The optics and performance of dual-focus fluorescence correlation
... an invariable length scale in the measurement: FCS probes the diffusion of molecules out of the detection volume of a confocal microscope, and any change of that detection volume will result in a change of the measured autocorrelation curve (ACF) and thus extracted value of a diffusion coefficient. ...
... an invariable length scale in the measurement: FCS probes the diffusion of molecules out of the detection volume of a confocal microscope, and any change of that detection volume will result in a change of the measured autocorrelation curve (ACF) and thus extracted value of a diffusion coefficient. ...
Non-specular reflection of convergent beams from Iiquid-solid interface
... Rayleigh angle from a liquid onto a solid has been studied for well collimated and divergent beams [13]; however, the reflection of convergent beams, such as those produced by a concave transducer or a lens, has not yet been examined explicitly . The reflection acoustic microscope [4] employs an ext ...
... Rayleigh angle from a liquid onto a solid has been studied for well collimated and divergent beams [13]; however, the reflection of convergent beams, such as those produced by a concave transducer or a lens, has not yet been examined explicitly . The reflection acoustic microscope [4] employs an ext ...
Gaussian Beam Optics [Hecht Ch. 13.1 pages 594
... the beam for several values of z>>zR. Then fit the data for each z using Eq. (1), which will yield values for w(z). Then one can use Eqs. (3) and (4) to determine w0 and calculate zR. ...
... the beam for several values of z>>zR. Then fit the data for each z using Eq. (1), which will yield values for w(z). Then one can use Eqs. (3) and (4) to determine w0 and calculate zR. ...
Asphere Metrology
... the surface’s deviation from spherical; the larger the deviation or local slope, the more fringes that form in a smaller area, and the larger the fringe density. This is not a null configuration; there is an expected fringe pattern and an actual fringe pattern, and these are compared, if the Nyquist ...
... the surface’s deviation from spherical; the larger the deviation or local slope, the more fringes that form in a smaller area, and the larger the fringe density. This is not a null configuration; there is an expected fringe pattern and an actual fringe pattern, and these are compared, if the Nyquist ...
The Truth About Base Curves - ABO-NCLE
... astigmatism. A Parisian oculist, F. Ostwalt, first presented this theory in 1898. Using this theory, Dr. Tscherning developed methods to further correct marginal astigmatism. The results of his work produced equations that, when plotted in a graph, produce a curve in the form of an ellipse. In 1904, ...
... astigmatism. A Parisian oculist, F. Ostwalt, first presented this theory in 1898. Using this theory, Dr. Tscherning developed methods to further correct marginal astigmatism. The results of his work produced equations that, when plotted in a graph, produce a curve in the form of an ellipse. In 1904, ...
z - at www.arxiv.org.
... rotation, which, in turn, agrees with the internal energy circulation shown by the grey arrow. Ultimately, the OV disappears in the shadow region (x > a) [21–23,33,35]. When the screen edge moves away from the z-axis, the spiral-like OV trajectory makes (theoretically) an infinite number of rotation ...
... rotation, which, in turn, agrees with the internal energy circulation shown by the grey arrow. Ultimately, the OV disappears in the shadow region (x > a) [21–23,33,35]. When the screen edge moves away from the z-axis, the spiral-like OV trajectory makes (theoretically) an infinite number of rotation ...
Single-plane multiple speckle pattern phase retrieval
... proposed technique is presented. It is emphasized that a phase diffuser plate is an integral part of the proposed setup, lending the technique especially adapted for low-curvature test wavefronts compared to, for example, the technique described in [19,20]. Without a diffuser plate in the path of su ...
... proposed technique is presented. It is emphasized that a phase diffuser plate is an integral part of the proposed setup, lending the technique especially adapted for low-curvature test wavefronts compared to, for example, the technique described in [19,20]. Without a diffuser plate in the path of su ...
1.5% root-mean-square flat-intensity laser beam
... Another diffractive approach is to use an annularphase plate containing two or more zones with binary phase values (usually 0 and π). Based on the original proposal by Veldkamp and Kastner [8], various schemes have been published to produce flat-top beams from an input Gaussian beam [9–12]. However, ...
... Another diffractive approach is to use an annularphase plate containing two or more zones with binary phase values (usually 0 and π). Based on the original proposal by Veldkamp and Kastner [8], various schemes have been published to produce flat-top beams from an input Gaussian beam [9–12]. However, ...
HOLO TEXT
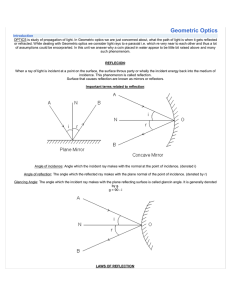
... divisions which focus upon these specific properties of light. In ascending order of complexity they are: Geometrical optics - this area of optics operates on the primary assumption that light travels in a straight line. Although this is an abstraction of reality, it nevertheless permits rather dire ...
... divisions which focus upon these specific properties of light. In ascending order of complexity they are: Geometrical optics - this area of optics operates on the primary assumption that light travels in a straight line. Although this is an abstraction of reality, it nevertheless permits rather dire ...
On the small-angle X-ray scattering of rigid-rod
... presumably cannot exceed the fibril diameter. This value, 13.2 nm, is slightly larger than those of the fibril diameter, 7nm, calculated from SAXS a9 and crystal width measured using selected-area electron diffraction, which range from 1.6 to 9.0 nm 1. The two-phase model as described for flexible-c ...
... presumably cannot exceed the fibril diameter. This value, 13.2 nm, is slightly larger than those of the fibril diameter, 7nm, calculated from SAXS a9 and crystal width measured using selected-area electron diffraction, which range from 1.6 to 9.0 nm 1. The two-phase model as described for flexible-c ...
1 Fundamental Optics www.cvimellesgriot.com
... A simple graphical method can also be used to determine paraxial image location and magnification. This graphical approach relies on two simple properties of an optical system. First, a ray that enters the system parallel to the optical axis crosses the optical axis at the focal point. Second, a ray ...
... A simple graphical method can also be used to determine paraxial image location and magnification. This graphical approach relies on two simple properties of an optical system. First, a ray that enters the system parallel to the optical axis crosses the optical axis at the focal point. Second, a ray ...
Geometric Optics - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... IMAGE FORMATION: Image is said to the formed when two rays meet. The image can be real or virtual. Real Image: If the rays actually at a point then the image formed is regarded as real image. Virtual image: If the reflected or refracted rays do not actually meet out only appear to diverge from the p ...
... IMAGE FORMATION: Image is said to the formed when two rays meet. The image can be real or virtual. Real Image: If the rays actually at a point then the image formed is regarded as real image. Virtual image: If the reflected or refracted rays do not actually meet out only appear to diverge from the p ...
LETTERS
... From different time-of-flight images taken after the mean field becomes negligible, we determine the rms momentum width of the released BEC. Along the direction of momentum transfer we measure DPrms 0.30s4dh̄k (all uncertainties in this paper represent one standard deviation combined statistical a ...
... From different time-of-flight images taken after the mean field becomes negligible, we determine the rms momentum width of the released BEC. Along the direction of momentum transfer we measure DPrms 0.30s4dh̄k (all uncertainties in this paper represent one standard deviation combined statistical a ...
Airy disk
In optics, the Airy disk (or Airy disc) and Airy pattern are descriptions of the best focused spot of light that a perfect lens with a circular aperture can make, limited by the diffraction of light. The Airy disk is of importance in physics, optics, and astronomy.The diffraction pattern resulting from a uniformly-illuminated circular aperture has a bright region in the center, known as the Airy disk which together with the series of concentric bright rings around is called the Airy pattern. Both are named after George Biddell Airy. The disk and rings phenomenon had been known prior to Airy; John Herschel described the appearance of a bright star seen through a telescope under high magnification for an 1828 article on light for the Encyclopedia Metropolitana:...the star is then seen (in favourable circumstances of tranquil atmosphere, uniform temperature, &c.) as a perfectly round, well-defined planetary disc, surrounded by two, three, or more alternately dark and bright rings, which, if examined attentively, are seen to be slightly coloured at their borders. They succeed each other nearly at equal intervals round the central disc....However, Airy wrote the first full theoretical treatment explaining the phenomenon (his 1835 ""On the Diffraction of an Object-glass with Circular Aperture"").Mathematically, the diffraction pattern is characterized by the wavelength of light illuminating the circular aperture, and the aperture's size. The appearance of the diffraction pattern is additionally characterized by the sensitivity of the eye or other detector used to observe the pattern.The most important application of this concept is in cameras and telescopes. Owing to diffraction, the smallest point to which a lens or mirror can focus a beam of light is the size of the Airy disk. Even if one were able to make a perfect lens, there is still a limit to the resolution of an image created by this lens. An optical system in which the resolution is no longer limited by imperfections in the lenses but only by diffraction is said to be diffraction limited.