
Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 32: An Introduction to Animal
... 13) Almost all of the major animal body plans seen today appeared in the fossil record over 500 million years ago at the beginning of the A) Cambrian period. B) Ediacaran period. C) Permian period. D) Carboniferous period. E) Cretaceous period. Answer: A Topic: Concept 32.2 Skill: Knowledge ...
... 13) Almost all of the major animal body plans seen today appeared in the fossil record over 500 million years ago at the beginning of the A) Cambrian period. B) Ediacaran period. C) Permian period. D) Carboniferous period. E) Cretaceous period. Answer: A Topic: Concept 32.2 Skill: Knowledge ...
The mouth, the anus, and the blastopore—open
... seems that a large extended blastopore closes laterally and both ends stay open and give rise to the mouth and anus (Balfour, 1883; Sedgwick, 1885). In contrast, Kennel (1885) draws a different picture for Peripatus edwardsii, showing that the opening that gives rise to the mouth and anus is separat ...
... seems that a large extended blastopore closes laterally and both ends stay open and give rise to the mouth and anus (Balfour, 1883; Sedgwick, 1885). In contrast, Kennel (1885) draws a different picture for Peripatus edwardsii, showing that the opening that gives rise to the mouth and anus is separat ...
Classifying animals
... Kingdoms – Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia ...
... Kingdoms – Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia ...
Animals may be characterized by the presence of a coelom
... epithelial covering of the body surface and the central nervous system; and the mesoderm becomes all muscle tissues, connective tissues, and most other organs. Triploblasts can be further categorized into those without acoelom (acoelomates), those with a true coelom (eucoelomates), and those with "f ...
... epithelial covering of the body surface and the central nervous system; and the mesoderm becomes all muscle tissues, connective tissues, and most other organs. Triploblasts can be further categorized into those without acoelom (acoelomates), those with a true coelom (eucoelomates), and those with "f ...
Aurelia aurita (Moon Jellyfish)
... towards the edge of the bell where it is then moved to the mouth (Wildscreen, 2017). The animal uses stinging cells to capture other prey and small fish. POPULATION ECOLOGY. Aurelia aurita is one of the most common species of jellyfish. It is almost morphologically identical to a few other species o ...
... towards the edge of the bell where it is then moved to the mouth (Wildscreen, 2017). The animal uses stinging cells to capture other prey and small fish. POPULATION ECOLOGY. Aurelia aurita is one of the most common species of jellyfish. It is almost morphologically identical to a few other species o ...
the body of a cnidarian
... List some examples of cnidarians provided in the first paragraph: Two characteristics all cnidarians share are: ...
... List some examples of cnidarians provided in the first paragraph: Two characteristics all cnidarians share are: ...
Negligible senescence in the longest living rodent, the
... Mortality rates of naked mole-rats are highest in their Wrst 2 months of life, and death in this age cohort is generally attributed to inadequate maternal care, cannibalism by siblings and poor inoculation of gastrointestinal Xora and fauna. Thereafter, age-speciWc rates of mortality are not evident ...
... Mortality rates of naked mole-rats are highest in their Wrst 2 months of life, and death in this age cohort is generally attributed to inadequate maternal care, cannibalism by siblings and poor inoculation of gastrointestinal Xora and fauna. Thereafter, age-speciWc rates of mortality are not evident ...
Creature features - Natural Resources South Australia
... earthworms and bristle worms) and there are four species known in South Australian inland waters. Over 500 species are known throughout the world. Although many people are disgusted by leeches, they have been used in medicine for thousands of years. Today, captive-bred leeches are used in microsurge ...
... earthworms and bristle worms) and there are four species known in South Australian inland waters. Over 500 species are known throughout the world. Although many people are disgusted by leeches, they have been used in medicine for thousands of years. Today, captive-bred leeches are used in microsurge ...
Chordate Evolution and Autonomous Specification of Cell Fate: The
... first recorded in 1828. Between 1816 and 1850, at least four other investigators independently published figures depicting the ascidian larva: J. C. Savigny, Michael Sars, John Dalyell, and Louis Agassiz. Charles Darwin had studied the larvae of a colonial ascidian in 1833 during his voyage on the H ...
... first recorded in 1828. Between 1816 and 1850, at least four other investigators independently published figures depicting the ascidian larva: J. C. Savigny, Michael Sars, John Dalyell, and Louis Agassiz. Charles Darwin had studied the larvae of a colonial ascidian in 1833 during his voyage on the H ...
Coelomates
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Species Account For Catagonus Wagneri
... dealing with this annoying feature of cactus. C. wagneri also has a tough, two chambered stomach which is needed to digest the tough food that it so often has to eat (Raffo 2000). Some interesting remarks: This peccary species was thought to be extinct until it was discovered in 1972. There are an e ...
... dealing with this annoying feature of cactus. C. wagneri also has a tough, two chambered stomach which is needed to digest the tough food that it so often has to eat (Raffo 2000). Some interesting remarks: This peccary species was thought to be extinct until it was discovered in 1972. There are an e ...
Explore the Great Barrier Reef!
... The students who will view the lesson will be 8th grade students who are in a geography and world history class. ...
... The students who will view the lesson will be 8th grade students who are in a geography and world history class. ...
Chapter 32(Introduction to Animal Diversity)
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Downloaded - Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B
... pathways were already present in the most recent common ancestor of these animals. Examples include the anterior–posterior patterning mechanism using HOX genes, the sog/chordin dpp/BMP 2/4 in dorsoventral patterning (Arendt & Nübler-Jung 1994; De Robertis & Sasai 1996) and PAX6/eyeless for eye deve ...
... pathways were already present in the most recent common ancestor of these animals. Examples include the anterior–posterior patterning mechanism using HOX genes, the sog/chordin dpp/BMP 2/4 in dorsoventral patterning (Arendt & Nübler-Jung 1994; De Robertis & Sasai 1996) and PAX6/eyeless for eye deve ...
Galapagos Exploration
... Uses its strong legs and webbed feet to swim and capture fish, eels, and octopuses ...
... Uses its strong legs and webbed feet to swim and capture fish, eels, and octopuses ...
Ch. 11 Notes
... A sponge in adult form, is attached to an object in the water and does not move Animals that do not move are called sessile ...
... A sponge in adult form, is attached to an object in the water and does not move Animals that do not move are called sessile ...
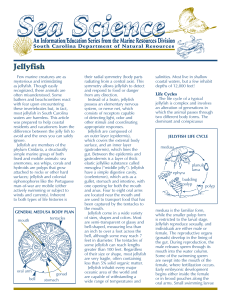
Jellyfish - Island Beach State Park
... nettle stings are similar to those of the lion’s mane. Given that they are most abundant in the summer, when the greatest number of people are likely to be swimming in the ocean, this species is thought to be responsible for most of the jellyfish stings that occur in South Carolina. Exercise caution ...
... nettle stings are similar to those of the lion’s mane. Given that they are most abundant in the summer, when the greatest number of people are likely to be swimming in the ocean, this species is thought to be responsible for most of the jellyfish stings that occur in South Carolina. Exercise caution ...
Phylum Echinodermata - Austin Community College
... 6. no real circulatory system 7. no excretory system 8. sense organs poorly developed 9. pedicellariae for protection Animals: Phylum Echinodermata; Ziser Lecture Notes 2008 ...
... 6. no real circulatory system 7. no excretory system 8. sense organs poorly developed 9. pedicellariae for protection Animals: Phylum Echinodermata; Ziser Lecture Notes 2008 ...
Invertebrate Classification
... • Arthropoda: Invertebrate phylum of animals characterized by a segmented body, jointed appendages, exoskeleton, and brain. • Cnidaria: Invertebrate phylum that includes animals such as jellyfish and corals; characterized by radial symmetry, tissues, and a stinger called a nematocyst. • deuterostome ...
... • Arthropoda: Invertebrate phylum of animals characterized by a segmented body, jointed appendages, exoskeleton, and brain. • Cnidaria: Invertebrate phylum that includes animals such as jellyfish and corals; characterized by radial symmetry, tissues, and a stinger called a nematocyst. • deuterostome ...
flatworm
... parenchyma tissue. There is no true circulatory or respiratory system, but like all other animals, flatworms do take in oxygen. Extracellular body fluids (interstitial fluids) percolate between cells to help distribute nutrients, gases, and waste products. Flatworms respire at their integument; gass ...
... parenchyma tissue. There is no true circulatory or respiratory system, but like all other animals, flatworms do take in oxygen. Extracellular body fluids (interstitial fluids) percolate between cells to help distribute nutrients, gases, and waste products. Flatworms respire at their integument; gass ...
Echinoderms - Advanced
... Echinoderms are marine organisms that make up the phylum Echinodermata. Members of the phylum include sea stars (starfish), sea urchins, sea cucumbers, sand dollars, brittle stars, and feather stars. There are 7000 different living species of echinoderms and 13,000 identified fossil species. Althoug ...
... Echinoderms are marine organisms that make up the phylum Echinodermata. Members of the phylum include sea stars (starfish), sea urchins, sea cucumbers, sand dollars, brittle stars, and feather stars. There are 7000 different living species of echinoderms and 13,000 identified fossil species. Althoug ...
WHALE WORMS
... material has been consumed. However, sulfur-reducing bacteria continue to feed on fats and oils deep within the whale bones. This process gradually releases hydrogen sulfide, which provides the basis for a third-stage, “sulphophilic” (sulfurloving) whalefall community. This sulphophilic community i ...
... material has been consumed. However, sulfur-reducing bacteria continue to feed on fats and oils deep within the whale bones. This process gradually releases hydrogen sulfide, which provides the basis for a third-stage, “sulphophilic” (sulfurloving) whalefall community. This sulphophilic community i ...
[edit] Reproduction
... (polyspermy), only one spermatozoal nucleus actually merges with the egg nucleus. The most important result of fertilization is egg activation, which allows the egg to undergo cell division. Activation, however, does not necessarily require the intervention of a spermatozoon; during parthenogenesis, ...
... (polyspermy), only one spermatozoal nucleus actually merges with the egg nucleus. The most important result of fertilization is egg activation, which allows the egg to undergo cell division. Activation, however, does not necessarily require the intervention of a spermatozoon; during parthenogenesis, ...
Seaside Sanctuaries: A Concept Review
... of health. Some might need minimal intervention on a daily basis, while others might need regular intensive veterinary intervention. A sanctuary must be able to provide for these varying levels of care. Quarantine and medical enclosures and full veterinary facilities must be on-site. Bidirectional r ...
... of health. Some might need minimal intervention on a daily basis, while others might need regular intensive veterinary intervention. A sanctuary must be able to provide for these varying levels of care. Quarantine and medical enclosures and full veterinary facilities must be on-site. Bidirectional r ...





















![[edit] Reproduction](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004262089_1-11e1f262a9daa1eb642481be5091f0d7-300x300.png)
