian Beams
... waist of the beam diverges very slowly when properly collimated. This is widely applicable to lab setups where inaccuracies in position are bound to occur due to limitations in ability to place lenses with the precision of micrometers. To create this collimated region the first image resulting from ...
... waist of the beam diverges very slowly when properly collimated. This is widely applicable to lab setups where inaccuracies in position are bound to occur due to limitations in ability to place lenses with the precision of micrometers. To create this collimated region the first image resulting from ...
Lecture 11
... approximation), through collections of optical elements (thin films, prisms, lenses, mirrors etc.), can be derived using simple equations that describe classical ray optics (which totally ignore the wavelike properties of the light). The diffraction properties are “magically” taken account of. ...
... approximation), through collections of optical elements (thin films, prisms, lenses, mirrors etc.), can be derived using simple equations that describe classical ray optics (which totally ignore the wavelike properties of the light). The diffraction properties are “magically” taken account of. ...
3.7 Dielectrics and Optics 3.7.1 Basics
... If we now consider the refracted beam, we know that it travels under an angle β, has the same frequency as the incident beam, but a wavelength λd and a velocity c that is different from λi and c0. Moreover, we must expect that it is damped or attenuated, i.e. that its amplitude decreases as a functi ...
... If we now consider the refracted beam, we know that it travels under an angle β, has the same frequency as the incident beam, but a wavelength λd and a velocity c that is different from λi and c0. Moreover, we must expect that it is damped or attenuated, i.e. that its amplitude decreases as a functi ...
Arbitrary GRIN component fabrication in optically
... monomer and a small amount of photoinitiator. To formulate sample the material components, described in table 1, were mixed together, degassed and then cast between two millimeter thick glass slides at thicknesses ranging from 250 micrometers to two millimeters. To create high quality optical compon ...
... monomer and a small amount of photoinitiator. To formulate sample the material components, described in table 1, were mixed together, degassed and then cast between two millimeter thick glass slides at thicknesses ranging from 250 micrometers to two millimeters. To create high quality optical compon ...
THE FARADAY EFFECT AND DISPERSION IN LIQUIDS
... In practice, one finds that measured Verdet constants follow this form, but with a numerical constant somewhat less than the Becquerel result. This is handled by invoking a correction factor called the magnetooptic constant, γ, and writing V = γVC . One of your tasks in this experiment will be to es ...
... In practice, one finds that measured Verdet constants follow this form, but with a numerical constant somewhat less than the Becquerel result. This is handled by invoking a correction factor called the magnetooptic constant, γ, and writing V = γVC . One of your tasks in this experiment will be to es ...
Home Lab 8 Curved Mirrors, Ray Diagrams, and Simulations
... Determine the focal length of a concave mirror – quickly with a minimum of materials. For a spherical concave mirror – parallel rays of light focus to a point. The distance from the mirror to the focused point image is the focal length of the mirror. Materials Included: • Economy Optical ...
... Determine the focal length of a concave mirror – quickly with a minimum of materials. For a spherical concave mirror – parallel rays of light focus to a point. The distance from the mirror to the focused point image is the focal length of the mirror. Materials Included: • Economy Optical ...
Diffraction-managed superlensing using metallodielectric heterostructures
... source in the input interface of the first MD finite lattice. The light rays emerging from the point object are conveniently deviated at the surface that separates the periodic media, by means of negative refraction, in such a way that at the plane z = L1 + L2 all of them are focused. In order words, ...
... source in the input interface of the first MD finite lattice. The light rays emerging from the point object are conveniently deviated at the surface that separates the periodic media, by means of negative refraction, in such a way that at the plane z = L1 + L2 all of them are focused. In order words, ...
Orbital Dynamics of the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna
... any higher order diffractions and insure a clean Gaussian beam. The light is then reflected off a mirror (6) and sent through a λ/2 wave plate (7) and onto the SLM (8). The λ/2 wave plate has two purposes. The first purpose is to allow the user to control the orientation of the plane polarized light ...
... any higher order diffractions and insure a clean Gaussian beam. The light is then reflected off a mirror (6) and sent through a λ/2 wave plate (7) and onto the SLM (8). The λ/2 wave plate has two purposes. The first purpose is to allow the user to control the orientation of the plane polarized light ...
Presentation
... A multi-plane optical see-through head mounted display design for augmented reality applications. Liu, Shuxin, Yikai Su et al. Journal of the Society for Information Display 24.4 (2016): 246-251. Fast-response switchable lens for 3D and wearable displays. ...
... A multi-plane optical see-through head mounted display design for augmented reality applications. Liu, Shuxin, Yikai Su et al. Journal of the Society for Information Display 24.4 (2016): 246-251. Fast-response switchable lens for 3D and wearable displays. ...
Specifying an Aspheric Surface
... The conic constant in the formula essentially defines the surface profile, as surfaces having different conic constants can have the same radius of curvature. Table 1 lists a range of conic constant, k, values and their associated surface types. The particularly unique property of these conic surfac ...
... The conic constant in the formula essentially defines the surface profile, as surfaces having different conic constants can have the same radius of curvature. Table 1 lists a range of conic constant, k, values and their associated surface types. The particularly unique property of these conic surfac ...
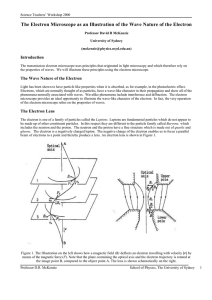
The Electron Microscope as an Illustration of the Wave Nature of the
... Where sinα is known as the numerical aperture with α the acceptance angle of the objective. Since the electron wave has a wavelength of 10-12 metres, while the light wave has a value of 5 x 10-7 metres, at first sight it would seem that the resolving power of the electron microscope should be nearly ...
... Where sinα is known as the numerical aperture with α the acceptance angle of the objective. Since the electron wave has a wavelength of 10-12 metres, while the light wave has a value of 5 x 10-7 metres, at first sight it would seem that the resolving power of the electron microscope should be nearly ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.