Sources of Gravitational Waves Peter Shawhan
... Orbit will continue to decay (inspiral) over the next ~300 million years, until… ...
... Orbit will continue to decay (inspiral) over the next ~300 million years, until… ...
The hydrogen line spectrum explained as Raman shift
... In Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom, an electron is moving in a certain (allowed) orbit around the nucleus, which is the proton. An energy input excites the atom as follows: The electron gains energy and its orbit is grows. But for the energy only certain energy levels are allowed which correspond ...
... In Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom, an electron is moving in a certain (allowed) orbit around the nucleus, which is the proton. An energy input excites the atom as follows: The electron gains energy and its orbit is grows. But for the energy only certain energy levels are allowed which correspond ...
THE ROLE OF BLACK HOLES IN GALAXY FORMATION Tiziana Di Matteo
... BH forms an accretion disk. Gas particles interact as they move around. They heat up, lose energy and ang. mom. emit radiation. ...
... BH forms an accretion disk. Gas particles interact as they move around. They heat up, lose energy and ang. mom. emit radiation. ...
WFIRSTSurveyScience
... Stellar and Substellar Populations in Galactic Star Forming Regions Background Studies of low mass populations (encompassing stars, brown dwarfs, and even free-floating planetary mass objects) are hindered in star forming regions due to observational and astrophysical effects. These include: the lar ...
... Stellar and Substellar Populations in Galactic Star Forming Regions Background Studies of low mass populations (encompassing stars, brown dwarfs, and even free-floating planetary mass objects) are hindered in star forming regions due to observational and astrophysical effects. These include: the lar ...
Massive z~1.3 evolved galaxies revealed
... by means of a nearby brighter reference object put in the slit. Dithering of the targets along the slit in a A-B-B-A pattern with small offset about each of the two positions were used. Integrations of 2 min for each exposure were adopted for all the observations in order to be background limited in ...
... by means of a nearby brighter reference object put in the slit. Dithering of the targets along the slit in a A-B-B-A pattern with small offset about each of the two positions were used. Integrations of 2 min for each exposure were adopted for all the observations in order to be background limited in ...
Light and Optics Unit
... NOTE: focal length is negative if the mirror is diverging distance of image is negative if image is virtual height of image is negative if inverted be able to state, explain, and draw applications of concave mirrors: headlights, telescopes, satellite dishes, parabolic cooker, makeup mirrors, ...
... NOTE: focal length is negative if the mirror is diverging distance of image is negative if image is virtual height of image is negative if inverted be able to state, explain, and draw applications of concave mirrors: headlights, telescopes, satellite dishes, parabolic cooker, makeup mirrors, ...
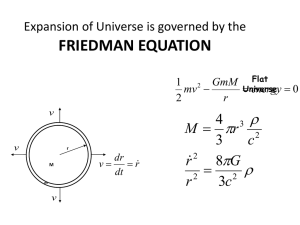
Cosmology and Astrophysics II
... universe was first derived using General Relativity but we have seen that they can be derived from Newton’s equations. ...
... universe was first derived using General Relativity but we have seen that they can be derived from Newton’s equations. ...
Useful equations - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... is the distance between star and the edge of the habitable zone which corresponds with temperature T – in whatever system of units – and r [AU ] is that distance expressed in astronomical units (AU), the distance between Earth and Sun. ...
... is the distance between star and the edge of the habitable zone which corresponds with temperature T – in whatever system of units – and r [AU ] is that distance expressed in astronomical units (AU), the distance between Earth and Sun. ...
class 1,F10
... (which is a member of the Local Group of galaxies in the Local Supercluster) • How did we come to be? • How can we know what the universe was like in the past? • Can we see the entire universe? ...
... (which is a member of the Local Group of galaxies in the Local Supercluster) • How did we come to be? • How can we know what the universe was like in the past? • Can we see the entire universe? ...
The Universe - The Ohio State University
... The cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation is known as the relic radiation from the creation of the universe. It fills the space in all directions regardless of presence of other astronomical objects. The radiation can be seen as a faint background glow. CMB is the result of transperent univers ...
... The cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation is known as the relic radiation from the creation of the universe. It fills the space in all directions regardless of presence of other astronomical objects. The radiation can be seen as a faint background glow. CMB is the result of transperent univers ...
4550-15Lecture33
... The energy released in the supernova is astounding. In its first 10 seconds, the 1987A supernova released more energy than the entire visible universe, and 100 times more energy than the Sun will release in its entire 10 billion year lifetime. The supernova begins with the collapse of the stellar co ...
... The energy released in the supernova is astounding. In its first 10 seconds, the 1987A supernova released more energy than the entire visible universe, and 100 times more energy than the Sun will release in its entire 10 billion year lifetime. The supernova begins with the collapse of the stellar co ...
Jupiter, the fifth planet from the sun and the largest planet in our
... more than a quarter that of Earth. The pull of gravity at its surface is about 17% (one-sixth) that of Earth. The Moon is in synchronous rotation about Earth which means that it rotates about its axis in about the same time it takes to orbit Earth. This causes one side of the moon to face Earth. Sma ...
... more than a quarter that of Earth. The pull of gravity at its surface is about 17% (one-sixth) that of Earth. The Moon is in synchronous rotation about Earth which means that it rotates about its axis in about the same time it takes to orbit Earth. This causes one side of the moon to face Earth. Sma ...
Hierarchical galaxy formation
... mass black holes • Intense X-ray emission from gas falling onto an extremely compact object (< 3km across) • Wobble of companion star indicates a mass of over 3 times the mass of the Sun Physics suggests such an object can only be a black hole ...
... mass black holes • Intense X-ray emission from gas falling onto an extremely compact object (< 3km across) • Wobble of companion star indicates a mass of over 3 times the mass of the Sun Physics suggests such an object can only be a black hole ...
Document
... 25 times as much light, and allow much fainter objects to be studied. Its very large aperture also means that it will be able to create much sharper images. Put together this means a huge step in observational power.” ...
... 25 times as much light, and allow much fainter objects to be studied. Its very large aperture also means that it will be able to create much sharper images. Put together this means a huge step in observational power.” ...
Finding the Andromeda Galaxy
... that you can not see it from Australia. In fact it can be seen fairly easily from anywhere on the mainland; the further north the better. Even from Hobart it can be seen, but only very low above the horizon and you have to pick your date and time very carefully. On the back of this sheet is an examp ...
... that you can not see it from Australia. In fact it can be seen fairly easily from anywhere on the mainland; the further north the better. Even from Hobart it can be seen, but only very low above the horizon and you have to pick your date and time very carefully. On the back of this sheet is an examp ...
TTh HW06 key
... justifications must be in your own words. If you are unsure about a question, make an educated guess, and justify your guess (which can include why you can rule out certain choices from the list). If you get stuck, please seek assistance from your peers, the TA, or the professor. Note: It may be hel ...
... justifications must be in your own words. If you are unsure about a question, make an educated guess, and justify your guess (which can include why you can rule out certain choices from the list). If you get stuck, please seek assistance from your peers, the TA, or the professor. Note: It may be hel ...
Wednesday, November 5 - Otterbein University
... the Sun, the more gravitational pull the more massive the Sun • Earth takes 1 year to travel 2π (93 million miles) Sun’s Mass = 300,000 that of Earth ...
... the Sun, the more gravitational pull the more massive the Sun • Earth takes 1 year to travel 2π (93 million miles) Sun’s Mass = 300,000 that of Earth ...
PowerPoint Presentation - E/PO at LHEA
... * A reflector costs the least per inch of aperture compared to refractors and catadioptrics since mirrors can be produced at less cost than lenses Disadvantages * Generally, not suited for terrestrial applications * Slight light loss due to secondary obstruction when compared with refractors * The t ...
... * A reflector costs the least per inch of aperture compared to refractors and catadioptrics since mirrors can be produced at less cost than lenses Disadvantages * Generally, not suited for terrestrial applications * Slight light loss due to secondary obstruction when compared with refractors * The t ...
Universe Standards - Harvard
... to form countless trillions of stars. Billions of galaxies, each of which is a gravitationally bound cluster of billions of stars, now form most of the visible mass in the universe.” 4. Component Concept: The universe began as being very uniform and has gotten more “lumpy” with time. i. matter was n ...
... to form countless trillions of stars. Billions of galaxies, each of which is a gravitationally bound cluster of billions of stars, now form most of the visible mass in the universe.” 4. Component Concept: The universe began as being very uniform and has gotten more “lumpy” with time. i. matter was n ...
Where Do Baby Stars Come From?
... almost like a little galaxy – with a ball at the middle where the star’s starting to form. Pamela: That’s exactly what it looks like. These systems form rather quickly. You can go from fragment to a star starting to ignite hydrogen in its core in about 100 thousand years give or take (depending on t ...
... almost like a little galaxy – with a ball at the middle where the star’s starting to form. Pamela: That’s exactly what it looks like. These systems form rather quickly. You can go from fragment to a star starting to ignite hydrogen in its core in about 100 thousand years give or take (depending on t ...
Asteroseismology of white dwarf stars provides important constraints
... convection across the DAV instability strip. R808 was discovered to be a pulsating DA white dwarf in 1976 (McGraw & Robinson 1976). It is a large amplitude, multiperiodic pulsator with an extremely nonlinear light curve (Figure 1), making it a perfect candidate for Montgomery's technique. With Teff= ...
... convection across the DAV instability strip. R808 was discovered to be a pulsating DA white dwarf in 1976 (McGraw & Robinson 1976). It is a large amplitude, multiperiodic pulsator with an extremely nonlinear light curve (Figure 1), making it a perfect candidate for Montgomery's technique. With Teff= ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.