
Top-down influence in early visual processing: a Bayesian perspective
... Neurons in the primary visual cortex are known to be tuned to specific elementary local features in the visual scenes. These features include location, line orientation, stereo disparity, movement direction, color and spatial frequency [1,2]. It is also known that V1 neurons are also influenced by t ...
... Neurons in the primary visual cortex are known to be tuned to specific elementary local features in the visual scenes. These features include location, line orientation, stereo disparity, movement direction, color and spatial frequency [1,2]. It is also known that V1 neurons are also influenced by t ...
The Integrative Role of Posterior Parietal Cortex and related Clinical S
... posterior parietal cortex critical for the spatial attention is in the intraparietal region. When this area is injured, the modality-specific channel of information related to the external space can remain intact, but cannot be recombined to generate an interactive and coherent representation necess ...
... posterior parietal cortex critical for the spatial attention is in the intraparietal region. When this area is injured, the modality-specific channel of information related to the external space can remain intact, but cannot be recombined to generate an interactive and coherent representation necess ...
On-center off surround ganglion cells
... LoadEnv to load the 512x512 image - for the training 10 images were used, here is one random one, processed into on/off points. StepTrain – observe the oscillation of learning for phases – and + Complementarity of on/off: stronger "on" activation for images which are brighter in the middle than on t ...
... LoadEnv to load the 512x512 image - for the training 10 images were used, here is one random one, processed into on/off points. StepTrain – observe the oscillation of learning for phases – and + Complementarity of on/off: stronger "on" activation for images which are brighter in the middle than on t ...
VL_CHAPTER_4
... the mapping of receptive fields of neurons in the visual cortex of the cat. The three main types of visual cortical neurons are isolated and their activity in response to visual stimuli is recorded using a microelectrode. He also demonstrates visual neurons arranged in columns within the visual cort ...
... the mapping of receptive fields of neurons in the visual cortex of the cat. The three main types of visual cortical neurons are isolated and their activity in response to visual stimuli is recorded using a microelectrode. He also demonstrates visual neurons arranged in columns within the visual cort ...
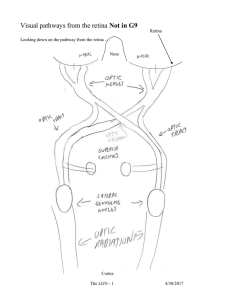
CHAPTER 15 THE CENTRAL VISUAL PATHWAYS
... specific layers of the LGN, and specific spatial domains within V1. The visual cortex is organized as an array of spatial domains, or hypercolumns, somewhat like a repeating mosaic pattern of tiles on a floor. Each hypercolumn comprises several different populations of neurons, arranged in a stereot ...
... specific layers of the LGN, and specific spatial domains within V1. The visual cortex is organized as an array of spatial domains, or hypercolumns, somewhat like a repeating mosaic pattern of tiles on a floor. Each hypercolumn comprises several different populations of neurons, arranged in a stereot ...
A coincidence detector neural network model of selective attention
... perceptual load experiment that involves high and low perceptual load visual searches executed with and without spatial cues. To preview our findings, the model succeeds in accounting for behavioral results, providing thus insights about the possible nature of the neural mechanisms that underlie the ...
... perceptual load experiment that involves high and low perceptual load visual searches executed with and without spatial cues. To preview our findings, the model succeeds in accounting for behavioral results, providing thus insights about the possible nature of the neural mechanisms that underlie the ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... FIGURE 46.8 (A) LIP responses are modulated by reward probability. Monkeys performed a dynamic foraging task in which they tracked the changing reward values of each of two saccade targets. Traces represent population responses for neurons with significant effects of reward probability. Blue traces ...
... FIGURE 46.8 (A) LIP responses are modulated by reward probability. Monkeys performed a dynamic foraging task in which they tracked the changing reward values of each of two saccade targets. Traces represent population responses for neurons with significant effects of reward probability. Blue traces ...
III
... and tract, from the retina to the pretectal region of the midbrain. The efferent pathway is in the oculomotor nerve: parasympathetic fibers from the accessory oculomotor nucleus (E-W nucleus), synapsing in the ciliary ganglion, and supplying the sphincter pupillae. Because of contralateral connectio ...
... and tract, from the retina to the pretectal region of the midbrain. The efferent pathway is in the oculomotor nerve: parasympathetic fibers from the accessory oculomotor nucleus (E-W nucleus), synapsing in the ciliary ganglion, and supplying the sphincter pupillae. Because of contralateral connectio ...
The Cerebral Association Cortex
... Evidence for: Some lesions do impair the recognition of faces selectively. Some cells are activated only by a particular face. Evidence against: Brain cell death is common, yet the memory loss observed is a general fuzziness in remembering faces, not an absolute loss of one face and not of another. ...
... Evidence for: Some lesions do impair the recognition of faces selectively. Some cells are activated only by a particular face. Evidence against: Brain cell death is common, yet the memory loss observed is a general fuzziness in remembering faces, not an absolute loss of one face and not of another. ...
Visual Dysfunction in Brain Injury
... and may present as a temporary increase in myopia • If this additional myopia is “corrected” with increased Rx in glasses/contact lenses, the patient may report more headaches and blur at near ...
... and may present as a temporary increase in myopia • If this additional myopia is “corrected” with increased Rx in glasses/contact lenses, the patient may report more headaches and blur at near ...
Symmetry Breaking in Deterministic Planning as Forward Search
... In order to allow for symmetry elimination in A∗ search, Domshlak et al. (2012) introduced a sound and complete optimal search algorithm (hereafter referred to as DKS, depicted in Figure 1). DKS extends the duplicate elimination mechanism of A∗ to consider symmetrical states as duplicates. Two state ...
... In order to allow for symmetry elimination in A∗ search, Domshlak et al. (2012) introduced a sound and complete optimal search algorithm (hereafter referred to as DKS, depicted in Figure 1). DKS extends the duplicate elimination mechanism of A∗ to consider symmetrical states as duplicates. Two state ...
19. Visual (2)
... for vision in dim lighting conditions. They are predominate in the peripheral parts but their numbers decrease towards the macula lutea ( the surrounding 1cm to fovea centralis ) , where Cons are more . Cons are responsible for colour vision and due to their arrangement and neuronal connections , th ...
... for vision in dim lighting conditions. They are predominate in the peripheral parts but their numbers decrease towards the macula lutea ( the surrounding 1cm to fovea centralis ) , where Cons are more . Cons are responsible for colour vision and due to their arrangement and neuronal connections , th ...
What do Babies See? By Dr. Lin Day, Baby Sensory. When a baby
... visually guided movements, such as the act of reaching for a toy or holding a pencil also increase. Neurons respond best to moving stimuli, notably objects that excite the movement of both eyes. If the baby has nothing to look at, then the neurons may become inactive or minimally active. ...
... visually guided movements, such as the act of reaching for a toy or holding a pencil also increase. Neurons respond best to moving stimuli, notably objects that excite the movement of both eyes. If the baby has nothing to look at, then the neurons may become inactive or minimally active. ...
Task demands determine the specificity of the search template Mary
... observers searched for a line oriented at 55 degrees among lines oriented at 50 degrees. Using a physiologically plausible model, the authors demonstrated that 55and 50-degree lines are best discriminated by a feature detector tuned to 60 degrees. They then showed that observers do indeed use a 60- ...
... observers searched for a line oriented at 55 degrees among lines oriented at 50 degrees. Using a physiologically plausible model, the authors demonstrated that 55and 50-degree lines are best discriminated by a feature detector tuned to 60 degrees. They then showed that observers do indeed use a 60- ...
Perception - Vision
... case how to explain awareness of all details in the observed image? The interactive theory of visual consciousness emphasizes interactions between lower and higher visual areas where higher areas send feedback signals down to early visual area. ...
... case how to explain awareness of all details in the observed image? The interactive theory of visual consciousness emphasizes interactions between lower and higher visual areas where higher areas send feedback signals down to early visual area. ...
P312 Ch05_PerceivingObjectsII
... RBC theory assumes that visual scene is analyzed into the different geons present in the scene. Analyzed – If a geon is present in the visual stimulus, a neuron or group of neurons in a specific part of the brain – the “detector” for that geon responds. There are parts of the brain “looking” for ge ...
... RBC theory assumes that visual scene is analyzed into the different geons present in the scene. Analyzed – If a geon is present in the visual stimulus, a neuron or group of neurons in a specific part of the brain – the “detector” for that geon responds. There are parts of the brain “looking” for ge ...
Neural correlates of decision processes
... of random noise, by shifting their gaze to one of two targets. Performance on this task is based on the representation of the motion stimulus in the middle temporal (MT) area [12]. However, the signals in MT are not sufficient to produce the saccade by which the discrimination is reported. To unders ...
... of random noise, by shifting their gaze to one of two targets. Performance on this task is based on the representation of the motion stimulus in the middle temporal (MT) area [12]. However, the signals in MT are not sufficient to produce the saccade by which the discrimination is reported. To unders ...
Overview of the Seven Perceptual Styles
... Often talks at length…just to hear him/herself talk! ...
... Often talks at length…just to hear him/herself talk! ...
[pdf]
... as gratings or oriented bars, which have been shown to elicit different response patterns than those obtained during natural vision [4,5]. It is not yet clear whether attention mechanisms revealed using synthetic stimuli generalize to a more complex, but ecologically valid context that is characteri ...
... as gratings or oriented bars, which have been shown to elicit different response patterns than those obtained during natural vision [4,5]. It is not yet clear whether attention mechanisms revealed using synthetic stimuli generalize to a more complex, but ecologically valid context that is characteri ...
The Binding Problem
... system. Stereotyped, frequently occurring conjunctions are represented by specific binding units, because this strategy is faster and less susceptible to binding errors. However, because there are not enough neurons to exhaust the whole combinatorial space, population codes provide a possibility to ...
... system. Stereotyped, frequently occurring conjunctions are represented by specific binding units, because this strategy is faster and less susceptible to binding errors. However, because there are not enough neurons to exhaust the whole combinatorial space, population codes provide a possibility to ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 46.1 Lateral viewof a human brain
... to copy the two models (clock, house). In each case, the copies exclude important elements that appeared on the left side of the model, indicating that the patient was unable to process information about the left side of the model. FIGURE 46.3 Regions in human brain activated by attention and region ...
... to copy the two models (clock, house). In each case, the copies exclude important elements that appeared on the left side of the model, indicating that the patient was unable to process information about the left side of the model. FIGURE 46.3 Regions in human brain activated by attention and region ...

















![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008855303_1-42c5934975f83fadb4141440e1a86c3f-300x300.png)


