Chapter 7: Animals and Infection Control
... Pets may enhance the experience of pupils in schools. However, some animals including exotic species such as reptiles, fish or birds that are often kept as pets can be a source of human infection. Infections that are passed from animals to humans are known as zoonoses. Some people such as pregnant w ...
... Pets may enhance the experience of pupils in schools. However, some animals including exotic species such as reptiles, fish or birds that are often kept as pets can be a source of human infection. Infections that are passed from animals to humans are known as zoonoses. Some people such as pregnant w ...
Vertebrate Zoology
... of the mesoderm separates to form the coelom in a process called schizocoely. In deuterostomes, the mesoderm pinches off to form the coelom in a process called enterocoely. ...
... of the mesoderm separates to form the coelom in a process called schizocoely. In deuterostomes, the mesoderm pinches off to form the coelom in a process called enterocoely. ...
Most animal phyla originated in a brief span of geological time
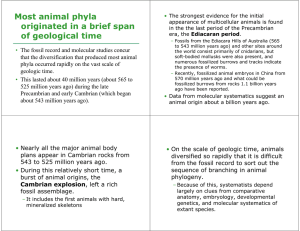
... • Data from molecular systematics suggest an animal origin about a billion years ago. ...
... • Data from molecular systematics suggest an animal origin about a billion years ago. ...
AnimalDiversity3
... • It can be frustrating that the phylogenetic trees in textbooks cannot be memorized as infallible truths. • On the other hand, the current revolution in systematics is a healthy reminder that science is both a process of inquiry and dynamic. – Emerging technologies such as molecular biology and fre ...
... • It can be frustrating that the phylogenetic trees in textbooks cannot be memorized as infallible truths. • On the other hand, the current revolution in systematics is a healthy reminder that science is both a process of inquiry and dynamic. – Emerging technologies such as molecular biology and fre ...
animal import request form
... Klebsiella pneumoniae Klebsiella oxytoca Staphylococcus aureus Pseudomonas aeruginosa Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Ectoparasites Intestinal protozoa Helminths ...
... Klebsiella pneumoniae Klebsiella oxytoca Staphylococcus aureus Pseudomonas aeruginosa Yersinia pseudotuberculosis Ectoparasites Intestinal protozoa Helminths ...
Florida FFA Association
... any stray marks. You have forty-five (45) minutes. 1. Which species was the first to be domesticated? A. Cattle B. Horses C. Sheep D. Swine 2. Feeds such as hay, silage, and pasture grass are referred to as: A. Concentrates B. Roughages C. Supplements D. None of the above 3. The process by which dig ...
... any stray marks. You have forty-five (45) minutes. 1. Which species was the first to be domesticated? A. Cattle B. Horses C. Sheep D. Swine 2. Feeds such as hay, silage, and pasture grass are referred to as: A. Concentrates B. Roughages C. Supplements D. None of the above 3. The process by which dig ...
Chapter 32: Intro to Animal Diversity Kingdom Animalia • Multi
... o 2.5 bya-540 mya o Ediacaran biota – earliest animals in fossil record From Ediacaran Period 565 to 550 mya 3 Eras in Phanerozoic Eon o Paleozoic Era Cambrian (Period) Explosion (535-525 mya) – earliest fossils of many major animal phyla Arthropods, Chordates, Echinoderms Predator-prey ...
... o 2.5 bya-540 mya o Ediacaran biota – earliest animals in fossil record From Ediacaran Period 565 to 550 mya 3 Eras in Phanerozoic Eon o Paleozoic Era Cambrian (Period) Explosion (535-525 mya) – earliest fossils of many major animal phyla Arthropods, Chordates, Echinoderms Predator-prey ...
Workshop: The Evolution of Animalia
... Over the course of this workshop, you will review the major changes that occurred during the evolution of Kingdom Animalia. By the end of the workshop, you should be able to 1. List the synapomorphies that distinguish animals from other eukaryotes 2. Understand the meaning of asymmetry, radial symme ...
... Over the course of this workshop, you will review the major changes that occurred during the evolution of Kingdom Animalia. By the end of the workshop, you should be able to 1. List the synapomorphies that distinguish animals from other eukaryotes 2. Understand the meaning of asymmetry, radial symme ...
Vertebrate Zoology
... The branch of biology that deals with animals an animal life, including the study of the structure, physiology, development, and classification of animals . • Taxonomy: The study of naming and classifying organisms. ...
... The branch of biology that deals with animals an animal life, including the study of the structure, physiology, development, and classification of animals . • Taxonomy: The study of naming and classifying organisms. ...
Chapter 27: Introduction to Animals
... Segmentation Segmentation in body structure underlies the organization of all advanced animals. ...
... Segmentation Segmentation in body structure underlies the organization of all advanced animals. ...
4/20 & 4/21 - 7th Grade Agenda
... Most don’t have a brain (except Box Jellyfish) • Most only detect light. Some have 24 eyes (Box Jellyfish) • When stung, Vinegar (not urine) is the best treatment • Irukandji Jellyfish (size of fingernail) can kill you with a single sting. ...
... Most don’t have a brain (except Box Jellyfish) • Most only detect light. Some have 24 eyes (Box Jellyfish) • When stung, Vinegar (not urine) is the best treatment • Irukandji Jellyfish (size of fingernail) can kill you with a single sting. ...
- Danville High School
... of two gametes is called asexual reproduction. A sponge, for example, can reproduce by fragmenting its body. Each fragment grows into a new sponge. Some species of sea anemone reproduce by ...
... of two gametes is called asexual reproduction. A sponge, for example, can reproduce by fragmenting its body. Each fragment grows into a new sponge. Some species of sea anemone reproduce by ...
waf fact sheets - World Animal Foundation
... other. Queens lay eggs while all other females are workers who feed the babies, take out the trash, forage for food and supplies and defend the nest. Males only have to mate with the queen. Ants have two stomachs, one to hold food for themselves, and one for others. Some ants keep other ants, or oth ...
... other. Queens lay eggs while all other females are workers who feed the babies, take out the trash, forage for food and supplies and defend the nest. Males only have to mate with the queen. Ants have two stomachs, one to hold food for themselves, and one for others. Some ants keep other ants, or oth ...
Document
... Animals respond to their environment using: Receptor cells = sound, light, external stimuli Nerve cells => nervous system ...
... Animals respond to their environment using: Receptor cells = sound, light, external stimuli Nerve cells => nervous system ...
Animals in God`s Creation - The Institute for Creation Research
... Charles Darwin proposed that various creatures share evolutionary lines of descent with modification from common ancestors. In fact, in one of his notebooks, he drew a “tree” with the words “I think” written by it to illustrate his idea. The problem is that his idea of a “phylogenetic tree” has neve ...
... Charles Darwin proposed that various creatures share evolutionary lines of descent with modification from common ancestors. In fact, in one of his notebooks, he drew a “tree” with the words “I think” written by it to illustrate his idea. The problem is that his idea of a “phylogenetic tree” has neve ...
Chap 7 part 2
... –The most parsimonious tree is the one that requires the fewest evolutionary events to have occurred in the form of shared derived characters. • The best hypotheses for phylogenetic trees –Are those that fit the most data: morphological, molecular, and fossil. ...
... –The most parsimonious tree is the one that requires the fewest evolutionary events to have occurred in the form of shared derived characters. • The best hypotheses for phylogenetic trees –Are those that fit the most data: morphological, molecular, and fossil. ...
Chapter 32: An Introduction to Animal Diversity
... 7. The blastula undergoes gastrulation, forming a gastrula with different layers of embryonic tissues 8. Many animals have at least one larval stage 9. A larva is sexually immature and morphologically distinct from the adult; it eventually undergoes metamorphosis ...
... 7. The blastula undergoes gastrulation, forming a gastrula with different layers of embryonic tissues 8. Many animals have at least one larval stage 9. A larva is sexually immature and morphologically distinct from the adult; it eventually undergoes metamorphosis ...
Unit VI Anatomy and Physiology of Plants and Animals
... by mitosis it exhibits a pattern of spiral cleavage. Cleavage is determinate, meaning that each cell’s development is determined as the cell is produced. In other words it won’t develop on its own. Deuterstomes Includes some invertebrates and all vertebrate phyla. Embryos exhibit radial cleavage. Ea ...
... by mitosis it exhibits a pattern of spiral cleavage. Cleavage is determinate, meaning that each cell’s development is determined as the cell is produced. In other words it won’t develop on its own. Deuterstomes Includes some invertebrates and all vertebrate phyla. Embryos exhibit radial cleavage. Ea ...
Systematic Zoology: Invertebrates
... describe the detailed morphology of organisms, as well as to designate taxa or clades of strictly defined membership. Luckily, there exists at least some logical connection between these realms of nomenclature. Many of the names attached to certain clades of invertebrates reflect the nature of the u ...
... describe the detailed morphology of organisms, as well as to designate taxa or clades of strictly defined membership. Luckily, there exists at least some logical connection between these realms of nomenclature. Many of the names attached to certain clades of invertebrates reflect the nature of the u ...
Bilateral Symmetry
... functions of various animal groups. Taxonomy – the science of finding, describing, and classifying animals. Entomology – the study of insects. Ichthyology – the study of fish Herpetology – the study of reptiles and amphibians. Ethology – the study of animal behavior. Malacology – the study of ...
... functions of various animal groups. Taxonomy – the science of finding, describing, and classifying animals. Entomology – the study of insects. Ichthyology – the study of fish Herpetology – the study of reptiles and amphibians. Ethology – the study of animal behavior. Malacology – the study of ...
Animal Evolution
... Unique inter-cellular junctions Unique tissues: nervous, muscular Hox gene complex (developmental genes) Diplontic life cycle Gastrulation & tissue development from germ layers ...
... Unique inter-cellular junctions Unique tissues: nervous, muscular Hox gene complex (developmental genes) Diplontic life cycle Gastrulation & tissue development from germ layers ...
Animal cognition

Animal cognition describes the mental capacities of animals and its study. It has developed out of comparative psychology, including the study of animal conditioning and learning, but has also been strongly influenced by research in ethology, behavioral ecology, and evolutionary psychology. The alternative name cognitive ethology is therefore sometimes used; much of what used to be considered under the title of animal intelligence is now thought of under this heading.Research has examined animal cognition in mammals (especially primates, cetaceans, elephants, dogs, cats, horses, livestock, raccoons and rodents), birds (including parrots, corvids and pigeons), reptiles (lizards and snakes), fish and invertebrates (including cephalopods, spiders and insects).