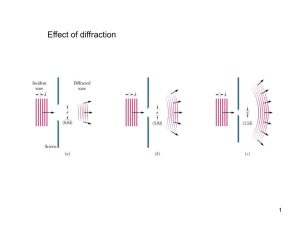
A high numerical aperture (NA = 0.92)
... than 100 × 100 lattice sites in a typical optical lattice. Figure 1(b) shows a close-up, recorded with our objective lens, of two adjacent cesium atoms, which are trapped in an optical lattice with a lattice constant of 612 nm. Lens design. Due to their large collection angle, objective lenses with ...
... than 100 × 100 lattice sites in a typical optical lattice. Figure 1(b) shows a close-up, recorded with our objective lens, of two adjacent cesium atoms, which are trapped in an optical lattice with a lattice constant of 612 nm. Lens design. Due to their large collection angle, objective lenses with ...
light is - msmcgartland
... 2. Draw the normals from the mirror surface to significant points, such as the top and bottom of the object. The number of other points depends on the object. ...
... 2. Draw the normals from the mirror surface to significant points, such as the top and bottom of the object. The number of other points depends on the object. ...
Diode pumped distributed Bragg reflector lasers
... The PLQY is the ratio of photons emitted to photons absorbed, and is measured for films mounted inside an integrating sphere in order to collect light emitted in all directions [15]. In Fig. 1(b), the PLQY is plotted as a function of the doping concentration for both the direct excitation of the pol ...
... The PLQY is the ratio of photons emitted to photons absorbed, and is measured for films mounted inside an integrating sphere in order to collect light emitted in all directions [15]. In Fig. 1(b), the PLQY is plotted as a function of the doping concentration for both the direct excitation of the pol ...
Laser Cooling
... atom moves toward the laser. Using equation [1], the photons of this wavelength have a momentum in the order of 10-28 kg m/s. This number is about 104 times smaller than the momentum of an 87Rb atom moving at the 20 m/s critical velocity. There are many obstacles to overcome in order to get this fre ...
... atom moves toward the laser. Using equation [1], the photons of this wavelength have a momentum in the order of 10-28 kg m/s. This number is about 104 times smaller than the momentum of an 87Rb atom moving at the 20 m/s critical velocity. There are many obstacles to overcome in order to get this fre ...
Development of a Total Internal Reflection Illumination System for
... Many cell surface receptors consist of multiple subunits that non-‐covalently associate to form a complete receptor. The integrin receptor is one such example. It is hypothesized that a drug (Thioridazine) ...
... Many cell surface receptors consist of multiple subunits that non-‐covalently associate to form a complete receptor. The integrin receptor is one such example. It is hypothesized that a drug (Thioridazine) ...
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
... concave glass lens ! At the surface of the lens, the light rays are refracted toward the normal ! When the rays leave the lens, they are refracted away from the normal as shown ! The extrapolated line shown as a red and black dashed line that points to the focal point on the same side of the lens as ...
... concave glass lens ! At the surface of the lens, the light rays are refracted toward the normal ! When the rays leave the lens, they are refracted away from the normal as shown ! The extrapolated line shown as a red and black dashed line that points to the focal point on the same side of the lens as ...
Structure of Optical Vortices
... optical tweezer technique [10], and of their ability to exert torques on trapped materials. These measurements reveal qualitative discrepancies with predicted behavior, which we explain on the basis of scalar diffraction theory. A helical mode ψ` (~r) is distinguished by a phase factor proportional ...
... optical tweezer technique [10], and of their ability to exert torques on trapped materials. These measurements reveal qualitative discrepancies with predicted behavior, which we explain on the basis of scalar diffraction theory. A helical mode ψ` (~r) is distinguished by a phase factor proportional ...
ACOUSTO-OPTICS
... (graded-index) media was discussedat several points in Chaps. 1 and 2 (Sets. 1.3 and 2.4C). Since optical frequencies are much greater than acoustic frequencies, the variations of the refractive index in a medium perturbed by sound are usually very slow in comparison with an optical period. There ar ...
... (graded-index) media was discussedat several points in Chaps. 1 and 2 (Sets. 1.3 and 2.4C). Since optical frequencies are much greater than acoustic frequencies, the variations of the refractive index in a medium perturbed by sound are usually very slow in comparison with an optical period. There ar ...
4-2 Optical Heterodyne Detection for 60- GHz-Band Radio-on
... use a 60-GHz-band electroabsorption modulator (EAM) for downlinking and uplinking [2][3] . To receive optical power large enough to get high transmission quality, using some optical amplifiers is necessary in the optical link. However, accumulated amplified-spontaneous-emission (ASE) noise from the ...
... use a 60-GHz-band electroabsorption modulator (EAM) for downlinking and uplinking [2][3] . To receive optical power large enough to get high transmission quality, using some optical amplifiers is necessary in the optical link. However, accumulated amplified-spontaneous-emission (ASE) noise from the ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.