(III) Laser Detection of Wave Motion in Solids
... velocity of electromagnetic waves in vacuum divided by that in the material, and is greater than or equal to 1.0. The refractive index of air at atmospheric pressure is very close to 1.0, so we can assume that the wave velocity air is effectively the same as that in vacuum. Electromagnetic radiation ...
... velocity of electromagnetic waves in vacuum divided by that in the material, and is greater than or equal to 1.0. The refractive index of air at atmospheric pressure is very close to 1.0, so we can assume that the wave velocity air is effectively the same as that in vacuum. Electromagnetic radiation ...
21.pdf
... may be noticed that the high-energy features of PS280, expected near ⬃ 300– 350 nm, are observed clearly when the light is incident first on PS280, while the high-energy features of PMMA410, expected near ⬃ 410– 480 nm, are resolved better when the light is incident first on PMMA410. This justif ...
... may be noticed that the high-energy features of PS280, expected near ⬃ 300– 350 nm, are observed clearly when the light is incident first on PS280, while the high-energy features of PMMA410, expected near ⬃ 410– 480 nm, are resolved better when the light is incident first on PMMA410. This justif ...
Blue light hazard
... exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Wavelengths shorter than 320 nm are most effective in causing this condition. The peak of the action spectrum is approximately at 270 nm. Note: Different action spectra have been published for photokeratitis and photoconjuctivitis (CIE 106/2 and CIE 106/3– 199 ...
... exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Wavelengths shorter than 320 nm are most effective in causing this condition. The peak of the action spectrum is approximately at 270 nm. Note: Different action spectra have been published for photokeratitis and photoconjuctivitis (CIE 106/2 and CIE 106/3– 199 ...
Efficient output coupling of intracavity high harmonic generation
... yet, is a near perfect high-reflector for the 1070 nm fundamental light. We find this optic produces no measurable decrease in the cavity finesse and power enhancement. It also seems to have a minimal effect on the cavity dispersion as determined from the measured transmitted spectrum of the fundame ...
... yet, is a near perfect high-reflector for the 1070 nm fundamental light. We find this optic produces no measurable decrease in the cavity finesse and power enhancement. It also seems to have a minimal effect on the cavity dispersion as determined from the measured transmitted spectrum of the fundame ...
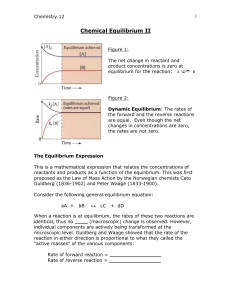
Chemical Equilibrium II
... individual components are actively being transformed at the microscopic level. Guldberg and Waage showed that the rate of the reaction in either direction is proportional to what they called the “active masses” of the various components: Rate of forward reaction = ________________ Rate of reverse re ...
... individual components are actively being transformed at the microscopic level. Guldberg and Waage showed that the rate of the reaction in either direction is proportional to what they called the “active masses” of the various components: Rate of forward reaction = ________________ Rate of reverse re ...
Bichromatic Frequency Conversion in Potassium Niobate.
... lating fundamental power (Fig. 3). The strong suppression of the harmonic components suggests the presence of an additional optical process that discriminates between the harmonic and the sum components. Third-order nonlinear processes such as four-wave mixing and two-photon absorption of an IR and ...
... lating fundamental power (Fig. 3). The strong suppression of the harmonic components suggests the presence of an additional optical process that discriminates between the harmonic and the sum components. Third-order nonlinear processes such as four-wave mixing and two-photon absorption of an IR and ...
Lenses form images by refracting light.
... from the camera lens, which means the image formed is upside down and smaller. If the penguin were between one and two focal lengths away from a convex lens, the image formed would be upside down and larger. Overhead projectors form this type of image, which is then turned right side up by a mirror ...
... from the camera lens, which means the image formed is upside down and smaller. If the penguin were between one and two focal lengths away from a convex lens, the image formed would be upside down and larger. Overhead projectors form this type of image, which is then turned right side up by a mirror ...
Atomic Spectroscopy
... release electrons from metallic surfaces and imparts to these electrons sufficient kinetic energy to cause them to travel to a ...
... release electrons from metallic surfaces and imparts to these electrons sufficient kinetic energy to cause them to travel to a ...
software development life cycle
... The work towards a silicon-based emitter is ongoing but still far from nature. Until an efficient, reliable silicon based light source is available, a photonic integrated system will need to use a conventional III-V material light emitter. ...
... The work towards a silicon-based emitter is ongoing but still far from nature. Until an efficient, reliable silicon based light source is available, a photonic integrated system will need to use a conventional III-V material light emitter. ...
Modulation Transfer Function
... Figure 1: Illustration of diffraction of light passing through an aperture, seen as wavefronts. Diffraction follows from the wave nature of light, and implies that any concentration of light, like a beam or light passing through an aperture, will spread. It places a fundamental limit on the spot siz ...
... Figure 1: Illustration of diffraction of light passing through an aperture, seen as wavefronts. Diffraction follows from the wave nature of light, and implies that any concentration of light, like a beam or light passing through an aperture, will spread. It places a fundamental limit on the spot siz ...
Test 1 w/answers
... 1. _______ 2. _______ 3. _______ 4. _______ 5. _______ 6. _______ 7. _______ ...
... 1. _______ 2. _______ 3. _______ 4. _______ 5. _______ 6. _______ 7. _______ ...
Optical Third-Harmonic Generation in Alkali Metal Vapors
... where ml = I, 1 - 1,. . , - I, and rn, = &. Selection rules terms: those for which the b levels are s states, and those AI = fl,Aml = for which the b levels are d states. TheAap,bd,cp for the dipole z-matrix elements state that factor is the 0, Am, = 0 [ 5 ] . These differ from the total dipole matr ...
... where ml = I, 1 - 1,. . , - I, and rn, = &. Selection rules terms: those for which the b levels are s states, and those AI = fl,Aml = for which the b levels are d states. TheAap,bd,cp for the dipole z-matrix elements state that factor is the 0, Am, = 0 [ 5 ] . These differ from the total dipole matr ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.