11. Electro
... If we confine the photons in a tube or crystal rod with a mirror at one end and a half –silvered mirror at the other end, photons with a very specific wavelength and phase will reflect off the mirrors and travel back and forth through the crystal In the process, they stimulate other electrons to ...
... If we confine the photons in a tube or crystal rod with a mirror at one end and a half –silvered mirror at the other end, photons with a very specific wavelength and phase will reflect off the mirrors and travel back and forth through the crystal In the process, they stimulate other electrons to ...
Life Cycle of Stars Powerpoint
... nothing can escape, not even light. This is a black hole. • No light, radio waves, or any form of radiation can get out of a black hole. Astronomers can not see black holes directly. • Astronomers can detect black holes indirectly – Gas pulled in rotates so fast that it heats up and gives off X-rays ...
... nothing can escape, not even light. This is a black hole. • No light, radio waves, or any form of radiation can get out of a black hole. Astronomers can not see black holes directly. • Astronomers can detect black holes indirectly – Gas pulled in rotates so fast that it heats up and gives off X-rays ...
Chemistry 330
... of radiation and the attainment of thermal equilibrium. The excited state can return to the lower state – spontaneously – stimulated by radiation already present at the transition frequency. ...
... of radiation and the attainment of thermal equilibrium. The excited state can return to the lower state – spontaneously – stimulated by radiation already present at the transition frequency. ...
Ch17_lecture
... dust content and some are more “active” than others • Galaxies tend to cluster together and these clusters appear to be separating from each other, caught up in a Universe that is expanding • The reason for all this diversity is as yet unanswered ...
... dust content and some are more “active” than others • Galaxies tend to cluster together and these clusters appear to be separating from each other, caught up in a Universe that is expanding • The reason for all this diversity is as yet unanswered ...
Stats talk - Harvard University
... The test case • Nearby galaxy (60 kpc) • Recent star-formation (a bit complex) • … but can observe very deep and set good constraints on star-formation also can obtain additional constrains from spectroscopy ...
... The test case • Nearby galaxy (60 kpc) • Recent star-formation (a bit complex) • … but can observe very deep and set good constraints on star-formation also can obtain additional constrains from spectroscopy ...
Astronomy 103: Midterm 2 Answers Correct answer in bold
... 26. If the Sun had a cooler surface, it would be ...
... 26. If the Sun had a cooler surface, it would be ...
Prisms Lab - Mr. Ahearn`s Science
... (for example, from air into the glass of the prism). This speed change causes the light to be refracted and to enter the new medium at a different angle. In Newton’s time, it was believed that white light was colorless, and that the prism itself produced the color. Newton's experiments convinced him ...
... (for example, from air into the glass of the prism). This speed change causes the light to be refracted and to enter the new medium at a different angle. In Newton’s time, it was believed that white light was colorless, and that the prism itself produced the color. Newton's experiments convinced him ...
Chapter 17 Galaxies Galaxies Early Observations
... stars, and vast clouds of interstellar gas • Each star moves in its own orbit guided by the gravity generated by other stars in the galaxy ...
... stars, and vast clouds of interstellar gas • Each star moves in its own orbit guided by the gravity generated by other stars in the galaxy ...
Big Bang
... • Before a time classified as a Planck time, all of the four fundamental forces are presumed to have been unified into one force. • All matter, energy, space and time are presumed to have exploded outward from the original ...
... • Before a time classified as a Planck time, all of the four fundamental forces are presumed to have been unified into one force. • All matter, energy, space and time are presumed to have exploded outward from the original ...
Notes - SFA Physics and Astronomy
... the universal expansion. The relationship, however, would not be nearly so good if this conclusion were not the fact. Hubble's Law stands today as one of the pillars of Modern Cosmology. The question still remains, however, as to how the universe began. Two cosmologies developed from Hubble's work: ...
... the universal expansion. The relationship, however, would not be nearly so good if this conclusion were not the fact. Hubble's Law stands today as one of the pillars of Modern Cosmology. The question still remains, however, as to how the universe began. Two cosmologies developed from Hubble's work: ...
weather/seasons
... Earth: Earth is the fifth largest planet in the Solar System and third from the Sun. It was formed around four and a half billion years ago and is the only place in the Universe where life is known to exist. Galaxy: A galaxy is a large group of stars, dust, gas and dark matter held together by gravi ...
... Earth: Earth is the fifth largest planet in the Solar System and third from the Sun. It was formed around four and a half billion years ago and is the only place in the Universe where life is known to exist. Galaxy: A galaxy is a large group of stars, dust, gas and dark matter held together by gravi ...
observingopenclusters-2-2-1
... Locate brightest star Sirius (Canis Major - underneath Orion) Note: reason for its brightness is both its intrinsic luminosity and closeness to the Sun Slide your scope or binoculars parallel to the dog’s back and then move west of that line. You will pick up a large rich field of stars – Open Clust ...
... Locate brightest star Sirius (Canis Major - underneath Orion) Note: reason for its brightness is both its intrinsic luminosity and closeness to the Sun Slide your scope or binoculars parallel to the dog’s back and then move west of that line. You will pick up a large rich field of stars – Open Clust ...
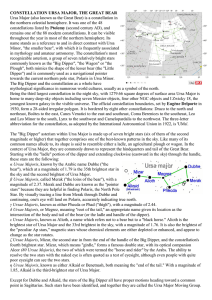
CONSTELLATION URSA MAJOR, THE GREAT
... Being the third largest constellation in the night sky, with 1279.66 square degrees of surface area Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe. The official constellation bound ...
... Being the third largest constellation in the night sky, with 1279.66 square degrees of surface area Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe. The official constellation bound ...
driving galaxy evolution since z=1
... 1. What we know about galaxy formation a) The local Universe b) Evolution since z<1 ...
... 1. What we know about galaxy formation a) The local Universe b) Evolution since z<1 ...
AMUSE-Virgo on the survival of super-massive black holes
... is the chance probability of having a LMXB Lx within the ACIS PSF, based on X-ray luminosity function of LMXBs: in the FIELD (Gilfanov 2004) in the absence of nuclear star clusters in GLOBULAR CLUSTERS (Sivakoff et al. 2007) in the presence of a nuclear cluster ...
... is the chance probability of having a LMXB Lx within the ACIS PSF, based on X-ray luminosity function of LMXBs: in the FIELD (Gilfanov 2004) in the absence of nuclear star clusters in GLOBULAR CLUSTERS (Sivakoff et al. 2007) in the presence of a nuclear cluster ...
Beginning With a Bang
... explosion 15 billion years ago Matter, gravity, and electromagnetism were created by the blast Universe expanded ...
... explosion 15 billion years ago Matter, gravity, and electromagnetism were created by the blast Universe expanded ...
Homework PHY121 (Astronomy
... A: When we say, “if the Earth did not rotate”, we mean that relative to space (i.e. to the rest of the Universe) the Earth would not rotate. In that case, the sky would stand still. We would always see the same stars on our sky. The only changes on our sky would come from the moving planets, the Moo ...
... A: When we say, “if the Earth did not rotate”, we mean that relative to space (i.e. to the rest of the Universe) the Earth would not rotate. In that case, the sky would stand still. We would always see the same stars on our sky. The only changes on our sky would come from the moving planets, the Moo ...
Beta-delayed two-neutron emission
... nuclei are also of interest for the modeling of the astrophysical rapid-neutron caption process. ...
... nuclei are also of interest for the modeling of the astrophysical rapid-neutron caption process. ...
The Realm of Physics
... • Ie. We live approximately 102 years, each year contains approximately 107 seconds, and our heart beats about 1 time per second. So, your heart beats about 109 times in your lifetime. ...
... • Ie. We live approximately 102 years, each year contains approximately 107 seconds, and our heart beats about 1 time per second. So, your heart beats about 109 times in your lifetime. ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.