The Visual System: From Eye to Cortex - U
... vertebrates, most mammals have two eyes on the front of their heads, rather than one on each side; this cuts down the field of view, but it insures that most of what is seen is seen through both eyes ...
... vertebrates, most mammals have two eyes on the front of their heads, rather than one on each side; this cuts down the field of view, but it insures that most of what is seen is seen through both eyes ...
lecture9
... Catching and anticipating target motion at 6 months. Distance accuracy develops more slowly, improving by 7 ...
... Catching and anticipating target motion at 6 months. Distance accuracy develops more slowly, improving by 7 ...
The Visual System: From Eye to Cortex - U
... vertebrates, most mammals have two eyes on the front of their heads, rather than one on each side; this cuts down the field of view, but it insures that most of what is seen is seen through both eyes ...
... vertebrates, most mammals have two eyes on the front of their heads, rather than one on each side; this cuts down the field of view, but it insures that most of what is seen is seen through both eyes ...
Innervation of the Eye and Orbit
... There are a lot of terms, anatomy and pathways you’ll need to know. ...
... There are a lot of terms, anatomy and pathways you’ll need to know. ...
The role of early visual cortex in visual integration: a neural model of
... the number of distractors. This suggests a parallel and ‘preattentive’ mechanism that can be implemented by the early retinotopic visual areas. On the other hand, when both target and distractors are composed of similar elementary features, the amount of time required to distinguish between them inc ...
... the number of distractors. This suggests a parallel and ‘preattentive’ mechanism that can be implemented by the early retinotopic visual areas. On the other hand, when both target and distractors are composed of similar elementary features, the amount of time required to distinguish between them inc ...
Visual Coding and the Retinal Receptors
... in space from which light strikes it. • For other visual cells, receptive fields are derived from the visual field of cells that either excite or inhibit. – Example: ganglion cells converge to form the receptive field of the next level of cells. ...
... in space from which light strikes it. • For other visual cells, receptive fields are derived from the visual field of cells that either excite or inhibit. – Example: ganglion cells converge to form the receptive field of the next level of cells. ...
Innervation of the Eye and Orbit
... There are a lot of terms, anatomy and pathways you’ll need to know. ...
... There are a lot of terms, anatomy and pathways you’ll need to know. ...
Now you see it: frontal eye field responses to invisible targets
... response to the stimulus. If this interpretation is correct, it would be remarkable. One possible caveat is that FEF neurons are also active during eye movements, and the monkeys signaled their perception with an eye movement, so that the slightly larger responses on target-perceived trials might be ...
... response to the stimulus. If this interpretation is correct, it would be remarkable. One possible caveat is that FEF neurons are also active during eye movements, and the monkeys signaled their perception with an eye movement, so that the slightly larger responses on target-perceived trials might be ...
Document
... responded when the light was turned off, and ON/OFF cells responded briefly when the light went on and again when it went off. • Kuffler (1952, 1953), recording from ganglion cells in the retina of the cat, discovered that their receptive field consists of a roughly circular center, surrounded by a ...
... responded when the light was turned off, and ON/OFF cells responded briefly when the light went on and again when it went off. • Kuffler (1952, 1953), recording from ganglion cells in the retina of the cat, discovered that their receptive field consists of a roughly circular center, surrounded by a ...
Neuro-ophthalmology
... Transient monocular visual loss or dimming May last from 2-3 minutes to 30 minutes or more Due to decrease blood flow to the eye Causes: • Carotid atheroma • Cardiac valvular disease • Atrial myxoma • Retinal migraine • Giant cell arteritis • Hyperviscousity syndromes ...
... Transient monocular visual loss or dimming May last from 2-3 minutes to 30 minutes or more Due to decrease blood flow to the eye Causes: • Carotid atheroma • Cardiac valvular disease • Atrial myxoma • Retinal migraine • Giant cell arteritis • Hyperviscousity syndromes ...
Visual7
... cortex and serves visual perception. A recurrent theme: this nucleus is also laminated (6 layers) with alternating input from ipslateral and contralateral retina. There is also a division between 2 important input systems: Magnocellular – input from M ganglion cells with wide dendritic arbours (inte ...
... cortex and serves visual perception. A recurrent theme: this nucleus is also laminated (6 layers) with alternating input from ipslateral and contralateral retina. There is also a division between 2 important input systems: Magnocellular – input from M ganglion cells with wide dendritic arbours (inte ...
Visual System - UAB School of Optometry
... -> Neurons can have very large receptive fields… -> …but specificity for visual stimuli can be VERY high -> Lesions of IT can have devastating consequences for the ability to recognize specific objects (e.g. faces: PROSOPAGNOSIA) with no corresponding loss of acuity or visual field deficits. ...
... -> Neurons can have very large receptive fields… -> …but specificity for visual stimuli can be VERY high -> Lesions of IT can have devastating consequences for the ability to recognize specific objects (e.g. faces: PROSOPAGNOSIA) with no corresponding loss of acuity or visual field deficits. ...
Slide - Reza Shadmehr
... cup in the right visual field. Information arrives in the left hemisphere. She is asked what she sees, and she answers “a cup”. She is asked to reach with the left arm towards the cup. She can reach with left arm normally. 2. Left hemisphere has very poor control over the left finger muscles: Subjec ...
... cup in the right visual field. Information arrives in the left hemisphere. She is asked what she sees, and she answers “a cup”. She is asked to reach with the left arm towards the cup. She can reach with left arm normally. 2. Left hemisphere has very poor control over the left finger muscles: Subjec ...
Lecture 13A
... processing a few select signals at the expense of others… consciousness evolved gradually over the past half billion years and is present in a range of vertebrate species” “Even before the evolution of a central brain, nervous systems took advantage of a simple computing trick: competition. Neurons ...
... processing a few select signals at the expense of others… consciousness evolved gradually over the past half billion years and is present in a range of vertebrate species” “Even before the evolution of a central brain, nervous systems took advantage of a simple computing trick: competition. Neurons ...
LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization Primary Visual Cortex
... results in low performance in spatial tasks, most often poor visuo-motor control. Some patients with optic ataxia have no difficulty identifying an object, but their visually guided behavior is so impaired that they cannot grasp it properly! ...
... results in low performance in spatial tasks, most often poor visuo-motor control. Some patients with optic ataxia have no difficulty identifying an object, but their visually guided behavior is so impaired that they cannot grasp it properly! ...
Area MST has been thought be involved in heading perception not
... perception of our own movement through space (heading). However, accurate judgments of heading often require integration of visual and nonvisual cues, including vestibular, kinesthetic, and eye movement signals. This sensory integration is complicated by the fact that signals from different modaliti ...
... perception of our own movement through space (heading). However, accurate judgments of heading often require integration of visual and nonvisual cues, including vestibular, kinesthetic, and eye movement signals. This sensory integration is complicated by the fact that signals from different modaliti ...
CVI
... Objects of varying colors, textures, and shapes may be used with students who have CVI. Parents and teachers should decide what objects are typically used with the child during everyday activities or routines. To establish familiarity, the same object(s) should be used each time. Objects should be ...
... Objects of varying colors, textures, and shapes may be used with students who have CVI. Parents and teachers should decide what objects are typically used with the child during everyday activities or routines. To establish familiarity, the same object(s) should be used each time. Objects should be ...
The Art and Science of Breakthrough Thinking
... (1) Where do the insights come from? (2) Can we articulate specific obstacles to creative problem solving? Relying on past experience can often hide the path to success, and results in failure. Mindlessness and Mindfulness : Ellen J. Langer, Psychology professor at Harvard ...
... (1) Where do the insights come from? (2) Can we articulate specific obstacles to creative problem solving? Relying on past experience can often hide the path to success, and results in failure. Mindlessness and Mindfulness : Ellen J. Langer, Psychology professor at Harvard ...
Document
... pinholes and holding them in exact coincidence, and yet at the same time he can concentrate his attention on any part of the dark field he likes, so that when the spark comes, he will get an impression about objects in that particular region only. In this experiment the attention is entirely indepen ...
... pinholes and holding them in exact coincidence, and yet at the same time he can concentrate his attention on any part of the dark field he likes, so that when the spark comes, he will get an impression about objects in that particular region only. In this experiment the attention is entirely indepen ...
perceptionlecture5
... Referring to Campbell and Robson's experiment, the lecturer mentioned that if the cells adapt to seeing an upward motion, they will notice a "downward" motion after the motion stops. Is this the same kind of adaptation that sees an opposite color when the color disappears (like in the rotating color ...
... Referring to Campbell and Robson's experiment, the lecturer mentioned that if the cells adapt to seeing an upward motion, they will notice a "downward" motion after the motion stops. Is this the same kind of adaptation that sees an opposite color when the color disappears (like in the rotating color ...
Viktor`s Notes * Visual Pathways and Cortex
... dorsal (parietal) pathway - concerned primarily with spatial orientation ("where"), motion; extension of magnocellular pathway; parietal lobe is devoted to directed attention. ventral (temporal) pathway - concerned with object recognition ("what") - shape and recognition of forms and faces; represen ...
... dorsal (parietal) pathway - concerned primarily with spatial orientation ("where"), motion; extension of magnocellular pathway; parietal lobe is devoted to directed attention. ventral (temporal) pathway - concerned with object recognition ("what") - shape and recognition of forms and faces; represen ...
Second-Order Patterns in Human Visual Cortex`` on ``Orientation
... from their background. Despite the ease with which we perceive the two zebras in a background of black and white stripes this is a challenging operation for the visual system. The edges that separate the two zebras from each other and their background divide the image in homogeneous regions that dif ...
... from their background. Despite the ease with which we perceive the two zebras in a background of black and white stripes this is a challenging operation for the visual system. The edges that separate the two zebras from each other and their background divide the image in homogeneous regions that dif ...
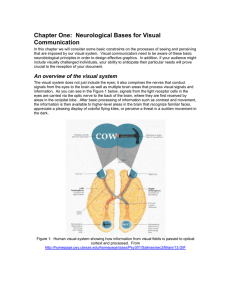
Chapter One: Neurological Bases for Visual Communication
... The optic nerve If you refer to Figure 1 again, you’ll see that the nerves connecting the eyes with the visual cortex take some interesting twists and turns. The first thing to notice is that the left side of both eyeballs are fed by the same nerve; same with the right side of both eyeballs. This st ...
... The optic nerve If you refer to Figure 1 again, you’ll see that the nerves connecting the eyes with the visual cortex take some interesting twists and turns. The first thing to notice is that the left side of both eyeballs are fed by the same nerve; same with the right side of both eyeballs. This st ...
Localization of Cognitive Operations
... connected to a more general attention system that is also involved in the processing of language stimuli (22). When normal subjects and patients had to pay close attention to auditory, or spoken, words, the ability of a visual cue to draw their visual spatial attention was retarded. Cognitive studie ...
... connected to a more general attention system that is also involved in the processing of language stimuli (22). When normal subjects and patients had to pay close attention to auditory, or spoken, words, the ability of a visual cue to draw their visual spatial attention was retarded. Cognitive studie ...
Chapter 6
... Apperceptive visual agnosia – failure to perceive objects, even though visual acuity is normal (e.g. cannot name an object by looking at it, but can if allowed to touch it) Prosopagnosia – failure to recognize particular people by the sight of their faces (i.e. can recognize by voice, hair color, et ...
... Apperceptive visual agnosia – failure to perceive objects, even though visual acuity is normal (e.g. cannot name an object by looking at it, but can if allowed to touch it) Prosopagnosia – failure to recognize particular people by the sight of their faces (i.e. can recognize by voice, hair color, et ...