Coordinate Plane
... When a line segment crosses over an quadrant, you have to find the distance the endpoints are from the axis that is crossed. Since the axes have a value of 0, find the absolute value of the coordinates that are different in the two ordered pairs. Finally, instead of subtracting, you add the two dist ...
... When a line segment crosses over an quadrant, you have to find the distance the endpoints are from the axis that is crossed. Since the axes have a value of 0, find the absolute value of the coordinates that are different in the two ordered pairs. Finally, instead of subtracting, you add the two dist ...
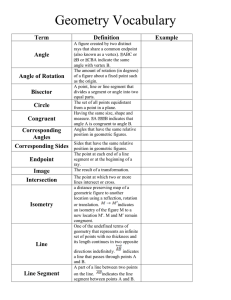
Vocabulary Chapter 1A
... Measure of an angle- number that corresponds to the size of the angle, usually given in degrees Acute angles- angles with a measure greater than 0° and less than 90° Right Angles- angles with a measure of 90° Obtuse Angles- angles with a measure greater than 90° and less than 180° Perimeter (of a pl ...
... Measure of an angle- number that corresponds to the size of the angle, usually given in degrees Acute angles- angles with a measure greater than 0° and less than 90° Right Angles- angles with a measure of 90° Obtuse Angles- angles with a measure greater than 90° and less than 180° Perimeter (of a pl ...
Unit 3: Algebraic Connections
... that follows a given rule. Identify apparent features of the pattern that were not explicit in the rule itself. ...
... that follows a given rule. Identify apparent features of the pattern that were not explicit in the rule itself. ...
Final Exam Review File
... the coordinates of the midpoint of the line segment? 17. One endpoint of a line segment in the (x, y) coordinate plane has coordinates (6, -10). The midpoint of the segment has coordinates (-2, 3). What are the coordinates of the other endpoint of the segment? 18. For triangle ∆XYZ, where side XZ is ...
... the coordinates of the midpoint of the line segment? 17. One endpoint of a line segment in the (x, y) coordinate plane has coordinates (6, -10). The midpoint of the segment has coordinates (-2, 3). What are the coordinates of the other endpoint of the segment? 18. For triangle ∆XYZ, where side XZ is ...
Honors Geometry Test 1 Topics I. Definitions and undefined terms A
... Know which terms are the three undefined terms B. Definitions in Topic 1 up through “angle” and “vertex of an angle” on page 6 (You might especially want to look at opposite rays, space, vertex, and midpoint) II. Notation and naming A. Notation for point, line, and plane B. Appropriate names for lin ...
... Know which terms are the three undefined terms B. Definitions in Topic 1 up through “angle” and “vertex of an angle” on page 6 (You might especially want to look at opposite rays, space, vertex, and midpoint) II. Notation and naming A. Notation for point, line, and plane B. Appropriate names for lin ...
Cartesian coordinate system
A Cartesian coordinate system is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely in a plane by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances from the point to two fixed perpendicular directed lines, measured in the same unit of length. Each reference line is called a coordinate axis or just axis of the system, and the point where they meet is its origin, usually at ordered pair (0, 0). The coordinates can also be defined as the positions of the perpendicular projections of the point onto the two axes, expressed as signed distances from the origin.One can use the same principle to specify the position of any point in three-dimensional space by three Cartesian coordinates, its signed distances to three mutually perpendicular planes (or, equivalently, by its perpendicular projection onto three mutually perpendicular lines). In general, n Cartesian coordinates (an element of real n-space) specify the point in an n-dimensional Euclidean space for any dimension n. These coordinates are equal, up to sign, to distances from the point to n mutually perpendicular hyperplanes.The invention of Cartesian coordinates in the 17th century by René Descartes (Latinized name: Cartesius) revolutionized mathematics by providing the first systematic link between Euclidean geometry and algebra. Using the Cartesian coordinate system, geometric shapes (such as curves) can be described by Cartesian equations: algebraic equations involving the coordinates of the points lying on the shape. For example, a circle of radius 2 in a plane may be described as the set of all points whose coordinates x and y satisfy the equation x2 + y2 = 4.Cartesian coordinates are the foundation of analytic geometry, and provide enlightening geometric interpretations for many other branches of mathematics, such as linear algebra, complex analysis, differential geometry, multivariate calculus, group theory and more. A familiar example is the concept of the graph of a function. Cartesian coordinates are also essential tools for most applied disciplines that deal with geometry, including astronomy, physics, engineering and many more. They are the most common coordinate system used in computer graphics, computer-aided geometric design and other geometry-related data processing.