T3-W10-0501student
... Point the slit end of the spectrograph towards the light source. Look through the other end for the spectra that will appear to side of the slit. Compare and contrast the different light sources. ...
... Point the slit end of the spectrograph towards the light source. Look through the other end for the spectra that will appear to side of the slit. Compare and contrast the different light sources. ...
Astro 1 & 100 Levine Homework Stars Name:____________________________
... 4. Rank these stars in order of color from reddest to bluest: Reddest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Bluest Or, all have the same color ______________ 5. Rank these stars in order of temperature from hottest to coolest: Hottest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Coolest Or, all hav ...
... 4. Rank these stars in order of color from reddest to bluest: Reddest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Bluest Or, all have the same color ______________ 5. Rank these stars in order of temperature from hottest to coolest: Hottest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Coolest Or, all hav ...
Document
... very common in the universe and raised the prospect that life began far sooner than most scientists ever imagined. ...
... very common in the universe and raised the prospect that life began far sooner than most scientists ever imagined. ...
Friday, April 26
... Small, rapidly rotating objects Can’t be white dwarfs; must be neutron stars ...
... Small, rapidly rotating objects Can’t be white dwarfs; must be neutron stars ...
From studying our solar system to searching for worlds beyond and
... with serendipity,” she admits, “but luck favors the prepared. In this field, you have to be prepared if you want to make important discoveries.” Such a mantra has proven valuable for Soderberg, who in 2008 became one of the first astronomers to see a star in the act of exploding — a major milestone ...
... with serendipity,” she admits, “but luck favors the prepared. In this field, you have to be prepared if you want to make important discoveries.” Such a mantra has proven valuable for Soderberg, who in 2008 became one of the first astronomers to see a star in the act of exploding — a major milestone ...
Round 1
... An ’HR diagram’ is a plot of which two quantities. (T (or spectral type) vs. L (or absolute magnitude)) $1200 More luminous stars tend to live this. (shorter lives) $1600 This tells you how much energy is released in the fusion of hydrogen to helium. (E = ∆mc2 where ∆m is the mass difference between ...
... An ’HR diagram’ is a plot of which two quantities. (T (or spectral type) vs. L (or absolute magnitude)) $1200 More luminous stars tend to live this. (shorter lives) $1600 This tells you how much energy is released in the fusion of hydrogen to helium. (E = ∆mc2 where ∆m is the mass difference between ...
Ch14 Review
... Describe the nature of images formed by flat mirrors. Calculate distances and focal lengths using the mirror equation for concave and convex spherical mirrors. Draw ray diagrams to find the image distance and magnification for concave and convex spherical mirrors. Distinguish between real an ...
... Describe the nature of images formed by flat mirrors. Calculate distances and focal lengths using the mirror equation for concave and convex spherical mirrors. Draw ray diagrams to find the image distance and magnification for concave and convex spherical mirrors. Distinguish between real an ...
ASTRONOMY 1303 Syllabus Fall 2015
... 5 miles off campus. During this time students will be using telescopes to explore heavenly objects like clusters, double stars and nebulas. The date of this lab is dependent upon the weather and phase of the Moon. This fall we will also have an opportunity to view a total lunar eclipse. It is happen ...
... 5 miles off campus. During this time students will be using telescopes to explore heavenly objects like clusters, double stars and nebulas. The date of this lab is dependent upon the weather and phase of the Moon. This fall we will also have an opportunity to view a total lunar eclipse. It is happen ...
Life Cycle of Stars: Chapter 21
... Life as High-Mass Star = 8x’s sun • Birthed from nebula • Core contains convective zone • Nuclear fusion of heavier elements – Requires high temperatures – More gravitational contraction ...
... Life as High-Mass Star = 8x’s sun • Birthed from nebula • Core contains convective zone • Nuclear fusion of heavier elements – Requires high temperatures – More gravitational contraction ...
notes
... Most galaxies are between 3,000 and 400,000 light years in diameter and can contain billions or trillions of stars. The Milky Way, our galaxy, is thought to be between 100,000 and 200,000 light years in diameter and contain between 100 and 400 billion stars, the most ancient of which are 13.7 billio ...
... Most galaxies are between 3,000 and 400,000 light years in diameter and can contain billions or trillions of stars. The Milky Way, our galaxy, is thought to be between 100,000 and 200,000 light years in diameter and contain between 100 and 400 billion stars, the most ancient of which are 13.7 billio ...
Galaxies 1) What are galaxies? 2) The birth of galaxies 3
... Most galaxies are between 3,000 and 400,000 light years in diameter and can contain billions or trillions of stars. The Milky Way, our galaxy, is thought to be between 100,000 and 200,000 light years in diameter and contain between 100 and 400 billion stars, the most ancient of which are 13.7 billio ...
... Most galaxies are between 3,000 and 400,000 light years in diameter and can contain billions or trillions of stars. The Milky Way, our galaxy, is thought to be between 100,000 and 200,000 light years in diameter and contain between 100 and 400 billion stars, the most ancient of which are 13.7 billio ...
Lecture - UMass Amherst
... 1. The Sun would hold 1.3 million Earths. i.e. the radius of the Sun is about 100 times that of the Earth. 2. There are ~100 billion "Suns" in a galaxy like our own Milky Way Galaxy. 3.Astronomers can see billions of galaxies. ...
... 1. The Sun would hold 1.3 million Earths. i.e. the radius of the Sun is about 100 times that of the Earth. 2. There are ~100 billion "Suns" in a galaxy like our own Milky Way Galaxy. 3.Astronomers can see billions of galaxies. ...
First Light: Physical Characterization of Early Star Formation in the
... the merging of clumps of gas and stars, accompanied by slower accretion of gas. In this picture, dwarf galaxies may represent protogalactic fragments that have not yet been accreted into larger galaxies. However, a recent VLT spectroscopic study of red giants in four dwarf spheroidal companions to t ...
... the merging of clumps of gas and stars, accompanied by slower accretion of gas. In this picture, dwarf galaxies may represent protogalactic fragments that have not yet been accreted into larger galaxies. However, a recent VLT spectroscopic study of red giants in four dwarf spheroidal companions to t ...
Unit 49-59 Review
... b. 9 times greater than the Sun c. 3 times greater than the Sun d. Cannot be determined with information given 22. If the surface temperature of a star is doubled, but its radius remains the same, its new luminosity is _____________ its old luminosity. a. 16 times smaller b. 4 times smaller c. the s ...
... b. 9 times greater than the Sun c. 3 times greater than the Sun d. Cannot be determined with information given 22. If the surface temperature of a star is doubled, but its radius remains the same, its new luminosity is _____________ its old luminosity. a. 16 times smaller b. 4 times smaller c. the s ...
Heading for the Pole - MNASSA Page
... from the brightest northern 7.2 magnitude HD 189487 to the faintest star at the southern end, about 20’ in size. This string could be part of the group, seeing that the cluster is listed as 70′ in size. In line with this, heading just 50′ SW of Nu Octantis, you will find another of my so-called aste ...
... from the brightest northern 7.2 magnitude HD 189487 to the faintest star at the southern end, about 20’ in size. This string could be part of the group, seeing that the cluster is listed as 70′ in size. In line with this, heading just 50′ SW of Nu Octantis, you will find another of my so-called aste ...
Chapter 30 Section 2 Handout
... They all start like our sun converting hydrogen into helium by high temperature and nuclear fusion ...
... They all start like our sun converting hydrogen into helium by high temperature and nuclear fusion ...
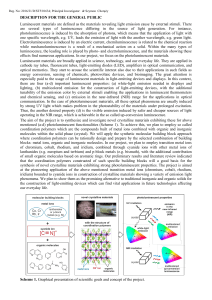
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.























