Concepts for the simulation of volume and surface scattering based
... Volume Scattering • There exists several different scattering effects. • Scattering caused by particles, schlieres/reams, mechanical stress. • Size of scattering structures ranges from atomic size to large extensions. • We will discuss scattering at volume structures with dimension of several 10 nm ...
... Volume Scattering • There exists several different scattering effects. • Scattering caused by particles, schlieres/reams, mechanical stress. • Size of scattering structures ranges from atomic size to large extensions. • We will discuss scattering at volume structures with dimension of several 10 nm ...
Composite Optical Vortices Formed by Collinear Laguerre-Gauss Beams
... Let us start with the simplest situation that we have found: 1 = +1 and 2 = +2. The calculations can be seen in Fig. 1, which displays in row (a) the intensity profile of the beam, and in row (b) the phase of the field. In both types of images we have deliberately discretized the gray scale to appreci ...
... Let us start with the simplest situation that we have found: 1 = +1 and 2 = +2. The calculations can be seen in Fig. 1, which displays in row (a) the intensity profile of the beam, and in row (b) the phase of the field. In both types of images we have deliberately discretized the gray scale to appreci ...
Quantifying Temperature Changes in Tissue
... damage in the vasculature 7. The efficiency of the cryosurgery is dependent on the repetition of a freeze-thaw cycle, but clinical studies have exhibited that the minimum requirements to guarantee cell necrosis is two freeze-thaw cycles at a freezing temperature of -40°C, for a duration of three min ...
... damage in the vasculature 7. The efficiency of the cryosurgery is dependent on the repetition of a freeze-thaw cycle, but clinical studies have exhibited that the minimum requirements to guarantee cell necrosis is two freeze-thaw cycles at a freezing temperature of -40°C, for a duration of three min ...
PDF
... vortex lines in electron beams8 are hard to obtain and study but often can be understood by probing defects in other topologically similar but more easily accessible systems, such as LCs and laser beams1–5,8,14. A nematic LC is typically comprised of rod-like molecules that spontaneously orient them ...
... vortex lines in electron beams8 are hard to obtain and study but often can be understood by probing defects in other topologically similar but more easily accessible systems, such as LCs and laser beams1–5,8,14. A nematic LC is typically comprised of rod-like molecules that spontaneously orient them ...
Review Answers - cloudfront.net
... getting more disordered and therefore entropy is increased. ΔS° is positive b. What change, if any, will occur in ΔG° for the reaction as the temperature is increased? Explain your reasoning in terms of thermodynamics principles. Since when Temp is increased there are more molecules of PCl3 and Cl2, ...
... getting more disordered and therefore entropy is increased. ΔS° is positive b. What change, if any, will occur in ΔG° for the reaction as the temperature is increased? Explain your reasoning in terms of thermodynamics principles. Since when Temp is increased there are more molecules of PCl3 and Cl2, ...
Nanosecond laser-induced breakdown in pure and - AS
... measured the size of the focal spot using a knife edge and found a value <2% larger than that deduced from the third-harmonic. 2.5. Self focusing. The location and size of the focal spot were measured by the third-harmonic method under low irradiance conditions. The optical breakdown threshold irrad ...
... measured the size of the focal spot using a knife edge and found a value <2% larger than that deduced from the third-harmonic. 2.5. Self focusing. The location and size of the focal spot were measured by the third-harmonic method under low irradiance conditions. The optical breakdown threshold irrad ...
SACs and Pracs from the $2 shop
... • Use the data you have collected, and the definition of resistance, to calculate the thermistor’s resistance for each of the settings on the variable power supply. ...
... • Use the data you have collected, and the definition of resistance, to calculate the thermistor’s resistance for each of the settings on the variable power supply. ...
Digital Fourier Microscopy for Soft Matter Dynamics
... somehow restrictive conditions [34], the analysis of microscope images in the Fourier space - from here on Digital Fourier Microscopy (DFM) - of a sample can provide quantitative information about its structure and dynamics similar to the one obtained in SLS and DLS experiments. The reader should be ...
... somehow restrictive conditions [34], the analysis of microscope images in the Fourier space - from here on Digital Fourier Microscopy (DFM) - of a sample can provide quantitative information about its structure and dynamics similar to the one obtained in SLS and DLS experiments. The reader should be ...
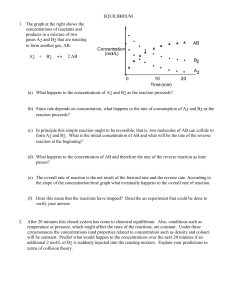
EQUILIBRIUM - SCH4U1-CCVI
... concentrations may be used to calculate the value of the equilibrium constant for this reaction. Then predictions may be made about the equilibrium concentrations in other solutions. To prepare a solution with a known concentration of the coloured complex, a dilute solution of thiocyanate ion is rea ...
... concentrations may be used to calculate the value of the equilibrium constant for this reaction. Then predictions may be made about the equilibrium concentrations in other solutions. To prepare a solution with a known concentration of the coloured complex, a dilute solution of thiocyanate ion is rea ...
Research Express@NCKU Form (English example) Item Content
... the incident polarization and interparticle distance using performing series measurements through a fiber-collection mode near-field scanning optical microscope (NSOM). The qualitative near-field observation and quantitative analysis facilitate more understanding of localized hot spots in surface-en ...
... the incident polarization and interparticle distance using performing series measurements through a fiber-collection mode near-field scanning optical microscope (NSOM). The qualitative near-field observation and quantitative analysis facilitate more understanding of localized hot spots in surface-en ...
Superresolution size determination in fluorescence microscopy: A
... may be used, with each parameter corresponding to a physically detectable value: The subscripts i and o are used for the inner and outer enveloping AID profiles 共cf. Fig. 1兲. M i,o are the maximum intensities of the enveloping functions; B i,o are constants proportional to the FWHM of the enveloping ...
... may be used, with each parameter corresponding to a physically detectable value: The subscripts i and o are used for the inner and outer enveloping AID profiles 共cf. Fig. 1兲. M i,o are the maximum intensities of the enveloping functions; B i,o are constants proportional to the FWHM of the enveloping ...
Raman spectroscopy: Watching a molecule breathe
... had proved very difficult, preventing VCSELs from being used in applications such as high-density optical data storage, displays, high-resolution printing, and chemical and biological sensing. Thus, the realization of ultraviolet emission from the polariton laser represents a significant technologic ...
... had proved very difficult, preventing VCSELs from being used in applications such as high-density optical data storage, displays, high-resolution printing, and chemical and biological sensing. Thus, the realization of ultraviolet emission from the polariton laser represents a significant technologic ...
D12 in docx
... “erases”) from all sides using a bottle beam. (b) Foci measured by scanning a gold bead through the focus in three dimensions. Taken from Ref.[D12:5]. ...
... “erases”) from all sides using a bottle beam. (b) Foci measured by scanning a gold bead through the focus in three dimensions. Taken from Ref.[D12:5]. ...
FREE Sample Here
... been that a great many theories have been proposed, only to be discarded. About 2,000 years ago, the characteristics of light were defined by the way it behaved under a variety of conditions (geometric optics). The premise was that light consists of rays that move outward from their source in straig ...
... been that a great many theories have been proposed, only to be discarded. About 2,000 years ago, the characteristics of light were defined by the way it behaved under a variety of conditions (geometric optics). The premise was that light consists of rays that move outward from their source in straig ...
Simultaneous Generation of Different Types of Ion Pairs upon
... decay upon ultrafast recombination.23 The discrepancy with the original study was due to two factors: (1) better time resolution (100 fs vs 30-50 ps) and (2) the possibility of calibrating the transient absorption signal arising from Pe•+ by independent photoconductivity measurements. This calibrati ...
... decay upon ultrafast recombination.23 The discrepancy with the original study was due to two factors: (1) better time resolution (100 fs vs 30-50 ps) and (2) the possibility of calibrating the transient absorption signal arising from Pe•+ by independent photoconductivity measurements. This calibrati ...
Stimulated Brillouin scattering parasitics in large
... thresholds because of the finite response time of fused silica. It should be noted that this buildup time will be longer for longer-wavelength ...
... thresholds because of the finite response time of fused silica. It should be noted that this buildup time will be longer for longer-wavelength ...
1994 AP Chemistry Multiple Choice
... 37. A sample of 3.30 grams of an ideal gas at 150.0_C and 1.25 atmospheres pressure has a volume of 2.00 liters. What is the molar mass of the gas? The gas constant, R, is 0.0821 (L.atm)/(mol.K). (A) 0.0218 gram/mole (B) 16.2 grams/mole (C) 37.0 grams/mole (D) 45.8 grams/mole (E) 71.6 grams/mole 38 ...
... 37. A sample of 3.30 grams of an ideal gas at 150.0_C and 1.25 atmospheres pressure has a volume of 2.00 liters. What is the molar mass of the gas? The gas constant, R, is 0.0821 (L.atm)/(mol.K). (A) 0.0218 gram/mole (B) 16.2 grams/mole (C) 37.0 grams/mole (D) 45.8 grams/mole (E) 71.6 grams/mole 38 ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.