Income as the Source of Long-Term Returns
... reluctance to consider a true long-term horizon. References to long-term investment performance often tend to cite 3- or 5-year asset class returns. We challenge this definition of a long-term horizon for two reasons. First, individuals and institutions may be investing for retirement purposes or wi ...
... reluctance to consider a true long-term horizon. References to long-term investment performance often tend to cite 3- or 5-year asset class returns. We challenge this definition of a long-term horizon for two reasons. First, individuals and institutions may be investing for retirement purposes or wi ...
determinants of capital structure of croatian enterprises before and
... issuing a sufficiently high amount of debt. The pecking order theory 4 describes the order in which firms prefer to finance firms’ future activities and growth. According to this theory, a firm will rather borrow than issue equity 5, when internal cash flow is not sufficient to fund capital expendit ...
... issuing a sufficiently high amount of debt. The pecking order theory 4 describes the order in which firms prefer to finance firms’ future activities and growth. According to this theory, a firm will rather borrow than issue equity 5, when internal cash flow is not sufficient to fund capital expendit ...
As filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission
... closed-end registered investment company with shares listed on the New York Stock Exchange (the “Fund”), announced today that the Board of Directors of the Fund approved a proposed acquisition of its assets, and the assumption of its liabilities, by AB Income Fund (“Income Fund”), a newly-formed ser ...
... closed-end registered investment company with shares listed on the New York Stock Exchange (the “Fund”), announced today that the Board of Directors of the Fund approved a proposed acquisition of its assets, and the assumption of its liabilities, by AB Income Fund (“Income Fund”), a newly-formed ser ...
The Pull of Active Management - Market Strategies International
... perhaps a reflection of the reliance on liabilitydriven investment (LDI) strategies among this cohort of the pension market. Finally, the proportion of pensions using other asset classes that cannot be accurately categorized as either active or passive and has remained relatively consistent year ove ...
... perhaps a reflection of the reliance on liabilitydriven investment (LDI) strategies among this cohort of the pension market. Finally, the proportion of pensions using other asset classes that cannot be accurately categorized as either active or passive and has remained relatively consistent year ove ...
T3.1 Chapter Outline
... Cost of goods sold Depreciation Earnings before interest and taxes Interest ...
... Cost of goods sold Depreciation Earnings before interest and taxes Interest ...
Prudential With
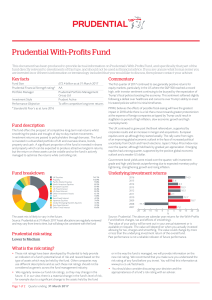
... The performance figures shown are overall annualised returns for contributions made on the dates specified. The returns include both regular and final bonuses added to a benefit paid at normal retirement date, but make no allowance for any applicable initial charges, allocation rates or early cash i ...
... The performance figures shown are overall annualised returns for contributions made on the dates specified. The returns include both regular and final bonuses added to a benefit paid at normal retirement date, but make no allowance for any applicable initial charges, allocation rates or early cash i ...
T t l d p t t - The University of Chicago Booth School of Business
... September. Inflows would now be only slightly higher with a small improvement in performance, but would be sharply lower with an inferior performance. Hence, the fund benefits from playing safe and locking in its gains throughout the fourth quarter. The incentives to alter the riskiness of a portfol ...
... September. Inflows would now be only slightly higher with a small improvement in performance, but would be sharply lower with an inferior performance. Hence, the fund benefits from playing safe and locking in its gains throughout the fourth quarter. The incentives to alter the riskiness of a portfol ...
Retained Earnings of Mutual Funds
... (1993 SNA, Para. 3.99). Interest is payable on an accrual basis (see BPM5, Para. 282). Under this interpretation, an MF will receive interest on a continuous basis and dividends periodically, and that it will pay dividends on a periodic basis. Any difference between these two will be deemed to be th ...
... (1993 SNA, Para. 3.99). Interest is payable on an accrual basis (see BPM5, Para. 282). Under this interpretation, an MF will receive interest on a continuous basis and dividends periodically, and that it will pay dividends on a periodic basis. Any difference between these two will be deemed to be th ...
PUF Investment Policy
... of low correlation with listed equities and fixed income instruments. The disadvantages of this asset class are that they may be illiquid, require higher and more complex fees, and are frequently dependent on the quality of external managers. In addition, they possess a limited return history versus ...
... of low correlation with listed equities and fixed income instruments. The disadvantages of this asset class are that they may be illiquid, require higher and more complex fees, and are frequently dependent on the quality of external managers. In addition, they possess a limited return history versus ...
Capital requirements under Basel III and their impact on the banking
... Given that the theory provides predictions that are ambiguous, all that remains is to make an empirical examination, based on historical experience, of the past relationship between these two variables: capital ratio and risk actually assumed. One can first approach this problem using the aggregate ...
... Given that the theory provides predictions that are ambiguous, all that remains is to make an empirical examination, based on historical experience, of the past relationship between these two variables: capital ratio and risk actually assumed. One can first approach this problem using the aggregate ...
IFRS Week Financial Instruments Presentation and
... in the assets of an entity after deducting all of its liabilities. A financial instrument may require the entity to deliver cash or another financial asset, or otherwise to settle it in such a way that it would be a financial liability, in the event of the occurrence or non-occurrence of uncertain ...
... in the assets of an entity after deducting all of its liabilities. A financial instrument may require the entity to deliver cash or another financial asset, or otherwise to settle it in such a way that it would be a financial liability, in the event of the occurrence or non-occurrence of uncertain ...
Supplement - Causeway Capital Management
... When investing the Fund’s assets, the Investment Manager follows a value style, performing fundamental research supplemented by quantitative analysis. Quantitative screens narrow the universe of investment candidates by applying market capitalization and valuation screens. To select investments, th ...
... When investing the Fund’s assets, the Investment Manager follows a value style, performing fundamental research supplemented by quantitative analysis. Quantitative screens narrow the universe of investment candidates by applying market capitalization and valuation screens. To select investments, th ...
Unconstrained fixed income: generating consistent returns
... For those Defined Contribution (DC) pension plan members, and for those individual savers, that have shorter-term time horizons and lower tolerance for losses, UFI can be a valuable strategy. These investors need to be prepared to accept meaningful levels of risk over a 3-year timescale; however a w ...
... For those Defined Contribution (DC) pension plan members, and for those individual savers, that have shorter-term time horizons and lower tolerance for losses, UFI can be a valuable strategy. These investors need to be prepared to accept meaningful levels of risk over a 3-year timescale; however a w ...
Mutual funds and our capital market
... investment securities (stocks, bonds, short-term money market instruments, other mutual funds, other securities, and/or commodities such as precious metals). The mutual fund will have a fund manager that trades (buys and sells) the fund's investments in accordance with the fund's investment objectiv ...
... investment securities (stocks, bonds, short-term money market instruments, other mutual funds, other securities, and/or commodities such as precious metals). The mutual fund will have a fund manager that trades (buys and sells) the fund's investments in accordance with the fund's investment objectiv ...
chapter 32 institutional investors
... compensation for risk. If they do, such evidence would suggest that markets might not be informationally efficient because agents can garner profits from exploiting these inefficiencies. Second, using publicly available datasets that are generally low frequency (i.e., quarterly or annual), academics ...
... compensation for risk. If they do, such evidence would suggest that markets might not be informationally efficient because agents can garner profits from exploiting these inefficiencies. Second, using publicly available datasets that are generally low frequency (i.e., quarterly or annual), academics ...
FL High Yield Distribution AL
... limited range of industry sectors, it may carry more risk than funds that invest across a broader range or variety of sectors. These funds can be more volatile and carry higher risk due to their lack of diversification. G - Derivatives: Where a fund uses derivatives for investment purposes, there ma ...
... limited range of industry sectors, it may carry more risk than funds that invest across a broader range or variety of sectors. These funds can be more volatile and carry higher risk due to their lack of diversification. G - Derivatives: Where a fund uses derivatives for investment purposes, there ma ...
Stable Value Fund
... Income Risk: The possibility that a fund’s income will decline as a result of falling interest rates. Investments are generally made for terms of at least two to five years, on average, producing a rate of fund income that will be higher than that earned on shorter-maturity money market funds. But b ...
... Income Risk: The possibility that a fund’s income will decline as a result of falling interest rates. Investments are generally made for terms of at least two to five years, on average, producing a rate of fund income that will be higher than that earned on shorter-maturity money market funds. But b ...
SLP Capital Structure and Dividends
... The dividend payout ratio is an important valuation method that investors apply to evaluate the company's general investment potentials and the revenues that the company can generate. The dividend payout ratio is the widely used metric by the investors. The dividend payout ratio of general electroni ...
... The dividend payout ratio is an important valuation method that investors apply to evaluate the company's general investment potentials and the revenues that the company can generate. The dividend payout ratio is the widely used metric by the investors. The dividend payout ratio of general electroni ...
Appendix F 151202-lgps-investment-pooling-next
... pool level’. The expectation is that this will rationalise the number of managers used leading to lower investment fees. Specific asset classes and approaches Active vs Passive Management The extent to which each authority or pool uses passive management will remain their own decision but the balanc ...
... pool level’. The expectation is that this will rationalise the number of managers used leading to lower investment fees. Specific asset classes and approaches Active vs Passive Management The extent to which each authority or pool uses passive management will remain their own decision but the balanc ...
Designing a New Utility Business Model? Better
... investor value over this period. (Moody’s, 2000) In contrast, the overall stock market, as represented by the S&P 500, increased by 50 percent over this period. Electric utility stocks sold at over twice book value in 1965, which was a reasonable valuation given the degree to which utility returns e ...
... investor value over this period. (Moody’s, 2000) In contrast, the overall stock market, as represented by the S&P 500, increased by 50 percent over this period. Electric utility stocks sold at over twice book value in 1965, which was a reasonable valuation given the degree to which utility returns e ...
Target Asset Allocation
... To produce the graphs, asset classes are mapped to market indexes that Morningstar deemed to be representative of the asset class. A description of the asset class mappings to indexes appears below with descriptions of the indexes. We assume an initial investment value of $100,000 for each graph, an ...
... To produce the graphs, asset classes are mapped to market indexes that Morningstar deemed to be representative of the asset class. A description of the asset class mappings to indexes appears below with descriptions of the indexes. We assume an initial investment value of $100,000 for each graph, an ...
Proposal - Mountain Plains Management Conference
... profits. Conclusion from DOI: outlook appears above average given recent increase in DOI. The ASI is the primary indicator for the auto industry and has shown a bouncy trend the last two years (http://www.dailyfx.com/calendar/briefing/auto.html ). High gasoline prices make fuel efficient imports and ...
... profits. Conclusion from DOI: outlook appears above average given recent increase in DOI. The ASI is the primary indicator for the auto industry and has shown a bouncy trend the last two years (http://www.dailyfx.com/calendar/briefing/auto.html ). High gasoline prices make fuel efficient imports and ...
LEVERAGE, HEDGE FUNDS AND RISK
... Return on Assets (ROA) ing a return on assets Gross Profit/Loss (P&L) (ROA) of 10% to an Cost of Leverage (at risk-free rate of 2%) ROE of 26% when 2x Net Profit/Loss (P&L) leverage (Debt/Equity) Return on Equity (ROE) is used. However, with a -10% ROA, 2x lever- Asset Prices Fall Leverage (Debt/Equ ...
... Return on Assets (ROA) ing a return on assets Gross Profit/Loss (P&L) (ROA) of 10% to an Cost of Leverage (at risk-free rate of 2%) ROE of 26% when 2x Net Profit/Loss (P&L) leverage (Debt/Equity) Return on Equity (ROE) is used. However, with a -10% ROA, 2x lever- Asset Prices Fall Leverage (Debt/Equ ...
Impact of cost of capital, financial leverage, and the Growth Rate of
... Among decisions concerned money procurement is the identification of funding type, and percentage of funds of each type, since there two types of funding, financing by owner's equity and financing by debts, the result of borrowed financing is what is called the financial leverage, defined as total l ...
... Among decisions concerned money procurement is the identification of funding type, and percentage of funds of each type, since there two types of funding, financing by owner's equity and financing by debts, the result of borrowed financing is what is called the financial leverage, defined as total l ...
To: Clients and Friends June 30, 2004 The articles below contain
... survey defined a hedge fund adviser as an advisory firm in which hedge funds represent 75% or more of the firm’s advisory clients. According to the survey, the number of registered hedge fund advisers rose from 508 a year ago to 601 this year, an increase of 18%. The registered hedge fund advisers m ...
... survey defined a hedge fund adviser as an advisory firm in which hedge funds represent 75% or more of the firm’s advisory clients. According to the survey, the number of registered hedge fund advisers rose from 508 a year ago to 601 this year, an increase of 18%. The registered hedge fund advisers m ...
Private equity

In finance, private equity is an asset class consisting of equity securities and debt in operating companies that are not publicly traded on a stock exchange.A private equity investment will generally be made by a private equity firm, a venture capital firm or an angel investor. Each of these categories of investor has its own set of goals, preferences and investment strategies; however, all provide working capital to a target company to nurture expansion, new-product development, or restructuring of the company’s operations, management, or ownership.Bloomberg Businessweek has called private equity a rebranding of leveraged-buyout firms after the 1980s. Common investment strategies in private equity include: leveraged buyouts, venture capital, growth capital, distressed investments and mezzanine capital. In a typical leveraged-buyout transaction, a private-equity firm buys majority control of an existing or mature firm. This is distinct from a venture-capital or growth-capital investment, in which the investors (typically venture-capital firms or angel investors) invest in young, growing or emerging companies, and rarely obtain majority control.Private equity is also often grouped into a broader category called private capital, generally used to describe capital supporting any long-term, illiquid investment strategy.