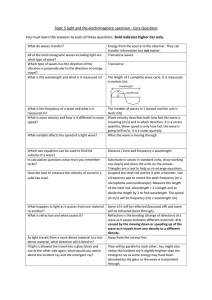
Topic 5 Core Questions
... divide the length by 2 to find wavelength. The speed (in m/s) will be frequency (Hz) x wavelength (m). Some of it will be reflected (bounced off) and some will be refracted (bent through). Refraction is the bending (change of direction) of a wave as it passes between different materials. It is cause ...
... divide the length by 2 to find wavelength. The speed (in m/s) will be frequency (Hz) x wavelength (m). Some of it will be reflected (bounced off) and some will be refracted (bent through). Refraction is the bending (change of direction) of a wave as it passes between different materials. It is cause ...
Lab 3: Wave Plates and Polarization of Light – Physical Science
... faster in the wave plate compared to the other. The birefringent material of the wave plate are asymmetric in that they have a different index of refraction in one polarization direction compared to the other. The “optical” or fast axis is usually indicated on the wave plate. Light polarized along t ...
... faster in the wave plate compared to the other. The birefringent material of the wave plate are asymmetric in that they have a different index of refraction in one polarization direction compared to the other. The “optical” or fast axis is usually indicated on the wave plate. Light polarized along t ...
Visible Light, Wide-Angle Graded Metasurface for Back Reflection
... stemming directly from reciprocity,28,29 and it is not limited to our particular configuration. More specifically, if the surface is designed to back reflect with x% efficiency for the AOI θi, it ensures (100 − x)% coupling to the specular direction (θr = θi). Reciprocity then ensures that, when the dire ...
... stemming directly from reciprocity,28,29 and it is not limited to our particular configuration. More specifically, if the surface is designed to back reflect with x% efficiency for the AOI θi, it ensures (100 − x)% coupling to the specular direction (θr = θi). Reciprocity then ensures that, when the dire ...
Physics 228 Today: Polarization, Scattering
... When light is incident upon a surface, it generally partially refracts and partially reflects. The ``plane of incidence’’ is the plane that contains the incident and reflected light rays. The electric field can be split into a component in the plane of incidence, and a component perpendicular to the ...
... When light is incident upon a surface, it generally partially refracts and partially reflects. The ``plane of incidence’’ is the plane that contains the incident and reflected light rays. The electric field can be split into a component in the plane of incidence, and a component perpendicular to the ...
Learning material
... Because the image cannot be formed on a screen it is said to be virtual. The image is rightleft inverted relative to the object. Incidentally, many people think that this inversion does not make any difference in looking at their face in the mirror, because faces are symmetric. In fact, most faces a ...
... Because the image cannot be formed on a screen it is said to be virtual. The image is rightleft inverted relative to the object. Incidentally, many people think that this inversion does not make any difference in looking at their face in the mirror, because faces are symmetric. In fact, most faces a ...
CP2: Optics Why study optics? The problem of teaching optics
... from glass into air will follow exactly the same path as a light ray travelling from air into glass, just in the ...
... from glass into air will follow exactly the same path as a light ray travelling from air into glass, just in the ...
Phase Change upon Reflection—CE Mungan, Spring 2008
... is analogous to a transverse wave pulse incident from a low-density to a high-density string, for which the reflected pulse is similarly inverted. Textbooks could improve their string/light wave analogy for phase reflection if they built their argument as follows: (i) A string wave is inverted when ...
... is analogous to a transverse wave pulse incident from a low-density to a high-density string, for which the reflected pulse is similarly inverted. Textbooks could improve their string/light wave analogy for phase reflection if they built their argument as follows: (i) A string wave is inverted when ...
Universidad de Cantabria ON LIGHT SCATTERING BY NANOPARTICLES WITH CONVENTIONAL AND NON-CONVENTIONAL
... of the LSPR spectral position to environmental changes. For this reason, several works have focused on the improvement of the sensitivity of metallic nanostructures. They are chemically modified with interesting properties for food-safety, medical treatments or for biological and environmental resea ...
... of the LSPR spectral position to environmental changes. For this reason, several works have focused on the improvement of the sensitivity of metallic nanostructures. They are chemically modified with interesting properties for food-safety, medical treatments or for biological and environmental resea ...
Intraocular Lenses
... concentric rings in the zone plate pictured above). The edge of each zone is /2 farther away from Po than the edge of the neighboring zone. 2. Notice that the wave that travels along the axis of the aperture experiences constructive interference with waves from some of the zones (OPD = m, m=intege ...
... concentric rings in the zone plate pictured above). The edge of each zone is /2 farther away from Po than the edge of the neighboring zone. 2. Notice that the wave that travels along the axis of the aperture experiences constructive interference with waves from some of the zones (OPD = m, m=intege ...
two-slit interference,one photon at a time
... 2. Two-Slit Interference, One Photon at a Time: (by filtrated bulb light) The channel is opened, the laser turned off and the bulb lifted into place. The bulb intensity is set to about half of maximum. Because of the green filter, the number of photon passing through the channel is too rare to be de ...
... 2. Two-Slit Interference, One Photon at a Time: (by filtrated bulb light) The channel is opened, the laser turned off and the bulb lifted into place. The bulb intensity is set to about half of maximum. Because of the green filter, the number of photon passing through the channel is too rare to be de ...
4 Lab 1: Scattering and Reflection of Polarized Light
... When θi > θc , there is no real (in the mathematical sense) solution for the angle of refraction and all of the incident light is reflected into the medium with index n1 . The phenomenon of total internal reflection is important for fiber optic communication technology because one would like the lig ...
... When θi > θc , there is no real (in the mathematical sense) solution for the angle of refraction and all of the incident light is reflected into the medium with index n1 . The phenomenon of total internal reflection is important for fiber optic communication technology because one would like the lig ...
Microscope
... feet for some tapeworms. Because nearly all parasites have life cycle stages that are microscopic (many large parasite produce small immature stages), the proper use of the microscope is crucial to successful parasitology. All microscopes provide two types of power—magnification and resolution (also ...
... feet for some tapeworms. Because nearly all parasites have life cycle stages that are microscopic (many large parasite produce small immature stages), the proper use of the microscope is crucial to successful parasitology. All microscopes provide two types of power—magnification and resolution (also ...
Document
... A reflecting surface is one that is highly polished, opaque and coated with special reflective materials. The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. The incident ray is the line AO, the reflected ray is OB and ON is the normal to the reflecting surf ...
... A reflecting surface is one that is highly polished, opaque and coated with special reflective materials. The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. The incident ray is the line AO, the reflected ray is OB and ON is the normal to the reflecting surf ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.