Physical Optics
... modeling phase retrieval wavefront measurement professor james fienup the phase retrieval and imaging science group, geometric optics physics science khan academy - geometric optics contents reflection and refraction mirrors lenses reflection and refraction in these videos and articles you ll learn ...
... modeling phase retrieval wavefront measurement professor james fienup the phase retrieval and imaging science group, geometric optics physics science khan academy - geometric optics contents reflection and refraction mirrors lenses reflection and refraction in these videos and articles you ll learn ...
The `IEC` LASERVIEW – kit of shapes
... Real optical cables can be made of special plastics or glass. The material must be very clear because any particles or loss of clarity will lose light. They usually are flexible and consist of many very fine strands of optical fibre (each one is a light guide) and they are sheathed with a material t ...
... Real optical cables can be made of special plastics or glass. The material must be very clear because any particles or loss of clarity will lose light. They usually are flexible and consist of many very fine strands of optical fibre (each one is a light guide) and they are sheathed with a material t ...
Chapter #35 Light and Optics Wave Fronts Electromagnetic Wave
... • Electromagnetic Wave moves outwards from a small source in three dimensions. It forms spherical wave. At far distance from the source front becomes flat and rays become parallel. ...
... • Electromagnetic Wave moves outwards from a small source in three dimensions. It forms spherical wave. At far distance from the source front becomes flat and rays become parallel. ...
PowerPoint version
... learned that white light is composed of all the colors of visible light. You also know that the different colors correspond to different wavelengths. Because of this, white light can be separated into different colors during refraction, as shown in the figure below. Color separation during refractio ...
... learned that white light is composed of all the colors of visible light. You also know that the different colors correspond to different wavelengths. Because of this, white light can be separated into different colors during refraction, as shown in the figure below. Color separation during refractio ...
12. confocal microscopy.
... imaging system can operate either in transmission or reflection, as shown in Fig. 1. In both cases, the out of focus light is rejected by the pinhole in front of the detector, which is placed at a plane conjugate to the illumination plane. The image reconstruction is performed either by scanning the ...
... imaging system can operate either in transmission or reflection, as shown in Fig. 1. In both cases, the out of focus light is rejected by the pinhole in front of the detector, which is placed at a plane conjugate to the illumination plane. The image reconstruction is performed either by scanning the ...
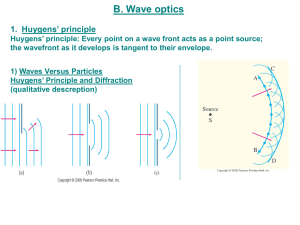
Wave Optics
... region directly behind barrier makes sense since light waves travel same distance, but what about other areas? ...
... region directly behind barrier makes sense since light waves travel same distance, but what about other areas? ...
PPT
... Add a barrier to block off most of the rays • This reduces blurring • The opening known as the aperture ...
... Add a barrier to block off most of the rays • This reduces blurring • The opening known as the aperture ...
Suman-AE-AOTFIntro-2..
... on the design of the AOTF. The wavelength of the light that is selected by this diffraction can therefore be varied simply by changing the frequency of the applied RF. As indicated in the figure, the diffracted light intensity is directed into two first order beams, termed the (+) and (-) beams. The ...
... on the design of the AOTF. The wavelength of the light that is selected by this diffraction can therefore be varied simply by changing the frequency of the applied RF. As indicated in the figure, the diffracted light intensity is directed into two first order beams, termed the (+) and (-) beams. The ...
3.7 Dielectrics and Optics 3.7.1 Basics
... The reflected beam follows one of the basic laws of optics, i.e. angle of incidence = angle of emergence, and its wavelength, frequency and magnitude of velocity are identical to that of the incident beam. What we do not know is its amplitude and its polarization, and these two quantities must someh ...
... The reflected beam follows one of the basic laws of optics, i.e. angle of incidence = angle of emergence, and its wavelength, frequency and magnitude of velocity are identical to that of the incident beam. What we do not know is its amplitude and its polarization, and these two quantities must someh ...
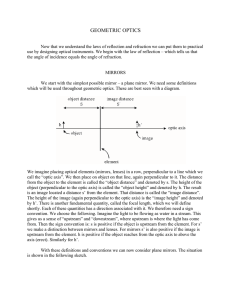
GEOMETRIC OPTICS
... comes from the image and those where it merely appears to. The first case we call “real images” and the second “virtual images”. In our case, there is no light behind the mirror, and hence the image is virtual. Summarizing we say that plane mirrors produce virtual images the same distance behind the ...
... comes from the image and those where it merely appears to. The first case we call “real images” and the second “virtual images”. In our case, there is no light behind the mirror, and hence the image is virtual. Summarizing we say that plane mirrors produce virtual images the same distance behind the ...
Parhelic-like Circle and Chaotic Light Scattering
... a complex behavior, for example, though the laws of ray reflection and refraction are simple, the boundary conditions for the light scattering are very difficult to be determined precisely due to many awkward technical aspects, such as nonlinearities, or if the thickness of the liquid films is suffi ...
... a complex behavior, for example, though the laws of ray reflection and refraction are simple, the boundary conditions for the light scattering are very difficult to be determined precisely due to many awkward technical aspects, such as nonlinearities, or if the thickness of the liquid films is suffi ...
Lecture 18
... Modulation transfer function • Resolution and performance of optical microscope can be characterized by the modulation transfer function (MTF) • MTF is measurement of microscope's ability to transfer contrast from the specimen to the image plane at specific resolution. • Incorporates resolution and ...
... Modulation transfer function • Resolution and performance of optical microscope can be characterized by the modulation transfer function (MTF) • MTF is measurement of microscope's ability to transfer contrast from the specimen to the image plane at specific resolution. • Incorporates resolution and ...
FarahWaheedaAhmadWahiddinMFKE2007TTTCHAP1
... Fiber optics is a relatively new technology that uses rays of light to send information over hair-thin fibers at blinding speeds. These fibers are used as an alternative to conventional copper wire in a variety of applications such as those associated with security, telecommunications, instrumentati ...
... Fiber optics is a relatively new technology that uses rays of light to send information over hair-thin fibers at blinding speeds. These fibers are used as an alternative to conventional copper wire in a variety of applications such as those associated with security, telecommunications, instrumentati ...
lecture20
... As the wavelets propagate from each point, they propagate more slowly in the medium of higher index of refraction. This leads to a bend in the wavefront and therefore in the ray. The frequency of the light does not change, but the wavelength does as it travels into a new medium. ...
... As the wavelets propagate from each point, they propagate more slowly in the medium of higher index of refraction. This leads to a bend in the wavefront and therefore in the ray. The frequency of the light does not change, but the wavelength does as it travels into a new medium. ...
UV-light microscope: improvements in optical imaging for a
... microscope system. These values are consistent with the resolution-calibration target images in Fig. 3b and c, respectively. We compare two images of the resolution-calibration targets illuminated by the blue LED and the UV-light LED using the same UV-light microscope system (Fig. S2, ESI-2†). Blue- ...
... microscope system. These values are consistent with the resolution-calibration target images in Fig. 3b and c, respectively. We compare two images of the resolution-calibration targets illuminated by the blue LED and the UV-light LED using the same UV-light microscope system (Fig. S2, ESI-2†). Blue- ...
The Truth About Base Curves - ABO-NCLE
... The base curve is the basis for all other curves on the lens. Curvature is responsible for the lens' dioptric power. By algebraically adding the base curve to the ocular curve (back curve), the dioptric power can be achieved. Any series of curves can produce dioptric power. Unfortunately the wrong c ...
... The base curve is the basis for all other curves on the lens. Curvature is responsible for the lens' dioptric power. By algebraically adding the base curve to the ocular curve (back curve), the dioptric power can be achieved. Any series of curves can produce dioptric power. Unfortunately the wrong c ...
Geometric Optics Converging Lenses and Mirrors
... drawn on the page should also be divided in half. Each person in your lab group should construct a ray diagram. 3. Measure to scale the image distance and the image height on your ray diagram. Remember to re-scale the image distance and height by multiplying the measured distances by two. Record the ...
... drawn on the page should also be divided in half. Each person in your lab group should construct a ray diagram. 3. Measure to scale the image distance and the image height on your ray diagram. Remember to re-scale the image distance and height by multiplying the measured distances by two. Record the ...
3D differential interference contrast microscopy using synthetic
... light field containing the sample information can be directly measured and then the acquired image can be processed into DIC image to enhance the contrast of the image.6,7 Through image processing, shearing direction can be chosen arbitrarily and 3-D imaging can be achieved with the numerical propag ...
... light field containing the sample information can be directly measured and then the acquired image can be processed into DIC image to enhance the contrast of the image.6,7 Through image processing, shearing direction can be chosen arbitrarily and 3-D imaging can be achieved with the numerical propag ...
UV Lenses - Machine Vision Systems
... UV rays having short wavelength are likely to hit atoms and molecules and tend to scatter. ...
... UV rays having short wavelength are likely to hit atoms and molecules and tend to scatter. ...
Paper Report on “Optical Computing: Need and Challenge”
... Lastly, the authors try to explain why optical computing systems have not yet developed and what are the challenges facing their development. They highlight 3 factors: cascadability, material development, and funding. Integrating a large number of optical gates is still a very complex problem and is ...
... Lastly, the authors try to explain why optical computing systems have not yet developed and what are the challenges facing their development. They highlight 3 factors: cascadability, material development, and funding. Integrating a large number of optical gates is still a very complex problem and is ...
Instructions - Physics Internal Website
... in the figure. (δ is the angle the reflected ray makes with the incident ray.) 9. (10 pts.) Radio waves are a form of electromagnetic radiation similar to visible light in every way other than their lower frequency. When radio waves travel through ice, you can consider to be the same as light travel ...
... in the figure. (δ is the angle the reflected ray makes with the incident ray.) 9. (10 pts.) Radio waves are a form of electromagnetic radiation similar to visible light in every way other than their lower frequency. When radio waves travel through ice, you can consider to be the same as light travel ...
12. Infrared and Visible Waves
... An infrared thermometer enables the remote sensing of temperature. It does this by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by an object and converting it into a temperature. The eardrum is an accurate point for measuring the body’s temperature, because it is deep within the head. A digital ear ther ...
... An infrared thermometer enables the remote sensing of temperature. It does this by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by an object and converting it into a temperature. The eardrum is an accurate point for measuring the body’s temperature, because it is deep within the head. A digital ear ther ...