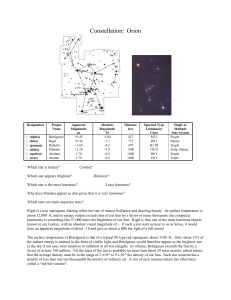
HW #5 Answers (Due 9/29)
... other words, why do high mass stars give off more energy every second than a low mass star? High mass stars have more mass, so their gravity is higher. The gravity squeezes the core more tightly causing the temperature and density to be higher in the core than in a low mass star. High temperature an ...
... other words, why do high mass stars give off more energy every second than a low mass star? High mass stars have more mass, so their gravity is higher. The gravity squeezes the core more tightly causing the temperature and density to be higher in the core than in a low mass star. High temperature an ...
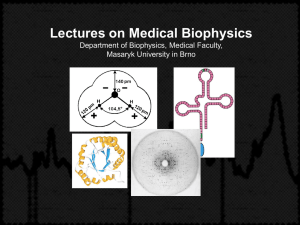
Biomolecular and cellular research devices.
... Rayleigh scattering of light. Interaction of photons with molecules can take place with no or very little change of wavelength. The intensity of the scattered light depends on molecular weight and also scattering angle which can be used for estimation of the macromolecule shape. Raman spectromet ...
... Rayleigh scattering of light. Interaction of photons with molecules can take place with no or very little change of wavelength. The intensity of the scattered light depends on molecular weight and also scattering angle which can be used for estimation of the macromolecule shape. Raman spectromet ...
ASTRONOMY TEST THE SUN
... 2._____ The sun’s mass is over a million times that of our earth 3._____ The sun is a fairly normal star 4._____ The energy of the sun is transported to its surface by convection 5._____ The “solar constant” refers to the observation that the sun’s brightness does not ever change 6._____ The solar c ...
... 2._____ The sun’s mass is over a million times that of our earth 3._____ The sun is a fairly normal star 4._____ The energy of the sun is transported to its surface by convection 5._____ The “solar constant” refers to the observation that the sun’s brightness does not ever change 6._____ The solar c ...
Seating Chart for Final Exam PHOTO ID REQUIRED! SIT IN YOUR ASSIGNED ROW!
... Slide 2: Stars convert HHe, then HeC and on up through Iron in their cores, then recycle a fraction of this “enriched” gas back into interstellar gas supply. Supernovae make the elements heavier than iron, and also recycle them back into the interstellar gas. Then new stars form from the enriched ...
... Slide 2: Stars convert HHe, then HeC and on up through Iron in their cores, then recycle a fraction of this “enriched” gas back into interstellar gas supply. Supernovae make the elements heavier than iron, and also recycle them back into the interstellar gas. Then new stars form from the enriched ...
Teacher`s Guide - Discovery Education
... across. Why would astronomers describe this distance in light-years rather than miles? 6. Tell students that the farthest objects ever seen in space are galaxies called “Hubble Deep Field.” Astronomers estimate these galaxies are billions of light-years away. In fact, they say that they offer a glim ...
... across. Why would astronomers describe this distance in light-years rather than miles? 6. Tell students that the farthest objects ever seen in space are galaxies called “Hubble Deep Field.” Astronomers estimate these galaxies are billions of light-years away. In fact, they say that they offer a glim ...
Olber`s Paradox
... sky should be bright But the sky is dark So the universe is not infinitely big So it should have collapsed ...
... sky should be bright But the sky is dark So the universe is not infinitely big So it should have collapsed ...
Questions for this book (Word format)
... Use your own words. Copying directly from the book is illegal (plagiarism) and will be penalised. 1. When Eddington suggested in 1926 that stars were powered by hydrogen fusion, why did most physicists quite reasonably reject this suggestion? Explain the phenomenon, unknown in 1926, that allows hydr ...
... Use your own words. Copying directly from the book is illegal (plagiarism) and will be penalised. 1. When Eddington suggested in 1926 that stars were powered by hydrogen fusion, why did most physicists quite reasonably reject this suggestion? Explain the phenomenon, unknown in 1926, that allows hydr ...
Chapter 1: A Modern View of the Universe
... Our galaxy itself contains a hundred billion stars. It's a hundred thousand light years side to side. It bulges in the middle, sixteen thousand light years thick, But out by us, it's just three thousand light years wide. We're thirty thousand light years from galactic central point We go 'round ever ...
... Our galaxy itself contains a hundred billion stars. It's a hundred thousand light years side to side. It bulges in the middle, sixteen thousand light years thick, But out by us, it's just three thousand light years wide. We're thirty thousand light years from galactic central point We go 'round ever ...
Star Sizes
... Pollux is about 34 light years away and can be found in the constellation Gemini. Pollux is the brightest star in this constellation. In 2006 it was discovered that Pollux has an extra solar planet orbiting it. Arcturus is the 3rd brightest star in the night sky from Northern latitudes. To the naked ...
... Pollux is about 34 light years away and can be found in the constellation Gemini. Pollux is the brightest star in this constellation. In 2006 it was discovered that Pollux has an extra solar planet orbiting it. Arcturus is the 3rd brightest star in the night sky from Northern latitudes. To the naked ...
tire
... 10. The time when our universe cooled enough that neutral atoms formed and space became transparent to electromagnetic radiation. 11. The astronomical objects used to determine that the expansion of the universe is accelerating. 12. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation. The electromagnetic radiatio ...
... 10. The time when our universe cooled enough that neutral atoms formed and space became transparent to electromagnetic radiation. 11. The astronomical objects used to determine that the expansion of the universe is accelerating. 12. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation. The electromagnetic radiatio ...
ppt
... • The main difference in galaxy properties seems to be between large and dwarf galaxies • In both spiral and elliptical galaxies, there is a difference in properties like total mass, surface brightness (both ↓ in dwarfs), and gas content of spirals (↑ in dwarfs) ...
... • The main difference in galaxy properties seems to be between large and dwarf galaxies • In both spiral and elliptical galaxies, there is a difference in properties like total mass, surface brightness (both ↓ in dwarfs), and gas content of spirals (↑ in dwarfs) ...
Physical and Chemical Tests
... 10-2 Defining Spectroscopy Spectroscopy is a technique for analyzing the structure of molecules, usually based on how they absorb electromagnetic radiation. Four types are most often used in organic chemistry: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy (NMR) Infrared spectroscopy (IR) Ultraviolet spec ...
... 10-2 Defining Spectroscopy Spectroscopy is a technique for analyzing the structure of molecules, usually based on how they absorb electromagnetic radiation. Four types are most often used in organic chemistry: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy (NMR) Infrared spectroscopy (IR) Ultraviolet spec ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram—7 Oct Outline • Thermal radiation
... emits a characteristic spectrum of light. (Called thermal or black‐body radiation.) – Intensity depends only on • Temperature • Area ...
... emits a characteristic spectrum of light. (Called thermal or black‐body radiation.) – Intensity depends only on • Temperature • Area ...
Dr. Vikram Panchal Institute Of Chemistry CH-2 Worksheet: -2
... (Bond dissociation enthalpy of iodine: 151 KJ/mole) 2. A near ultraviolet photons of 300 nm is absorbed by a gas and then re-emitted as two photon. One photon is red with wavelength 760 nm. What would be the wavelength of the second photon? 3. Electromagnetic radiation of wavelength 242 nm is just s ...
... (Bond dissociation enthalpy of iodine: 151 KJ/mole) 2. A near ultraviolet photons of 300 nm is absorbed by a gas and then re-emitted as two photon. One photon is red with wavelength 760 nm. What would be the wavelength of the second photon? 3. Electromagnetic radiation of wavelength 242 nm is just s ...
Lecture10
... not too hot and not too cold, many hydrogen atoms have their electron in the n = 2 orbit: hence strong absorption ...
... not too hot and not too cold, many hydrogen atoms have their electron in the n = 2 orbit: hence strong absorption ...
Test #3
... c. Pulsars slow down and quite producing the pulses before the supernova remnant dissipates. d. The pulsar may be tipped so that the beams do not sweep past Earth. 34. Synchrotron radiation is produced by a. objects with temperature below 10,000 K. b. high-velocity electrons moving through a magneti ...
... c. Pulsars slow down and quite producing the pulses before the supernova remnant dissipates. d. The pulsar may be tipped so that the beams do not sweep past Earth. 34. Synchrotron radiation is produced by a. objects with temperature below 10,000 K. b. high-velocity electrons moving through a magneti ...
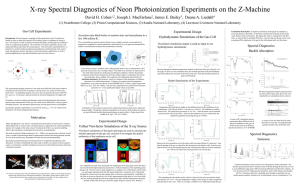
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.