Geometry standards Unit 2
... Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. 4. Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on th ...
... Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. 4. Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically. For example, prove or disprove that a figure defined by four given points in the coordinate plane is a rectangle; prove or disprove that the point (1, √3) lies on th ...
SRWColAlg6_01_01
... Similarly, points in a plane can be identified with ordered pairs of numbers to form the coordinate plane or Cartesian plane. ...
... Similarly, points in a plane can be identified with ordered pairs of numbers to form the coordinate plane or Cartesian plane. ...
Algebra I Vocabulary
... A method for solving a system of equations that uses substitution of one equation into the other equation to solve for the other variable. A set of equation (two or more) with the same variables. ...
... A method for solving a system of equations that uses substitution of one equation into the other equation to solve for the other variable. A set of equation (two or more) with the same variables. ...
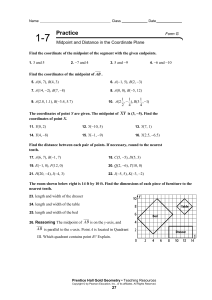
Line Segments in the Coordinate Grid
... To find the length of a line segment, you can count the units, or you can find the difference between the coordinates. ...
... To find the length of a line segment, you can count the units, or you can find the difference between the coordinates. ...
Example Example - Solution
... (positive) or left (negative) from the origin; always first in an ordered pair y-coordinate –tells how far to move up (positive) or down (negative); always second in an ordered pair ...
... (positive) or left (negative) from the origin; always first in an ordered pair y-coordinate –tells how far to move up (positive) or down (negative); always second in an ordered pair ...
Graph Ordered Pairs
... Objective The student will be able to: graph ordered pairs on a coordinate plane. ...
... Objective The student will be able to: graph ordered pairs on a coordinate plane. ...
What is Calculus?
... • Let O be the point of intersection. • We set one of the lines horizontally with the positive numbers to the right of O and the other vertically with the positive numbers above O. • The point O is called the origin, and the number lines are called the coordinate axes. • The horizontal axis is usual ...
... • Let O be the point of intersection. • We set one of the lines horizontally with the positive numbers to the right of O and the other vertically with the positive numbers above O. • The point O is called the origin, and the number lines are called the coordinate axes. • The horizontal axis is usual ...
Cartesian coordinate system
A Cartesian coordinate system is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely in a plane by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances from the point to two fixed perpendicular directed lines, measured in the same unit of length. Each reference line is called a coordinate axis or just axis of the system, and the point where they meet is its origin, usually at ordered pair (0, 0). The coordinates can also be defined as the positions of the perpendicular projections of the point onto the two axes, expressed as signed distances from the origin.One can use the same principle to specify the position of any point in three-dimensional space by three Cartesian coordinates, its signed distances to three mutually perpendicular planes (or, equivalently, by its perpendicular projection onto three mutually perpendicular lines). In general, n Cartesian coordinates (an element of real n-space) specify the point in an n-dimensional Euclidean space for any dimension n. These coordinates are equal, up to sign, to distances from the point to n mutually perpendicular hyperplanes.The invention of Cartesian coordinates in the 17th century by René Descartes (Latinized name: Cartesius) revolutionized mathematics by providing the first systematic link between Euclidean geometry and algebra. Using the Cartesian coordinate system, geometric shapes (such as curves) can be described by Cartesian equations: algebraic equations involving the coordinates of the points lying on the shape. For example, a circle of radius 2 in a plane may be described as the set of all points whose coordinates x and y satisfy the equation x2 + y2 = 4.Cartesian coordinates are the foundation of analytic geometry, and provide enlightening geometric interpretations for many other branches of mathematics, such as linear algebra, complex analysis, differential geometry, multivariate calculus, group theory and more. A familiar example is the concept of the graph of a function. Cartesian coordinates are also essential tools for most applied disciplines that deal with geometry, including astronomy, physics, engineering and many more. They are the most common coordinate system used in computer graphics, computer-aided geometric design and other geometry-related data processing.