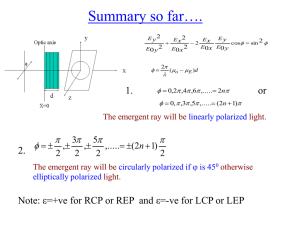
optically active substances.
... When principal plane of nicol N2 is equally inclined to two plane polarized beams means from glass portion and quartz portion Then two parts will appear equally bright or equally dark (Optic axis of N2 is in YY’ or ...
... When principal plane of nicol N2 is equally inclined to two plane polarized beams means from glass portion and quartz portion Then two parts will appear equally bright or equally dark (Optic axis of N2 is in YY’ or ...
WHITEPAPER Centration Measurement, Alignment
... OptiCentric® in the standard reflection mode relies on back-reflection from the lens surface, so the light intensity of the reflected reticule image strongly depends on the type of coating used. Typically, all infrared imaging lenses are AR-coated, however there is a wide variation in efficiency whi ...
... OptiCentric® in the standard reflection mode relies on back-reflection from the lens surface, so the light intensity of the reflected reticule image strongly depends on the type of coating used. Typically, all infrared imaging lenses are AR-coated, however there is a wide variation in efficiency whi ...
waveplates - CVI Laser Optics
... For the full-, half-, and quarter-wave waveplate examples given in standard waveplates, the order of the waveplate is given by the integer m. For m > 0, the waveplate is termed a multiple-order waveplate. For m = 0, we have a zero order waveplate. The birefringence of crystal quartz near 500 nm is a ...
... For the full-, half-, and quarter-wave waveplate examples given in standard waveplates, the order of the waveplate is given by the integer m. For m > 0, the waveplate is termed a multiple-order waveplate. For m = 0, we have a zero order waveplate. The birefringence of crystal quartz near 500 nm is a ...
Large-scale, white-light, transformation optics using integral imaging
... physical space are divided into simplices (triangles in 2D, tetrahedra in 3D). A similar approach was taken in [32]; a 2D example is shown in figure 1. Each physical-space simplex is uniformly sheared and/or strained with respect to the corresponding EM-space simplex. Mathematically, such a uniform d ...
... physical space are divided into simplices (triangles in 2D, tetrahedra in 3D). A similar approach was taken in [32]; a 2D example is shown in figure 1. Each physical-space simplex is uniformly sheared and/or strained with respect to the corresponding EM-space simplex. Mathematically, such a uniform d ...
Lab 5: Polarization of Light 1 Introduction 2 Linear Polarization 3
... Calcite. If the optic axis of a calcite (aka Iceland spar) crystal is oriented properly, and the crystal is placed on a piece of paper with printing on it, as you look through you will see a double image of the letters. Upon rotating the crystal, one of the images will stay fixed, while the other ro ...
... Calcite. If the optic axis of a calcite (aka Iceland spar) crystal is oriented properly, and the crystal is placed on a piece of paper with printing on it, as you look through you will see a double image of the letters. Upon rotating the crystal, one of the images will stay fixed, while the other ro ...
Modal and Material Dispersion
... decreases continuously with increasing radial distance r from center of fiber and constant in cladding r 1/ 2 ...
... decreases continuously with increasing radial distance r from center of fiber and constant in cladding r 1/ 2 ...
Three-dimensional imaging by optical sectioning in the aberration
... can see that they appear out of focus, while in figure 3b they now appear to be in focus compared with the other particles. From this, we can infer that these particles are at different heights on the support. To counter the effects of sample drift, each image in the focal series was aligned using a ...
... can see that they appear out of focus, while in figure 3b they now appear to be in focus compared with the other particles. From this, we can infer that these particles are at different heights on the support. To counter the effects of sample drift, each image in the focal series was aligned using a ...
File - Mr. Catt`s Class
... at which individual waves from an object strike each telescope. 2. Interferometry is possible because extremely accurate atomic clocks allow for precise timing of the signals received by radio telescopes from a distant object. 3. The farther apart the telescopes, the better the resolution. The VLBA ...
... at which individual waves from an object strike each telescope. 2. Interferometry is possible because extremely accurate atomic clocks allow for precise timing of the signals received by radio telescopes from a distant object. 3. The farther apart the telescopes, the better the resolution. The VLBA ...
Dynamic pulsed-beam shaping using a TAG lens in the
... the sharpness and width of the rings. The phase selects the nature of the instantaneous pattern. For instance, when the index of refraction is at a global maximum in the center, the instantaneous pattern is a spot, but at half a period later when it becomes a global minimum, the instantaneous patter ...
... the sharpness and width of the rings. The phase selects the nature of the instantaneous pattern. For instance, when the index of refraction is at a global maximum in the center, the instantaneous pattern is a spot, but at half a period later when it becomes a global minimum, the instantaneous patter ...
Full text
... the sharpness and width of the rings. The phase selects the nature of the instantaneous pattern. For instance, when the index of refraction is at a global maximum in the center, the instantaneous pattern is a spot, but at half a period later when it becomes a global minimum, the instantaneous patter ...
... the sharpness and width of the rings. The phase selects the nature of the instantaneous pattern. For instance, when the index of refraction is at a global maximum in the center, the instantaneous pattern is a spot, but at half a period later when it becomes a global minimum, the instantaneous patter ...
Click
... refracted rays is an ordinary ray and the other is an extraordinary. e. g. Calcite, tourmaline and Quartz. (ii)Biaxial Crystal: In biaxial crystal both the refracted rays ...
... refracted rays is an ordinary ray and the other is an extraordinary. e. g. Calcite, tourmaline and Quartz. (ii)Biaxial Crystal: In biaxial crystal both the refracted rays ...
Lecture 18
... How do you capture multiple focal planes without aberrations? • Spherical aberrations result if two focal planes more than a few microns apart • So multiple focal planes from camera translation limited in z-dimension ...
... How do you capture multiple focal planes without aberrations? • Spherical aberrations result if two focal planes more than a few microns apart • So multiple focal planes from camera translation limited in z-dimension ...
Lecture 11
... approximation), through collections of optical elements (thin films, prisms, lenses, mirrors etc.), can be derived using simple equations that describe classical ray optics (which totally ignore the wavelike properties of the light). The diffraction properties are “magically” taken account of. ...
... approximation), through collections of optical elements (thin films, prisms, lenses, mirrors etc.), can be derived using simple equations that describe classical ray optics (which totally ignore the wavelike properties of the light). The diffraction properties are “magically” taken account of. ...
powerpoint
... Large diameter telescopes have small fringes and we can see smaller details. Therefore the larger the telescope, the better its resolving power. Optical quality and atmospheric conditions limit the detail we can see. ...
... Large diameter telescopes have small fringes and we can see smaller details. Therefore the larger the telescope, the better its resolving power. Optical quality and atmospheric conditions limit the detail we can see. ...
Close-range videometry -
... as consisting of two cameras with imaginary positions and rotations because of the mirrors and split-image arrangements. Figure 7 shows the geometry of the imaging system. The two halves of the sensor form the two images of the imaginary cameras. The interior orientation denotes the estimation of th ...
... as consisting of two cameras with imaginary positions and rotations because of the mirrors and split-image arrangements. Figure 7 shows the geometry of the imaging system. The two halves of the sensor form the two images of the imaginary cameras. The interior orientation denotes the estimation of th ...
Optical Networks
... Optical Components: Couplers, Isolators & Circulators, Multiplexers & Filters (Grating, Fiber Bragg Grating, Fabry-Perot Filters, Dielectric filters, Acousto-optic filter, etc.), Some Optical Amplifiers (Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers, Raman Amplifiers, Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers), Switches (La ...
... Optical Components: Couplers, Isolators & Circulators, Multiplexers & Filters (Grating, Fiber Bragg Grating, Fabry-Perot Filters, Dielectric filters, Acousto-optic filter, etc.), Some Optical Amplifiers (Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers, Raman Amplifiers, Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers), Switches (La ...
Telescopes and spectrographs
... instrument movable. It is clear from Figure 3 that the physical length of a Keplerian refracting telescope cannot be less than fo. Hence, it would hardly be realistic to plan a telescope with a focal length of 100 metres using this design! However, it is important to remember that achieving high mag ...
... instrument movable. It is clear from Figure 3 that the physical length of a Keplerian refracting telescope cannot be less than fo. Hence, it would hardly be realistic to plan a telescope with a focal length of 100 metres using this design! However, it is important to remember that achieving high mag ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.