Mechanisms of drought in present and future climate
... 1930s and 1950s in terms of multi-decadal precipitation anomalies 2. Similar patterns of SSTs that drive present-day droughts (relative cool tropical Pacific SSTs) also drive future droughts; a warmer base state appears to qualitatively reduce drought severity somewhat with respect to the new future ...
... 1930s and 1950s in terms of multi-decadal precipitation anomalies 2. Similar patterns of SSTs that drive present-day droughts (relative cool tropical Pacific SSTs) also drive future droughts; a warmer base state appears to qualitatively reduce drought severity somewhat with respect to the new future ...
Document
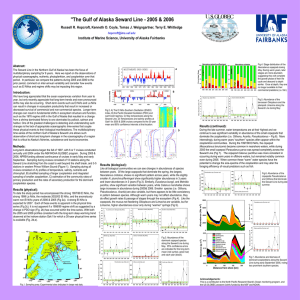
... change in PDO sign (Fig. 2b) has occurred within the time-series. With both the 2005 and 2006 profiles consistent with the long-term deep warming trend observed at the inshore station Gak1 for which a 30-year physical time series is available (Fig. 2d,e). ...
... change in PDO sign (Fig. 2b) has occurred within the time-series. With both the 2005 and 2006 profiles consistent with the long-term deep warming trend observed at the inshore station Gak1 for which a 30-year physical time series is available (Fig. 2d,e). ...
Earth`s Oceans
... The salinity is lower in areas where freshwater rivers run into the ocean. Salinity levels are also affected by animals such as clams and oysters that use calcium salts to build their shells. They remove salt from the water. In warm ocean areas where there is little rainfall and much evaporation, th ...
... The salinity is lower in areas where freshwater rivers run into the ocean. Salinity levels are also affected by animals such as clams and oysters that use calcium salts to build their shells. They remove salt from the water. In warm ocean areas where there is little rainfall and much evaporation, th ...
Meteorological and oceanographic data buoys
... Weather forecasts. Meteorological models routinely assimilate observational data from various sources including satellites, weather balloons, land stations, ships, and data buoys. Most of the models are global and assimilate observational data from all sources around the planet to make their nationa ...
... Weather forecasts. Meteorological models routinely assimilate observational data from various sources including satellites, weather balloons, land stations, ships, and data buoys. Most of the models are global and assimilate observational data from all sources around the planet to make their nationa ...
d64 - met ocean
... smoke, and typical areas where a smoke may be encountered describe methods of estimating the visibility at sea, by day and by night, and the difficulties involved ...
... smoke, and typical areas where a smoke may be encountered describe methods of estimating the visibility at sea, by day and by night, and the difficulties involved ...
Cold ocean = hot summer? - Science Journal for Kids
... What are the different factors causing a heat wave? This research explores one way in which the conditions in the ocean might affect life on land. Describe three other ways that the status of the ocean environment affects humans on land. Heat waves don’t affect everyone equally. Why are heat waves m ...
... What are the different factors causing a heat wave? This research explores one way in which the conditions in the ocean might affect life on land. Describe three other ways that the status of the ocean environment affects humans on land. Heat waves don’t affect everyone equally. Why are heat waves m ...
The Biosphere - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... moist air. As this air rises and flows toward the poles, it cools and loses most of its moisture (figure 29.6). Consequently, the greatest amounts of precipitation on earth fall near the equator. This equatorial region of rising air is one of low pressure, called the doldrums, which draws air from b ...
... moist air. As this air rises and flows toward the poles, it cools and loses most of its moisture (figure 29.6). Consequently, the greatest amounts of precipitation on earth fall near the equator. This equatorial region of rising air is one of low pressure, called the doldrums, which draws air from b ...
nakamoto4
... bulk nature of the effect of varying chlorophyll pigments on downward radiation transfer processes in the upper ocean, because atmospheric forcing in both model runs were the same. They analyze their model data in the Arabian Sea and compared with available ocean observations to examine the effect o ...
... bulk nature of the effect of varying chlorophyll pigments on downward radiation transfer processes in the upper ocean, because atmospheric forcing in both model runs were the same. They analyze their model data in the Arabian Sea and compared with available ocean observations to examine the effect o ...
Plastic Pollution and The Ocean
... • The ocean enables 90% of global trade through shipping1 • 80% of all global tourism is based near the sea2 In addition, the ocean protects our global environment. It drives our weather by determining rainfall, droughts and floods. Ocean waters absorb vast amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), helping ...
... • The ocean enables 90% of global trade through shipping1 • 80% of all global tourism is based near the sea2 In addition, the ocean protects our global environment. It drives our weather by determining rainfall, droughts and floods. Ocean waters absorb vast amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), helping ...
File
... water can increase ocean salinity. • In hotter areas, evaporation of water can increase ocean salinity. ...
... water can increase ocean salinity. • In hotter areas, evaporation of water can increase ocean salinity. ...
Ocean Floor
... Salinity ¤ Salinity is the amount of salt in the water ¤ The heat from the sun indirectly impacts the amount of salt in the ocean ¤ At the equator, where the sun has a greater impact on the ocean, the water becomes hotter and more water evaporates ¤ The more water that evaporates, the higher ...
... Salinity ¤ Salinity is the amount of salt in the water ¤ The heat from the sun indirectly impacts the amount of salt in the ocean ¤ At the equator, where the sun has a greater impact on the ocean, the water becomes hotter and more water evaporates ¤ The more water that evaporates, the higher ...
exploring the ocean floor - Brighten AcademyMiddle School
... deep ocean basin floor. Extends from the base of the continental rise into deep ocean basins. Among Earth’s flattest and smoothest regions an the least explored. Formed by particles of sediment slowly drifting onto the deep ocean floor. Most abyssal plains occur in the Atlantic and Indian oceans. Co ...
... deep ocean basin floor. Extends from the base of the continental rise into deep ocean basins. Among Earth’s flattest and smoothest regions an the least explored. Formed by particles of sediment slowly drifting onto the deep ocean floor. Most abyssal plains occur in the Atlantic and Indian oceans. Co ...
Earth Science Final Exam Study Guide Name Class Date ______
... a. It brings warm water from the tropics to the poles. b. It decreases winds along exposed coastlines. c. It helps warm the North Atlantic gyre. d. It brings dissolved nutrients to the ocean’s surface. 86. What causes density currents to form in the Mediterranean Sea? a. condensation c. transpiratio ...
... a. It brings warm water from the tropics to the poles. b. It decreases winds along exposed coastlines. c. It helps warm the North Atlantic gyre. d. It brings dissolved nutrients to the ocean’s surface. 86. What causes density currents to form in the Mediterranean Sea? a. condensation c. transpiratio ...
Southern Ocean Heat and Carbon Uptake
... responsible for supplying nutrients that fertilize threequarters of the biological production in the global ocean north of 30°S (Sarmiento et al., 2004) 3. It may account for up to 70 ± 30% of the excess heat that is transferred from the atmosphere into the ocean each year (see analysis of IPCC AR4 ...
... responsible for supplying nutrients that fertilize threequarters of the biological production in the global ocean north of 30°S (Sarmiento et al., 2004) 3. It may account for up to 70 ± 30% of the excess heat that is transferred from the atmosphere into the ocean each year (see analysis of IPCC AR4 ...
OCEAN CURRENTS
... Because ocean currents circulate water worldwide, they have a significant impact on the movement of energy and moisture between the oceans and the atmosphere. As a result, they are important to the world’s weather. The Gulf Stream for example is a warm current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico a ...
... Because ocean currents circulate water worldwide, they have a significant impact on the movement of energy and moisture between the oceans and the atmosphere. As a result, they are important to the world’s weather. The Gulf Stream for example is a warm current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico a ...
The Effects of Ocean Freshening on Marine and
... and seafloor topography (Price 1998). The water then spills out of the marginal seas and moves around the globe (Price 1998). Circulation patterns are largely influenced by the Coriolis effect, seafloor bathymetry, and the location of continents (Figure 1). In the Antarctic region, water sinking in ...
... and seafloor topography (Price 1998). The water then spills out of the marginal seas and moves around the globe (Price 1998). Circulation patterns are largely influenced by the Coriolis effect, seafloor bathymetry, and the location of continents (Figure 1). In the Antarctic region, water sinking in ...
Ocean life
... the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended pedagogical purposes and the needs of other instructors who rely on these materials. ...
... the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended pedagogical purposes and the needs of other instructors who rely on these materials. ...
Ocean life
... the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended pedagogical purposes and the needs of other instructors who rely on these materials. ...
... the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended pedagogical purposes and the needs of other instructors who rely on these materials. ...
Atmospheric Response to Atlantic Cold Blob - Blue
... • By Chance? Or did we overlook some other crucial element in the initial conditions? ...
... • By Chance? Or did we overlook some other crucial element in the initial conditions? ...
Ocean life - Oakton Community College
... • Lower surface temperatures are found in highlatitude regions • Higher temperatures found in low-latitude regions ...
... • Lower surface temperatures are found in highlatitude regions • Higher temperatures found in low-latitude regions ...
Earth Science, 11e Ocean Water and Ocean Life Chapter 14
... high-latitude regions • Higher temperatures found in low-latitude regions ...
... high-latitude regions • Higher temperatures found in low-latitude regions ...
Global Variations of Chemical Composition of Oceans
... salinity of the surface waters is markedly higher than that of the deep waters (34.734.9‰). This phenomenon causes formation of highly salt and cold intermediate, deep, and bottom North Atlantic water masses in the subarctic areas in winter. Influence of deep and bottom North Atlantic waters is noti ...
... salinity of the surface waters is markedly higher than that of the deep waters (34.734.9‰). This phenomenon causes formation of highly salt and cold intermediate, deep, and bottom North Atlantic water masses in the subarctic areas in winter. Influence of deep and bottom North Atlantic waters is noti ...
Chapter 14
... • Intertidal zone – area where land and ocean meet and overlap • Neritic zone – seaward from the low tide line, the continental shelf out to the shelf break • Oceanic zone – beyond the continental shelf ...
... • Intertidal zone – area where land and ocean meet and overlap • Neritic zone – seaward from the low tide line, the continental shelf out to the shelf break • Oceanic zone – beyond the continental shelf ...