The Dual-Listing Law:
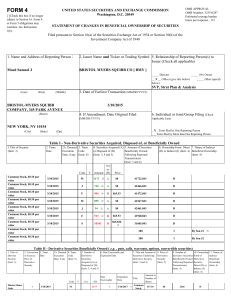
... American Stock Exchange, or the London Stock Exchange’s Main Market (Primary Listing) for at least a year since their IPOs are eligible to dual-list. Also eligible are companies that have traded for less than a year but maintain a market value exceeding $150 million. For companies traded on the Nasd ...
... American Stock Exchange, or the London Stock Exchange’s Main Market (Primary Listing) for at least a year since their IPOs are eligible to dual-list. Also eligible are companies that have traded for less than a year but maintain a market value exceeding $150 million. For companies traded on the Nasd ...
offensive selling – selling into strength
... Leading Stocks in the Group Break Down - A large percentage of a stock’s movement is directly tied to the performance of the industry group of which it is a part. As a result, stocks often run in “packs” - When one or more leading stocks in a group clearly top after an extended run: o The selling of ...
... Leading Stocks in the Group Break Down - A large percentage of a stock’s movement is directly tied to the performance of the industry group of which it is a part. As a result, stocks often run in “packs” - When one or more leading stocks in a group clearly top after an extended run: o The selling of ...
Balancing Public Market Benefits and Burdens for Smaller
... and benefits of being a public company under the SEC’s regulatory regime. Part II describes the OTCBB eligibility rule, Regulation FD, and Sarbanes-Oxley and then discusses how they have added to the regulatory burden on small businesses, such that the costs of being a pubic company often outweigh t ...
... and benefits of being a public company under the SEC’s regulatory regime. Part II describes the OTCBB eligibility rule, Regulation FD, and Sarbanes-Oxley and then discusses how they have added to the regulatory burden on small businesses, such that the costs of being a pubic company often outweigh t ...
M.I.T. 15.460 Sloan School of Management Financial Engineering
... Financial Engineering Course Description This course provides an introduction to financial engineering. The course covers the following topics: asset pricing theory and its applications, financial optimization, market equilibrium, market frictions, dynamics trading strategies, risk management, and s ...
... Financial Engineering Course Description This course provides an introduction to financial engineering. The course covers the following topics: asset pricing theory and its applications, financial optimization, market equilibrium, market frictions, dynamics trading strategies, risk management, and s ...
list of eu regulated markets - Agencija za trg vrednostnih papirjev
... Article 47 of Directive 2004/39/EC requires that each Member State maintains an updated list of regulated markets authorised by it. This information should be communicated to other Member States and the European Commission. Under the same Article (Article 47 of Directive 2004/39/EC), the Commission ...
... Article 47 of Directive 2004/39/EC requires that each Member State maintains an updated list of regulated markets authorised by it. This information should be communicated to other Member States and the European Commission. Under the same Article (Article 47 of Directive 2004/39/EC), the Commission ...
download
... Investors can use any or all of these different but somewhat complementary methods for stock picking. For example many fundamental investors use technicals for deciding entry and exit points. Many technical investors use fundamentals to limit their universe of possible stock to 'good' companies. The ...
... Investors can use any or all of these different but somewhat complementary methods for stock picking. For example many fundamental investors use technicals for deciding entry and exit points. Many technical investors use fundamentals to limit their universe of possible stock to 'good' companies. The ...
Externalities Pollution Smoking Ugly houses Drunk driving Loud
... Market Interventions Government is used for two main purposes, market failure and redistribution. Market failure refers to bad outcomes of competition, and the government may intervene in the market place to improve the outcome. In addition to monopoly, there are two other main sources of market fa ...
... Market Interventions Government is used for two main purposes, market failure and redistribution. Market failure refers to bad outcomes of competition, and the government may intervene in the market place to improve the outcome. In addition to monopoly, there are two other main sources of market fa ...
2010 Flash Crash

The May 6, 2010, Flash Crash also known as The Crash of 2:45, the 2010 Flash Crash or simply the Flash Crash, was a United States trillion-dollar stock market crash, which started at 2:32 and lasted for approximately 36 minutes. Stock indexes, such as the S&P 500, Dow Jones Industrial Average and Nasdaq 100, collapsed and rebounded very rapidly.The Dow Jones Industrial Average had its biggest intraday point drop (from the opening) up to that point, plunging 998.5 points (about 9%), most within minutes, only to recover a large part of the loss. It was also the second-largest intraday point swing (difference between intraday high and intraday low) up to that point, at 1,010.14 points. The prices of stocks, stock index futures, options and ETFs were volatile, thus trading volume spiked. A CFTC 2014 report described it as one of the most turbulent periods in the history of financial markets.On April 21, 2015, nearly five years after the incident, the U.S. Department of Justice laid ""22 criminal counts, including fraud and market manipulation"" against Navinder Singh Sarao, a trader. Among the charges included was the use of spoofing algorithms; just prior to the Flash Crash, he placed thousands of E-mini S&P 500 stock index futures contracts which he planned on canceling later. These orders amounting to about ""$200 million worth of bets that the market would fall"" were ""replaced or modified 19,000 times"" before they were canceled. Spoofing, layering and front-running are now banned.The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) investigation concluded that Sarao ""was at least significantly responsible for the order imbalances"" in the derivatives market which affected stock markets and exacerbated the flash crash. Sarao began his alleged market manipulation in 2009 with commercially available trading software whose code he modified ""so he could rapidly place and cancel orders automatically."" Traders Magazine journalist, John Bates, argued that blaming a 36-year-old small-time trader who worked from his parents' modest stucco house in suburban west London for sparking a trillion-dollar stock market crash is a little bit like blaming lightning for starting a fire"" and that the investigation was lengthened because regulators used ""bicycles to try and catch Ferraris."" Furthermore, he concluded that by April 2015, traders can still manipulate and impact markets in spite of regulators and banks' new, improved monitoring of automated trade systems.As recently as May 2014, a CFTC report concluded that high-frequency traders ""did not cause the Flash Crash, but contributed to it by demanding immediacy ahead of other market participants.""Recent research shows that Flash Crashes are not isolated occurrences, but have occurred quite often over the past century. For instance, Irene Aldridge, the author of High-Frequency Trading: A Practical Guide to Algorithmic Strategies and Trading Systems, 2nd ed., Wiley & Sons, shows that Flash Crashes have been frequent and their causes predictable in market microstructure analysis.