Physically-Based Glare Effects for Digital Images
... The ciliary corona is depicted in Figure 2 and consists of rays emanating from a point light source. These radial rays may extend beyond the lenticular halo, and are brighter and more pronounced as the angle subtended by the source decreases (Figure 4). The ciliary corona is caused by semi-random de ...
... The ciliary corona is depicted in Figure 2 and consists of rays emanating from a point light source. These radial rays may extend beyond the lenticular halo, and are brighter and more pronounced as the angle subtended by the source decreases (Figure 4). The ciliary corona is caused by semi-random de ...
Chapter 4
... phase-matching; a few examples are listed below (adapted from ref. 5). The important crystals ADP and KDP and their analogues belong to the point group 42m, and hence have tetragonal ...
... phase-matching; a few examples are listed below (adapted from ref. 5). The important crystals ADP and KDP and their analogues belong to the point group 42m, and hence have tetragonal ...
Observation of coupling between surface plasmons in index
... for the typical situation that the radiative loss is much larger than the intrinsic Ohmic loss. The number of fit parameters can be reduced by setting all phases j equal to . This corresponds to the normal situation, where the resonant channel is out of phase with the direct channel. This choice ...
... for the typical situation that the radiative loss is much larger than the intrinsic Ohmic loss. The number of fit parameters can be reduced by setting all phases j equal to . This corresponds to the normal situation, where the resonant channel is out of phase with the direct channel. This choice ...
Superresolution size determination in fluorescence microscopy: A
... may be used, with each parameter corresponding to a physically detectable value: The subscripts i and o are used for the inner and outer enveloping AID profiles 共cf. Fig. 1兲. M i,o are the maximum intensities of the enveloping functions; B i,o are constants proportional to the FWHM of the enveloping ...
... may be used, with each parameter corresponding to a physically detectable value: The subscripts i and o are used for the inner and outer enveloping AID profiles 共cf. Fig. 1兲. M i,o are the maximum intensities of the enveloping functions; B i,o are constants proportional to the FWHM of the enveloping ...
Design and investigation of properties of nanocrystalline diamond
... synthetically prepared NCD film usually has lower value but NCD deposited on silica on silicon substrate has still high index contrast. The waveguides created this way are known as high index contrast (HIC) waveguides and have much higher index contrast than common photonic materials (polymers, opti ...
... synthetically prepared NCD film usually has lower value but NCD deposited on silica on silicon substrate has still high index contrast. The waveguides created this way are known as high index contrast (HIC) waveguides and have much higher index contrast than common photonic materials (polymers, opti ...
Chapter 2 Optical Layout
... Figure 2.5: Reflection angle The “reflection angle” is so called by convention; it is the angle that the reflected or refracted central ray makes with the normal to the surface of the optical element. For most purposes it is set equal to the incidence angle shown in figure 2.5 but in many cases it i ...
... Figure 2.5: Reflection angle The “reflection angle” is so called by convention; it is the angle that the reflected or refracted central ray makes with the normal to the surface of the optical element. For most purposes it is set equal to the incidence angle shown in figure 2.5 but in many cases it i ...
Enhanced visualization of choroidal vessels using ultrahigh
... Optical coherence tomography is an imaging technique that permits retrieval of crosssectional morphological and functional information from superficial regions of biological tissue1-3. Since ocular media are essentially transparent in the visible and near-infrared wavelength region, and provide opti ...
... Optical coherence tomography is an imaging technique that permits retrieval of crosssectional morphological and functional information from superficial regions of biological tissue1-3. Since ocular media are essentially transparent in the visible and near-infrared wavelength region, and provide opti ...
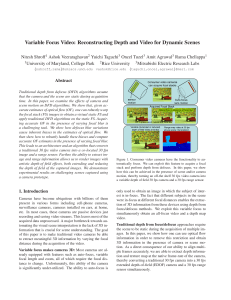
Variable Focus Video: Reconstructing Depth and Video
... In the first iteration, the depth and the texture maps are unavailable. Hence, flow estimation can be approached by first computing a coarse optical flow and then refining via reblurring during the subsequent iterations. Initial Flow: Several approaches to compute the coarse initial flow can be adop ...
... In the first iteration, the depth and the texture maps are unavailable. Hence, flow estimation can be approached by first computing a coarse optical flow and then refining via reblurring during the subsequent iterations. Initial Flow: Several approaches to compute the coarse initial flow can be adop ...
Resolution in Confocal Microscopy
... of images, the confocal microscope is a scanning microscope. This means that there must a time-lag between the collection of each point. When looking at two small objects simultaneously, methods such as fluorescence correlation spectroscopy[20][21] take advantage of this by looking at the location o ...
... of images, the confocal microscope is a scanning microscope. This means that there must a time-lag between the collection of each point. When looking at two small objects simultaneously, methods such as fluorescence correlation spectroscopy[20][21] take advantage of this by looking at the location o ...
Theory and Practice of Scanning Optical Microscopy - X
... The integral is the convolution of the object transmittance with the point spread function, the M's resulting in a magnification M in the image, and the positive sign in the argument of the spread function corresponding to an inverted image. Of the two complex exponential terms in (2.57) the first i ...
... The integral is the convolution of the object transmittance with the point spread function, the M's resulting in a magnification M in the image, and the positive sign in the argument of the spread function corresponding to an inverted image. Of the two complex exponential terms in (2.57) the first i ...
Eye Box Performance Parameters for Non Pupil Forming Head
... will require the eye box to be larger to allow for movement of the pupil caused by movement of the user’s pupil relative the HMD. This type of motion occurs when an HMD is used in a moving vehicle or designed to be used by while moving on foot. The amount movement seen in these situations comes from ...
... will require the eye box to be larger to allow for movement of the pupil caused by movement of the user’s pupil relative the HMD. This type of motion occurs when an HMD is used in a moving vehicle or designed to be used by while moving on foot. The amount movement seen in these situations comes from ...
Self-rotation of resonant elliptically polarized light in collision
... since the late 1960’s. The original interest in SR in atomic vapors was related to understanding the polarization of gas laser emission [17]. Later, SR was theoretically examined [18–21] in the context of high-resolution polarization spectroscopy [22]. The theory of SR has also been studied in relat ...
... since the late 1960’s. The original interest in SR in atomic vapors was related to understanding the polarization of gas laser emission [17]. Later, SR was theoretically examined [18–21] in the context of high-resolution polarization spectroscopy [22]. The theory of SR has also been studied in relat ...
Paraxial propagation of Mathieu beams through an apertured ABCD
... In recent years, the non-diffracting beams have received much attention in the optical domain. The interest in non-diffracting beams is due to the fact that, under ideal conditions, they propagate indefinitely without change in their transverse shape. This kind of beams has been used in different applic ...
... In recent years, the non-diffracting beams have received much attention in the optical domain. The interest in non-diffracting beams is due to the fact that, under ideal conditions, they propagate indefinitely without change in their transverse shape. This kind of beams has been used in different applic ...
Multi-photon absorption and third-order
... ranged from 38 to 123 µm for different wavelengths. As shown, α3 and α4 present nonlinear absorption coefficients for 3PA and 4PA. The peak intensity I00 at the sample is determined as I00 = laser_power / [(πω02) × pulse_repetitions × pulse_width] × 40%, due to Fresnel reflection and back scattering ...
... ranged from 38 to 123 µm for different wavelengths. As shown, α3 and α4 present nonlinear absorption coefficients for 3PA and 4PA. The peak intensity I00 at the sample is determined as I00 = laser_power / [(πω02) × pulse_repetitions × pulse_width] × 40%, due to Fresnel reflection and back scattering ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.