ref.3 Optical properties in semiconductors
... can describe high energy electrons (short waves) in terms of phase difference between adjacent atoms (unit cells) described by ‘k’, and shape of wave function within unit cell, described by function uk(r) Behavior within unit cell gives rise to energy bands We can describe electron behavior with wav ...
... can describe high energy electrons (short waves) in terms of phase difference between adjacent atoms (unit cells) described by ‘k’, and shape of wave function within unit cell, described by function uk(r) Behavior within unit cell gives rise to energy bands We can describe electron behavior with wav ...
AP `99 Multiple Choice
... (NH4)2SO4(s) (E) Sr(NO3)2(s) 66. When solid ammonium chloride, NH4Cl(s), is added to water at 25_C it dissolves and the temperature of the solution decreases. Which of the following is true for the values of _H and _S for the dissolving process? (A) Positive ...
... (NH4)2SO4(s) (E) Sr(NO3)2(s) 66. When solid ammonium chloride, NH4Cl(s), is added to water at 25_C it dissolves and the temperature of the solution decreases. Which of the following is true for the values of _H and _S for the dissolving process? (A) Positive ...
1999 Advanced Placement Chemistry Exam
... (NH4)2SO4(s) (E) Sr(NO3)2(s) 66. When solid ammonium chloride, NH4Cl(s), is added to water at 25_C it dissolves and the temperature of the solution decreases. Which of the following is true for the values of _H and _S for the dissolving process? (A) Positive ...
... (NH4)2SO4(s) (E) Sr(NO3)2(s) 66. When solid ammonium chloride, NH4Cl(s), is added to water at 25_C it dissolves and the temperature of the solution decreases. Which of the following is true for the values of _H and _S for the dissolving process? (A) Positive ...
Period 3 Activity Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves – Radiant Energy II
... The absorption of photon causes the electron to move up two energy levels. The emission of photon #2 causes the electron to drop down only one energy level. b) Which photon has a larger frequency, the absorbed or either of the emitted photon? How do you know? The absorbed photon (photon #1) has a hi ...
... The absorption of photon causes the electron to move up two energy levels. The emission of photon #2 causes the electron to drop down only one energy level. b) Which photon has a larger frequency, the absorbed or either of the emitted photon? How do you know? The absorbed photon (photon #1) has a hi ...
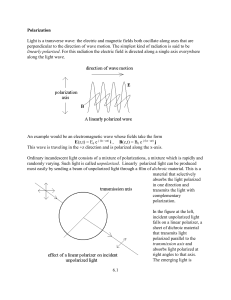
6.1 Polarization Light is a transverse wave: the electric and magnetic
... I = I0 cos2 . This relationship is called the law of Malus and holds only for incident linearly polarized light. Dichroism is not difficult to understand Common dichroic materials are formed from long chain-like molecules with electrons that can roam over the length of the molecule. A linearly polar ...
... I = I0 cos2 . This relationship is called the law of Malus and holds only for incident linearly polarized light. Dichroism is not difficult to understand Common dichroic materials are formed from long chain-like molecules with electrons that can roam over the length of the molecule. A linearly polar ...
Double Exposure Holography - Wooster Physics
... reflecting off the object and hitting your two eyes. Without two eyes, there would be no depth to the object, and without light, no object would be seen at all.1 A hologram simply replicates these two ideas, by using two beams of light, and catching the light waves reflected off an object. The first ...
... reflecting off the object and hitting your two eyes. Without two eyes, there would be no depth to the object, and without light, no object would be seen at all.1 A hologram simply replicates these two ideas, by using two beams of light, and catching the light waves reflected off an object. The first ...
Helium-Neon Laser 1 Introduction
... 1. Place a CCD camera with an appropriate choice of filters (neutral density and interference filters) near the exit of the output coupler (OC) with a weaker transmission. Be conscious of where the CCD array is located when positioning the camera with respect to the beam. Turn on the appropriate sof ...
... 1. Place a CCD camera with an appropriate choice of filters (neutral density and interference filters) near the exit of the output coupler (OC) with a weaker transmission. Be conscious of where the CCD array is located when positioning the camera with respect to the beam. Turn on the appropriate sof ...
Word 97 Format
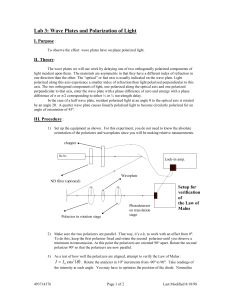
... your data. If your data matches the theoretical curve, then the polarizers are aligned. If not, repeat steps one and two. In your lab report, plot the theoretical curve and experimental curve on the same graph. 4) Place the half wave plate in the 1” rotation stage and put it in between the polarize ...
... your data. If your data matches the theoretical curve, then the polarizers are aligned. If not, repeat steps one and two. In your lab report, plot the theoretical curve and experimental curve on the same graph. 4) Place the half wave plate in the 1” rotation stage and put it in between the polarize ...
A transparent material like glass allows light to pass
... the two blunt corners of the crystal. Blunt corner is the corner at which three parallelograms meet with obtuse angles. There will be two blunt corners. In a uniaxial crystal there is only one optic axis. There some other crystals with more than one optic axis and they may be called biaxial crystals ...
... the two blunt corners of the crystal. Blunt corner is the corner at which three parallelograms meet with obtuse angles. There will be two blunt corners. In a uniaxial crystal there is only one optic axis. There some other crystals with more than one optic axis and they may be called biaxial crystals ...
Experimental observation of the far field diffraction patterns of
... center the smaller the peak intensity of the diffraction rings. The number of bright rings does not follow the same relation observed in the first case however it increases as the absolute value of the phase shift raises. ...
... center the smaller the peak intensity of the diffraction rings. The number of bright rings does not follow the same relation observed in the first case however it increases as the absolute value of the phase shift raises. ...
slides - Smith Lab
... Two basic types of lenses are convex and concave. A convex lens, also known as a plus power lens, focuses light behind the lens; whereas, a concave lens, also known as a minus power lens, focuses light in front of the lens. The power of a lens is measured in Diopters (D) and reflects the focusing di ...
... Two basic types of lenses are convex and concave. A convex lens, also known as a plus power lens, focuses light behind the lens; whereas, a concave lens, also known as a minus power lens, focuses light in front of the lens. The power of a lens is measured in Diopters (D) and reflects the focusing di ...
Niyaz_Ahmad_Report
... and microstructural characterization which have given enough evidence on the presence of nano and microcrystallites in the glass samples. Optical transmission studies have been done to evaluate various optical properties. There is a blue shift observed in the cut-off wavelength at the absorption edg ...
... and microstructural characterization which have given enough evidence on the presence of nano and microcrystallites in the glass samples. Optical transmission studies have been done to evaluate various optical properties. There is a blue shift observed in the cut-off wavelength at the absorption edg ...
Standard answers: 1 Basic concepts, Fuels, alkanes and alkenes
... 20. Why does ?? reaction not happen? It has a high activation energy 21. Calculating H – from temperature changes i) Q = mcT (Kj) ...
... 20. Why does ?? reaction not happen? It has a high activation energy 21. Calculating H – from temperature changes i) Q = mcT (Kj) ...
Velocity of sound in liquids
... The refractive index of the liquid also changes because of the pressure variations, and the change in refractive index %n can be regarded as proportional to the pressure variation %p. In phases t = 0 and t = 12 T (where T is the vibration period), well-defined interference fringes occur, spaced apar ...
... The refractive index of the liquid also changes because of the pressure variations, and the change in refractive index %n can be regarded as proportional to the pressure variation %p. In phases t = 0 and t = 12 T (where T is the vibration period), well-defined interference fringes occur, spaced apar ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.