71KB - NZQA
... Sunlight is made up of three primary colours: red, blue and green. Red is the longest wavelength colour, and blue is the shortest wavelength colour. Sunlight is made up of multiple colours of light, each with their own wavelengths. When there are lots of gas particles in the atmosphere that are smal ...
... Sunlight is made up of three primary colours: red, blue and green. Red is the longest wavelength colour, and blue is the shortest wavelength colour. Sunlight is made up of multiple colours of light, each with their own wavelengths. When there are lots of gas particles in the atmosphere that are smal ...
146KB - NZQA
... Sunlight is made up of three primary colours: red, blue and green. Red is the longest wavelength colour, and blue is the shortest wavelength colour. Sunlight is made up of multiple colours of light, each with their own wavelengths. When there are lots of gas particles in the atmosphere that are smal ...
... Sunlight is made up of three primary colours: red, blue and green. Red is the longest wavelength colour, and blue is the shortest wavelength colour. Sunlight is made up of multiple colours of light, each with their own wavelengths. When there are lots of gas particles in the atmosphere that are smal ...
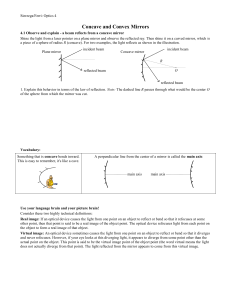
Concave and Convex Mirrors
... Virtual image: An optical device sometimes causes the light from one point on an object to reflect or bend so that it diverges and never refocuses. However, if your eye looks at this diverging light, it appears to diverge from some point other than the actual point on the object. This point is said ...
... Virtual image: An optical device sometimes causes the light from one point on an object to reflect or bend so that it diverges and never refocuses. However, if your eye looks at this diverging light, it appears to diverge from some point other than the actual point on the object. This point is said ...
The long march of slow photonics
... Bb the pulse (bit) bandwidth. This relation does not depend on the device’s dimensions and type, or on the slow-down factor. The guiding structure with the highest ratio ng/α will prevail. Furthermore, to be of practical use in many applications, slow-light schemes must allow the delay to be control ...
... Bb the pulse (bit) bandwidth. This relation does not depend on the device’s dimensions and type, or on the slow-down factor. The guiding structure with the highest ratio ng/α will prevail. Furthermore, to be of practical use in many applications, slow-light schemes must allow the delay to be control ...
Chapter 4 Optical Sources
... The photon produced by stimulated emission is generally of an identical energy to the one which caused it and hence the light associated with them is the same frequency – Monocromatic The light associated with the stimulating and stimulated photon is in phase and has a same polarization – Coherent F ...
... The photon produced by stimulated emission is generally of an identical energy to the one which caused it and hence the light associated with them is the same frequency – Monocromatic The light associated with the stimulating and stimulated photon is in phase and has a same polarization – Coherent F ...
Non-invasive ophthalmic imaging of adult zebrafish eye using
... reference signal with that reflected from a specific depth in the sample (such that the optical path length of the two interferometer arms are within coherence length) results in interference signal at Doppler frequency, which can be isolated from the rest of the backscattered signal by a suitable b ...
... reference signal with that reflected from a specific depth in the sample (such that the optical path length of the two interferometer arms are within coherence length) results in interference signal at Doppler frequency, which can be isolated from the rest of the backscattered signal by a suitable b ...
Basics in Confocal Microscopy Handouts
... Imaging e.g. CFP and YFP simultaneous is important for some biological applications. ...
... Imaging e.g. CFP and YFP simultaneous is important for some biological applications. ...
Converging Lens
... First, some definitions: a converging lens is defined as a lens with two convex surfaces. A diverging lens is a lens with two concave surfaces. An object is any article that is being viewed through an optical system; e.g., when one looks at a tree through a camera lens, telescope, or the naked eye ( ...
... First, some definitions: a converging lens is defined as a lens with two convex surfaces. A diverging lens is a lens with two concave surfaces. An object is any article that is being viewed through an optical system; e.g., when one looks at a tree through a camera lens, telescope, or the naked eye ( ...
Ray Tracing
... 1) the parallel ray passes through the focal point on the other side of the lens, 2) the straight through ray passes – straight through the lens, and 3) the focal length ray passes through the lens parallel to the horizontal axis. NOTE: ray 1 and ray 3 are the opposites of each other. This is in fac ...
... 1) the parallel ray passes through the focal point on the other side of the lens, 2) the straight through ray passes – straight through the lens, and 3) the focal length ray passes through the lens parallel to the horizontal axis. NOTE: ray 1 and ray 3 are the opposites of each other. This is in fac ...
Photoelectric Effect - Data Analysis Exercise
... http://phet.colorado.ed.au/en/simulation/photoelectric First, with the circuit set up so that the battery is attracting electrons: 1. The photoelectric effect occurs when ______________ shines on a metal. Electrons can absorb the energy from the light. If there is enough energy, they can __________ ...
... http://phet.colorado.ed.au/en/simulation/photoelectric First, with the circuit set up so that the battery is attracting electrons: 1. The photoelectric effect occurs when ______________ shines on a metal. Electrons can absorb the energy from the light. If there is enough energy, they can __________ ...
1 L2: Reflection and Refraction c3.L2 REFLECTION AND
... This chapter is concerned mostly with what happens to light when it encounters the boundary between two different materials. Before going into details of reflection and refraction we start with an overview of the processes that can happen. We can represent light travelling through empty space or air ...
... This chapter is concerned mostly with what happens to light when it encounters the boundary between two different materials. Before going into details of reflection and refraction we start with an overview of the processes that can happen. We can represent light travelling through empty space or air ...
Whispering-gallery-mode microdisk lasers
... also exhibits significant lasing actions characteristic of an abrupt increase of light output and the significant narrowing of the spectral lines when the threshold is approached. This work shows that the laser micronanofabrication technology is not only applicable to passive micro-optical component ...
... also exhibits significant lasing actions characteristic of an abrupt increase of light output and the significant narrowing of the spectral lines when the threshold is approached. This work shows that the laser micronanofabrication technology is not only applicable to passive micro-optical component ...
Optical Microscopy Beyond the Diffraction Limit
... high power semiconductor lasers using NSOM. In this case, the advantage of NSOM is to provide a means for localized high-resolution sensing of the propagating fields. The laser diodes we tested are designed to emit a nearly diffraction limited single lobe at 980 nm wavelength to be used for optical ...
... high power semiconductor lasers using NSOM. In this case, the advantage of NSOM is to provide a means for localized high-resolution sensing of the propagating fields. The laser diodes we tested are designed to emit a nearly diffraction limited single lobe at 980 nm wavelength to be used for optical ...
Study guide for Tools of Astronomy
... Refracting – uses convex lenses which cause the light rays to bend, can cause “chromatic aberrations” which cause the image to be blurry. Galileo first used a refracting telescope to view the night sky in 1609 Reflecting - uses a concave mirror to reflect the received starlight to the eyepiece resul ...
... Refracting – uses convex lenses which cause the light rays to bend, can cause “chromatic aberrations” which cause the image to be blurry. Galileo first used a refracting telescope to view the night sky in 1609 Reflecting - uses a concave mirror to reflect the received starlight to the eyepiece resul ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.