chm 158 course syllabus
... your name, it indicates that you are making satisfactory progress. You must continue to make satisfactory progress throughout the semester to ensure a passing grade. A “U” for unsatisfactory progress is intended to alert you to problems and to give you an opportunity to take steps to improve your pe ...
... your name, it indicates that you are making satisfactory progress. You must continue to make satisfactory progress throughout the semester to ensure a passing grade. A “U” for unsatisfactory progress is intended to alert you to problems and to give you an opportunity to take steps to improve your pe ...
Get
... attention due to their reproducibility, precision, cost, and so on [14–20]. Although many excellent fabrication techniques have been proposed to achieve the perfect geometry of nanograting structures, it has not always been successful during the actual micro/nanofabrication [19, 21, 22]. For example ...
... attention due to their reproducibility, precision, cost, and so on [14–20]. Although many excellent fabrication techniques have been proposed to achieve the perfect geometry of nanograting structures, it has not always been successful during the actual micro/nanofabrication [19, 21, 22]. For example ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... 380 and 440 nm are perceived as violet. With increasing wavelength, the color impression changes to blue, green, yellow, orange, and finally red. Red is perceived at wavelengths above 600 nm. The associated wavelengths are subject to individual variations in color perception. The so-called spectral ...
... 380 and 440 nm are perceived as violet. With increasing wavelength, the color impression changes to blue, green, yellow, orange, and finally red. Red is perceived at wavelengths above 600 nm. The associated wavelengths are subject to individual variations in color perception. The so-called spectral ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... In ISM resolution doubling is achieved, as in confocal microscopy, with an almost closed pinhole, but without the associated trade-off in signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). This is achieved by replacing the point detector in a conventional confocal microscope with a detector array, e.g., a CCD chip, and t ...
... In ISM resolution doubling is achieved, as in confocal microscopy, with an almost closed pinhole, but without the associated trade-off in signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). This is achieved by replacing the point detector in a conventional confocal microscope with a detector array, e.g., a CCD chip, and t ...
Triple resonance for a three-level system of a chiral molecule
... treatment may readily be extended to other wavelength regions, infrared, visible, and ultraviolet, and may thus be applicable to C2 chiral molecules as well, for which two of the three types of transitions can be vibrational, for example. As already stressed, one of the most crucial points of the pr ...
... treatment may readily be extended to other wavelength regions, infrared, visible, and ultraviolet, and may thus be applicable to C2 chiral molecules as well, for which two of the three types of transitions can be vibrational, for example. As already stressed, one of the most crucial points of the pr ...
McIntyre, Stuart (2013) Limitations to light microscope resolution in
... Fluorescence imaging has become a vital tool for understanding cardiac cell function. With the advent of calcium-sensitive and fast response voltage-sensitive dyes, it is now possible to gain complex physiological recordings from various cardiac muscle preparations, while simultaneously optically se ...
... Fluorescence imaging has become a vital tool for understanding cardiac cell function. With the advent of calcium-sensitive and fast response voltage-sensitive dyes, it is now possible to gain complex physiological recordings from various cardiac muscle preparations, while simultaneously optically se ...
Effective Area of Optical Fibres
... the mode field cannot be approximated by a Gaussian function. The simple relationship between MFD and Aeff given by equation 2-3 no longer holds and alternative methods are required to calculate the effective area. An example of this is shown in Figure 1, in which theoretical Gaussian and non-Gaussi ...
... the mode field cannot be approximated by a Gaussian function. The simple relationship between MFD and Aeff given by equation 2-3 no longer holds and alternative methods are required to calculate the effective area. An example of this is shown in Figure 1, in which theoretical Gaussian and non-Gaussi ...
Solubility
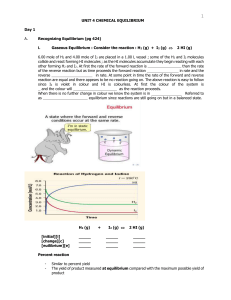
... The Formation & Dissolution of Precipitates • Solubility: maximum amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent (depends on solvent, temperature and pressure) No compound is infinitely soluble and no compound is perfectly insoluble. ...
... The Formation & Dissolution of Precipitates • Solubility: maximum amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent (depends on solvent, temperature and pressure) No compound is infinitely soluble and no compound is perfectly insoluble. ...
Observation of Localized States in Lieb Photonic
... diffracts all over the lattice. This shows the importance of setting the right phase structure (π) to effectively excite the flat-band states. Finally, as a proof of the numerical excitation of the ring mode, we generate a coherently combined state by summing two neighboring ring modes and propagati ...
... diffracts all over the lattice. This shows the importance of setting the right phase structure (π) to effectively excite the flat-band states. Finally, as a proof of the numerical excitation of the ring mode, we generate a coherently combined state by summing two neighboring ring modes and propagati ...
Review Packet Answers - Bremerton School District
... equilibrium constant, Kp, to remain constant, the equilibrium pressure of NH3 must decrease when the pressure of H2S is increased. Kp = (PNH3) (PH2S) (A complete explanation based on Le Chatelier's principle is also acceptable.) c) two points The mass of NH4HS increases. A decrease in volume causes ...
... equilibrium constant, Kp, to remain constant, the equilibrium pressure of NH3 must decrease when the pressure of H2S is increased. Kp = (PNH3) (PH2S) (A complete explanation based on Le Chatelier's principle is also acceptable.) c) two points The mass of NH4HS increases. A decrease in volume causes ...
Phase retrieval in X-ray phase-contrast imaging suitable for
... different distances from the source [17]. (The same effect can also be achieved by using different amounts of defocus in, e.g., phase-contrast microscopy [19], or by taking images at different wavelengths.) This relates to the uniqueness of the retrieved phase. If only one image is captured, at a ce ...
... different distances from the source [17]. (The same effect can also be achieved by using different amounts of defocus in, e.g., phase-contrast microscopy [19], or by taking images at different wavelengths.) This relates to the uniqueness of the retrieved phase. If only one image is captured, at a ce ...
High-Q Microresonators as Lasing Elements for Silicon Photonics
... precision and depth of their teachings on the subject. As part of the EPIC program, Axel Scherer provided us with essential materials and processing capabilities, and Eli Yablonovitch gave us unwavering encouragement and insightful advice on the complex nature of silicon surfaces. I also thank Joe S ...
... precision and depth of their teachings on the subject. As part of the EPIC program, Axel Scherer provided us with essential materials and processing capabilities, and Eli Yablonovitch gave us unwavering encouragement and insightful advice on the complex nature of silicon surfaces. I also thank Joe S ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.