The Sky from Your Point of View
... • must be able to predict when an object will be up • light from Sun, Moon should not interfere ...
... • must be able to predict when an object will be up • light from Sun, Moon should not interfere ...
L32
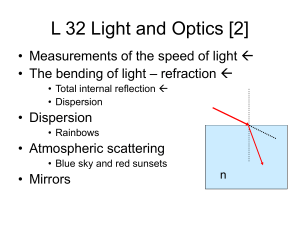
... particles • The water and ice scatter the sunlight • Scattering by water and ice (particles) is very different from scattering by molecules • The atoms are smaller than the wavelength of light, but the ice and water particles are larger • Scattering by particles does not favor any particular wavelen ...
... particles • The water and ice scatter the sunlight • Scattering by water and ice (particles) is very different from scattering by molecules • The atoms are smaller than the wavelength of light, but the ice and water particles are larger • Scattering by particles does not favor any particular wavelen ...
Lesson Plan: Supernova`s
... energy to make heat and light. When the star explodes, it will be brighter than all other stars. If a supernova explosion happened near the Earth, we could see it in the sky even during the day. Supernova explosions happen rarely. In our own galaxy, the Milky Way, the last supernova happened in the ...
... energy to make heat and light. When the star explodes, it will be brighter than all other stars. If a supernova explosion happened near the Earth, we could see it in the sky even during the day. Supernova explosions happen rarely. In our own galaxy, the Milky Way, the last supernova happened in the ...
Large Infrared Telescope in a Lunar South Polar Crater
... – Thermal emission of zodiacal clouds (~4.1K) around the Sun is too much for extrasolar planet studies unless the telescope aperture is large. – Minimum detectable flux density (S) improves proportionally to the collecting area (A) and the square root of integration time (t): ...
... – Thermal emission of zodiacal clouds (~4.1K) around the Sun is too much for extrasolar planet studies unless the telescope aperture is large. – Minimum detectable flux density (S) improves proportionally to the collecting area (A) and the square root of integration time (t): ...
Doomed, Insignificant, and Ignorant
... by adding up the light of the cluster galaxies. • Zwicky suggested that a component of "dark matter" adds extra gravity to hold the cluster together. • No suggestion that it is anything other than ordinary matter that is simply not glowing. ...
... by adding up the light of the cluster galaxies. • Zwicky suggested that a component of "dark matter" adds extra gravity to hold the cluster together. • No suggestion that it is anything other than ordinary matter that is simply not glowing. ...
CHAPTER @2- Solar Sun and Earth
... North America, a major continent on planet Earth, the third rock from the sun. That star, a typical yellow star in a solar system is our Sun, only one of billions in the Milky Way Galaxy, which is one of billions of galaxies in the Universe. Our Sun is located on a remote, trailing edge of the Milky ...
... North America, a major continent on planet Earth, the third rock from the sun. That star, a typical yellow star in a solar system is our Sun, only one of billions in the Milky Way Galaxy, which is one of billions of galaxies in the Universe. Our Sun is located on a remote, trailing edge of the Milky ...
The Formation of Stars Chapter 11 Guidepost Guidepost
... I. Making Stars from the Interstellar Medium A. Star Birth in Giant Molecular Clouds B. Heating By Contraction C. Protostars D. Evidence of Star Formation ...
... I. Making Stars from the Interstellar Medium A. Star Birth in Giant Molecular Clouds B. Heating By Contraction C. Protostars D. Evidence of Star Formation ...
Star Classification - University of Louisville
... surface temperatures are much higher, and shine white instead of red. When the Sun comes to the end of its life, it will become a White Dwarf. It will be much smaller than it is now, not quite as bright but twice as hot. Its matter (particles) will be more densely-packed together. ...
... surface temperatures are much higher, and shine white instead of red. When the Sun comes to the end of its life, it will become a White Dwarf. It will be much smaller than it is now, not quite as bright but twice as hot. Its matter (particles) will be more densely-packed together. ...
Physics 102 Lab 8: Measuring wavelengths with a
... everywhere one is positive, the other is negative by an equal amount. Although the diffraction of light waves ostensibly appears the same as the diffraction of classical waves such as water or sound waves, it is an intrinsically quantum mechanical process. Indeed, while the diffraction pattern of a ...
... everywhere one is positive, the other is negative by an equal amount. Although the diffraction of light waves ostensibly appears the same as the diffraction of classical waves such as water or sound waves, it is an intrinsically quantum mechanical process. Indeed, while the diffraction pattern of a ...
Measuring the Age of the Universe
... • Assume 5 meters is distance from Jupiter to Sun (= 5 “AU’s” Earth is at 1 AU -- the Sun is at one end, Jupiter at other. 1 AU = 1 meter is the distance from the sun to the earth. • Without thinking, search your heart and emotions for the best size circle (draw and cut out) that matches the scale s ...
... • Assume 5 meters is distance from Jupiter to Sun (= 5 “AU’s” Earth is at 1 AU -- the Sun is at one end, Jupiter at other. 1 AU = 1 meter is the distance from the sun to the earth. • Without thinking, search your heart and emotions for the best size circle (draw and cut out) that matches the scale s ...
Astronomy Teaching that Focuses on Learning Subtitled
... 8. If two stars have the same spectral class, do they necessarily have the same temperature? The Stefan-Boltzmann Law tells us about how the luminosity of a star is related to its temperature and size. It reads as follows: L Area T 4 ...
... 8. If two stars have the same spectral class, do they necessarily have the same temperature? The Stefan-Boltzmann Law tells us about how the luminosity of a star is related to its temperature and size. It reads as follows: L Area T 4 ...
5. Star Formation and the Interstellar Medium in the Milky Way
... The matter and energy between the stars, the interstellar medium (ISM), is vitally important to the evolution of galaxies, since it is in this environment that stars are formed, and to this environment that both young and aging stars return matter enriched in the heavy elements that are essential fo ...
... The matter and energy between the stars, the interstellar medium (ISM), is vitally important to the evolution of galaxies, since it is in this environment that stars are formed, and to this environment that both young and aging stars return matter enriched in the heavy elements that are essential fo ...
Matter Cycle in the Interstellar Medium (ISM)
... Survey of atomic absorption lines convinced astronomers that the space between stars was filled with interstellar gas, transparent in the visible, except for a few spectral lines arising from atomic ground states. (but this could not explain the dark clouds catalogued by Barnard.) Diameter ...
... Survey of atomic absorption lines convinced astronomers that the space between stars was filled with interstellar gas, transparent in the visible, except for a few spectral lines arising from atomic ground states. (but this could not explain the dark clouds catalogued by Barnard.) Diameter ...
Chapter 17 Measuring the Stars
... Once many stars are plotted on an H–R diagram, a pattern begins to form. These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but ...
... Once many stars are plotted on an H–R diagram, a pattern begins to form. These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but ...
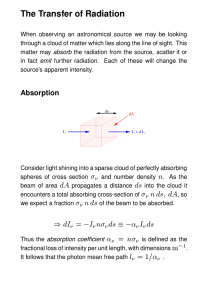
The Transfer of Radiation вб дже диз дж ¡ бгабдиз ¡ бдиз
... Kirchhoff’s law calculates the source function lnm for a body in thermal equilibrium. l m depends only upon the material and the temperature, so we can find its general form with a particular example. Consider a blackbody cavity at temperature T with a hole which is plugged by material also at tempe ...
... Kirchhoff’s law calculates the source function lnm for a body in thermal equilibrium. l m depends only upon the material and the temperature, so we can find its general form with a particular example. Consider a blackbody cavity at temperature T with a hole which is plugged by material also at tempe ...
I CAN SEE THE STARS IN YOUR EYES
... Your space craft begins to travel at the speed of light, taking you towards the sun. Traveling at this speed, the trip from Earth to the sun, a distance of 93 million miles, would take about 8 minutes, not very long for such a long trip! Yet, to get to the next closest star, Proxima Centauri, would ...
... Your space craft begins to travel at the speed of light, taking you towards the sun. Traveling at this speed, the trip from Earth to the sun, a distance of 93 million miles, would take about 8 minutes, not very long for such a long trip! Yet, to get to the next closest star, Proxima Centauri, would ...
The Sun Compared to Other Stars
... The Sun Compared to Other Stars • Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) Diagram: A graph plot indicating individual stars as points, with stellar luminosity on the vertical axis & surface temperature (spectral type) on the horizontal axis • We can use spectroscopy to determine the spectral type & luminosity of a ...
... The Sun Compared to Other Stars • Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) Diagram: A graph plot indicating individual stars as points, with stellar luminosity on the vertical axis & surface temperature (spectral type) on the horizontal axis • We can use spectroscopy to determine the spectral type & luminosity of a ...
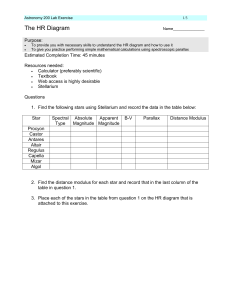
labex7
... magnitudes brighter than the Sun. Use the magnitude-brightness rule to convert this into a brightness factor or luminosity. See Chp 2.1 in the online notes to do this. You will find that Polaris is 2513 times more luminous than the Sun.) Record this information in the following table: Star ...
... magnitudes brighter than the Sun. Use the magnitude-brightness rule to convert this into a brightness factor or luminosity. See Chp 2.1 in the online notes to do this. You will find that Polaris is 2513 times more luminous than the Sun.) Record this information in the following table: Star ...
Probing the first stars through the abundance of metal poor stars
... Chemical abundances of metal poor stars Probing the first stars – Stellar archeology Looking for the fossil records of early star formation and Galaxy evolution In metal poor systems of Milky way and its satellite galaxies. Complementary to high redshift observations (IGM, GRB, SNs) Nature of Fir ...
... Chemical abundances of metal poor stars Probing the first stars – Stellar archeology Looking for the fossil records of early star formation and Galaxy evolution In metal poor systems of Milky way and its satellite galaxies. Complementary to high redshift observations (IGM, GRB, SNs) Nature of Fir ...
Stars and Stellar Evolution
... mass of sun Consume fuel slowly --> main sequence for up to 100 billion years Consume all their hydrogen --> collapse into white dwarfs Eventually ends up as a black dwarf ...
... mass of sun Consume fuel slowly --> main sequence for up to 100 billion years Consume all their hydrogen --> collapse into white dwarfs Eventually ends up as a black dwarf ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.