
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... Abstract: Imaging systems are typically partitioned into three components: focusing of incident light, scattering of incident light by an object and imaging of scattered light. We present a model of high Numerical Aperture (NA) imaging systems which differs from prior models as it treats each of the ...
... Abstract: Imaging systems are typically partitioned into three components: focusing of incident light, scattering of incident light by an object and imaging of scattered light. We present a model of high Numerical Aperture (NA) imaging systems which differs from prior models as it treats each of the ...
Studies of Lithium Hydride Systems. I. Solid
... of the sample. Thc vcrsatility in adjustment of this amplifier allowed heating and cooling rates to be changed from 0.2 to 10°/ min., thcrcby controlling vcry c10scly the hcat flow il1to and out of the sample. The differential d .c. amplifier activated n. proportionating controller which in turn ope ...
... of the sample. Thc vcrsatility in adjustment of this amplifier allowed heating and cooling rates to be changed from 0.2 to 10°/ min., thcrcby controlling vcry c10scly the hcat flow il1to and out of the sample. The differential d .c. amplifier activated n. proportionating controller which in turn ope ...
Optical amplifiers
... An erbium doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) consists of a few meters of optical fiber doped with a few parts per million of the rare earth element erbium. The optical signal is injected into this fiber, along with the light from a special “pump” laser that is designed to excite the erbium ions. Let us th ...
... An erbium doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) consists of a few meters of optical fiber doped with a few parts per million of the rare earth element erbium. The optical signal is injected into this fiber, along with the light from a special “pump” laser that is designed to excite the erbium ions. Let us th ...
Optical Metrology - Bogazici University Physics Department
... is proportional to the time average of I(x, y ,t) over one period: ...
... is proportional to the time average of I(x, y ,t) over one period: ...
revised Chemical Kinetics
... or for gases), pressure (for gases), surface area, nature of the reactants, temperature, and presence or absence of a catalyst. Concentration: In general, increasing reactant concentrations increases the reaction rate. This is because molecules must collide in order to react. The more concentrated t ...
... or for gases), pressure (for gases), surface area, nature of the reactants, temperature, and presence or absence of a catalyst. Concentration: In general, increasing reactant concentrations increases the reaction rate. This is because molecules must collide in order to react. The more concentrated t ...
unable_MEMS.pdf
... inventory stock and sparing for DWDM transmitters and receivers used in opaque networks capable of carrying more than 100 wavelengths per fiber. In case of hardware failure, a complete inventory of fixed-wavelength transmitters and receivers must be carried at numerous locations throughout the count ...
... inventory stock and sparing for DWDM transmitters and receivers used in opaque networks capable of carrying more than 100 wavelengths per fiber. In case of hardware failure, a complete inventory of fixed-wavelength transmitters and receivers must be carried at numerous locations throughout the count ...
Optical switches
... • Chromatic dispersion (cont.) • dispersion is measured in ps/(nm*km), i.e. delay per wavelength variation and fiber length • Dispersion depends on the wavelength • at some wavelength dispersion may be zero • in conventional single mode fiber this typically occurs at 1.3 µm - below, dispersion is ne ...
... • Chromatic dispersion (cont.) • dispersion is measured in ps/(nm*km), i.e. delay per wavelength variation and fiber length • Dispersion depends on the wavelength • at some wavelength dispersion may be zero • in conventional single mode fiber this typically occurs at 1.3 µm - below, dispersion is ne ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... materials [20, 23]. Simpler experimental approaches sometimes used to determine CD, such as alternating illumination with left and right circularly polarized light (which is equivalent to measuring only the Mueller matrix element m03 ), can give misleading results because the circular polarization i ...
... materials [20, 23]. Simpler experimental approaches sometimes used to determine CD, such as alternating illumination with left and right circularly polarized light (which is equivalent to measuring only the Mueller matrix element m03 ), can give misleading results because the circular polarization i ...
Influence of substrate configuration on the angular response pattern
... therefore their amplitudes add to the maximum. For all other directions, the radiated field amplitudes are between zero and the maximum. These field amplitudes, however, are altered if the antenna is placed at the interface of two materials. There, the antenna will radiate more strongly into the mat ...
... therefore their amplitudes add to the maximum. For all other directions, the radiated field amplitudes are between zero and the maximum. These field amplitudes, however, are altered if the antenna is placed at the interface of two materials. There, the antenna will radiate more strongly into the mat ...
Guide for the Measurement of Smooth Surface Topography using
... be used to create the two waves to be interfered. Typically in an interferometer, a wave is split into two parts, which travel different paths and the waves are then combined to create interference. When the paths differ by an even number of half-wavelengths, the superposed waves are in phase and co ...
... be used to create the two waves to be interfered. Typically in an interferometer, a wave is split into two parts, which travel different paths and the waves are then combined to create interference. When the paths differ by an even number of half-wavelengths, the superposed waves are in phase and co ...
Sample Chapter
... It has an inner glass core with an outer cladding. This is covered with a protective buffer and outer jacket. This design of fibre is light and has a very low loss, making it ideal for the transmission of information over long distances. light in a Fibre The light propagates along the fibre by the p ...
... It has an inner glass core with an outer cladding. This is covered with a protective buffer and outer jacket. This design of fibre is light and has a very low loss, making it ideal for the transmission of information over long distances. light in a Fibre The light propagates along the fibre by the p ...
Effect of TiO2 on optical properties of glasses in the soda
... Many applications of glass rely on their optical properties, where glasses are among the few solid materials which transmit visible light. This is because without the specific incorporation of localized electronic states with low activation energy, most inorganic glassy materials are electronic isol ...
... Many applications of glass rely on their optical properties, where glasses are among the few solid materials which transmit visible light. This is because without the specific incorporation of localized electronic states with low activation energy, most inorganic glassy materials are electronic isol ...
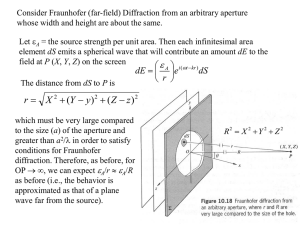
... where I(0) is the intensity at the center of the screen at point P0 (Y = 0, Z = 0). A typical far-field diffraction pattern is shown in Fig. 10.20. Note that when = 0 or = 0, we get the familiar single slit pattern. The approximate locations of the secondary maxima along the -axis (which is ...
Lecture-12-Optics
... where I(0) is the intensity at the center of the screen at point P0 (Y = 0, Z = 0). A typical far-field diffraction pattern is shown in Fig. 10.20. Note that when = 0 or = 0, we get the familiar single slit pattern. The approximate locations of the secondary maxima along the -axis (which is ...
... where I(0) is the intensity at the center of the screen at point P0 (Y = 0, Z = 0). A typical far-field diffraction pattern is shown in Fig. 10.20. Note that when = 0 or = 0, we get the familiar single slit pattern. The approximate locations of the secondary maxima along the -axis (which is ...
S P E C T R O S C O... F E R R O I C S Y S...
... carrier of information. Understanding of the nature of domain structure and its dynamics is therefore essential. At the same time the omnipresent need of keeping up with Moore law demands the dimensions of commercialized devices to decrease drastically. Hence the resolution of classical optical Kerr ...
... carrier of information. Understanding of the nature of domain structure and its dynamics is therefore essential. At the same time the omnipresent need of keeping up with Moore law demands the dimensions of commercialized devices to decrease drastically. Hence the resolution of classical optical Kerr ...
Electron diffraction for analysing crystal orientation of thin films
... Only 3 years after the revolutionary discovery of the wave nature of electrons, electron diffraction, a phenomenon based on the wave nature of these small particles, was able to provide diffraction patterns of crystalline materials very similar to those obtained by X-rays [4, 5, 18]. Today, electro ...
... Only 3 years after the revolutionary discovery of the wave nature of electrons, electron diffraction, a phenomenon based on the wave nature of these small particles, was able to provide diffraction patterns of crystalline materials very similar to those obtained by X-rays [4, 5, 18]. Today, electro ...
[pdf]
... sphere. We calculate the fluorescent DPDW generated by a point source inside and outside the sphere and then integrate the fluorescent DPDW over the corresponding source distribution to obtain the total fluorescent DPDW. Before proceeding, we specify the following notation convention: All background ...
... sphere. We calculate the fluorescent DPDW generated by a point source inside and outside the sphere and then integrate the fluorescent DPDW over the corresponding source distribution to obtain the total fluorescent DPDW. Before proceeding, we specify the following notation convention: All background ...
MEMS-based handheld confocal microscope for in
... The utility of confocal microscopy for skin imaging resides in its ability to provide crosssectional images with cellular detail similar to that of histological techniques [1]. Recent work has largely been aimed at in vivo confocal imaging of skin, with a goal of providing a noninvasive sectional im ...
... The utility of confocal microscopy for skin imaging resides in its ability to provide crosssectional images with cellular detail similar to that of histological techniques [1]. Recent work has largely been aimed at in vivo confocal imaging of skin, with a goal of providing a noninvasive sectional im ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.



















![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008852298_1-c287f813fc92478f173913ba3be9f759-300x300.png)
