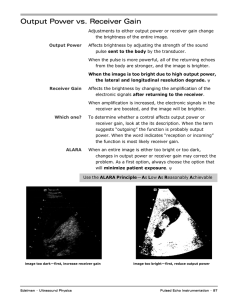
Slide 1
... 5 times larger of Maximum Permissible Exposure (MPE) than at 532 nm higher optical flux allowable into tissue Response time of GaAs PRC on the order of 1-10 ms or less (depending on the light intensity on PRC). sufficient to overcome the speckle decorrelation and is thus suitable for in-vivo ...
... 5 times larger of Maximum Permissible Exposure (MPE) than at 532 nm higher optical flux allowable into tissue Response time of GaAs PRC on the order of 1-10 ms or less (depending on the light intensity on PRC). sufficient to overcome the speckle decorrelation and is thus suitable for in-vivo ...
Looking through walls and around corners with
... typically 80ms. For imaging with incoherent illumination the integration times were 2-10s. The scattering samples used are a 10x20° Newport light shaping diffuser (Fig.2), and a white paper sticker with a thickness of 70±10µm (Fig.3). A white-light tungsten-halogen source (Schott KL1500LCD) was used ...
... typically 80ms. For imaging with incoherent illumination the integration times were 2-10s. The scattering samples used are a 10x20° Newport light shaping diffuser (Fig.2), and a white paper sticker with a thickness of 70±10µm (Fig.3). A white-light tungsten-halogen source (Schott KL1500LCD) was used ...
pdf-file - Max Planck Institut für Quantenoptik
... The conventional, atomic laser cooling technique mentioned above works as follows: atoms are irradiated with laser light of energy slightly below resonance. Hence the particles absorb the light whenever they travel towards the beam - only then they become resonant due to the Doppler effect - and are ...
... The conventional, atomic laser cooling technique mentioned above works as follows: atoms are irradiated with laser light of energy slightly below resonance. Hence the particles absorb the light whenever they travel towards the beam - only then they become resonant due to the Doppler effect - and are ...
File
... 10. Violet light is incident on a converging lens of focal length f. State with reason, how focal length of a lens will change, if violet is is replaced by a red light. 11. Two convex lenses of same focal length but of aperture 5 cm and 10 cm are used as objective lenses in two astronomical telescop ...
... 10. Violet light is incident on a converging lens of focal length f. State with reason, how focal length of a lens will change, if violet is is replaced by a red light. 11. Two convex lenses of same focal length but of aperture 5 cm and 10 cm are used as objective lenses in two astronomical telescop ...
Issues With Telescopes
... accomplishes feats of astrophotography that are simply unattainable with any other telescopic lens, telescope, or electronic imager. No other photo-optical instrument permits such extremely wide-field photography at such fast photographic speed and with such an amazingly flat imaging area to the fie ...
... accomplishes feats of astrophotography that are simply unattainable with any other telescopic lens, telescope, or electronic imager. No other photo-optical instrument permits such extremely wide-field photography at such fast photographic speed and with such an amazingly flat imaging area to the fie ...
Guided Discovery and Lesson Notes on Mirrors and Applications
... 1. Parallel rays far from the axis do converge at a point slightly closed to the mirror than the focal point: thus, the image formed by parallel rays is a disk instead of a point. 2. This deviation from an ideal point is called spherical aberration. 3. Spherical aberration can be eliminated using pa ...
... 1. Parallel rays far from the axis do converge at a point slightly closed to the mirror than the focal point: thus, the image formed by parallel rays is a disk instead of a point. 2. This deviation from an ideal point is called spherical aberration. 3. Spherical aberration can be eliminated using pa ...
Geometric Optics
... If height is negative the image is upside down if the magnification is negative the image is inverted (upside down) J.M. Gabrielse ...
... If height is negative the image is upside down if the magnification is negative the image is inverted (upside down) J.M. Gabrielse ...
Geometric Optics
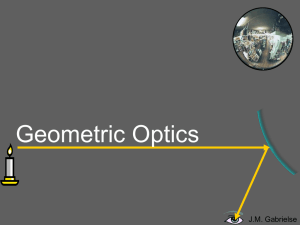
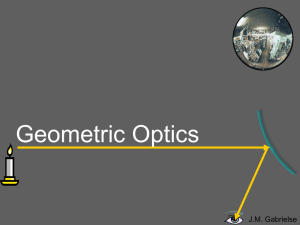
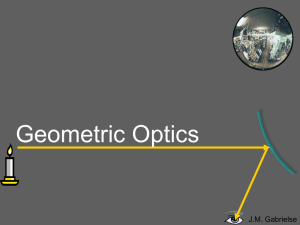
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The image forms where the rays converge. But they don’t seem to converge. J.M. Gabrielse ...
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The image forms where the rays converge. But they don’t seem to converge. J.M. Gabrielse ...
Geometric Optics - Mr. Gabrielse's Physics
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The image forms where the rays converge. But they don’t seem to converge. J.M. Gabrielse ...
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The image forms where the rays converge. But they don’t seem to converge. J.M. Gabrielse ...
Geometric Optics
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The image forms where the rays converge. But they don’t seem to converge. J.M. Gabrielse ...
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The image forms where the rays converge. But they don’t seem to converge. J.M. Gabrielse ...
Glencoe Physics Chapter 16
... luminous body - an object which emits its own light Example (sun) illuminous body - an object which reflects light Example (moon) transparent object - allows total light transmission Example (glass) translucent object - allows partial transmission Example (church window) opaque object - does not all ...
... luminous body - an object which emits its own light Example (sun) illuminous body - an object which reflects light Example (moon) transparent object - allows total light transmission Example (glass) translucent object - allows partial transmission Example (church window) opaque object - does not all ...
RAY OPTICS I
... Note that in Figure 6.2, we have drawn the rays as if the lens bends them suddenly at the exact center of the lens. Actually, each ray is bent a certain amount when it enters the lens and a certain amount more when it leaves the lens. If the lens is very thin compared to its focal length (or other i ...
... Note that in Figure 6.2, we have drawn the rays as if the lens bends them suddenly at the exact center of the lens. Actually, each ray is bent a certain amount when it enters the lens and a certain amount more when it leaves the lens. If the lens is very thin compared to its focal length (or other i ...
Controllable Optical Phase Shift Over One Radian from a Single
... polarised to eliminate optical pumping effects and its power is actively stabilised to minimise intensity fluctuations between reference and signal images. The light transmitted past the atom is reimaged onto a cooled CCD camera with a magnification of 585. To provide additional laser cooling, an au ...
... polarised to eliminate optical pumping effects and its power is actively stabilised to minimise intensity fluctuations between reference and signal images. The light transmitted past the atom is reimaged onto a cooled CCD camera with a magnification of 585. To provide additional laser cooling, an au ...
Kelley model of photographic process
... dependent: typically we get more blur near the edges of the field (narrower MTF ⇔broader PSF) • This, in addition, means that real–life optical systems are not shift invariant either! • ⇒the concept of MTF is approximate, near the region where the system is approximately shift invariant (recall: tra ...
... dependent: typically we get more blur near the edges of the field (narrower MTF ⇔broader PSF) • This, in addition, means that real–life optical systems are not shift invariant either! • ⇒the concept of MTF is approximate, near the region where the system is approximately shift invariant (recall: tra ...
High refractive index Fresnel lens on a fiber fabricated by
... lithography of a functional high refractive index material, which is suitable for mass production. The main advantage of the presented Fresnel lens compared to a conventional fiber lens is its high refractive index (n=1.69), which enables efficient light focusing even inside other media such as wate ...
... lithography of a functional high refractive index material, which is suitable for mass production. The main advantage of the presented Fresnel lens compared to a conventional fiber lens is its high refractive index (n=1.69), which enables efficient light focusing even inside other media such as wate ...
Technology for a better society
... Point resolution: related to the finest detail that can be directly interpreted in terms of the specimen structure. Since the CTF depends very sensitively on defocus, and in general shows an oscillatory behavior as a function of k, the contribution of the different scattered beams to the amplitude m ...
... Point resolution: related to the finest detail that can be directly interpreted in terms of the specimen structure. Since the CTF depends very sensitively on defocus, and in general shows an oscillatory behavior as a function of k, the contribution of the different scattered beams to the amplitude m ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... achieved by a broad–spectrum, incandescent lamp whose spectral properties conform to international commission on illumination (CIE) standards. The collimated light passes through the film and the transmitted component passes through a detecting aperture that usually can be from 1–3mm in diameter. Th ...
... achieved by a broad–spectrum, incandescent lamp whose spectral properties conform to international commission on illumination (CIE) standards. The collimated light passes through the film and the transmitted component passes through a detecting aperture that usually can be from 1–3mm in diameter. Th ...
blood group detection using fiber optics
... Blood grouping done so far is a manual process. As far as hospitals and blood banks are concerned, a number of blood samples have to be identified with in a short span of time. The manual process is a laborious and time-consuming one. Hence we have to device a new instrument cum method which elimina ...
... Blood grouping done so far is a manual process. As far as hospitals and blood banks are concerned, a number of blood samples have to be identified with in a short span of time. The manual process is a laborious and time-consuming one. Hence we have to device a new instrument cum method which elimina ...