Astronomy
... E) The core of the Sun collapses under its immense gravity 22. Which of the following does not convey approximately the same information as the rest? A) Color B) Surface temperature C) Spectral class D) Luminosity E) Actually, all of these do approximately correspond to each other 23. The hottest st ...
... E) The core of the Sun collapses under its immense gravity 22. Which of the following does not convey approximately the same information as the rest? A) Color B) Surface temperature C) Spectral class D) Luminosity E) Actually, all of these do approximately correspond to each other 23. The hottest st ...
Lecture 9/10 Stellar evolution Ulf Torkelsson 1 Main sequence stars
... the star, but in the extreme conditions that are now present in the core, the stellar material becomes opaque even to neutrinos, and these may give a push to the shock wave such that it gains momentum and continues outward. The shock wave eventually reaches the stellar surface after a few hours, at ...
... the star, but in the extreme conditions that are now present in the core, the stellar material becomes opaque even to neutrinos, and these may give a push to the shock wave such that it gains momentum and continues outward. The shock wave eventually reaches the stellar surface after a few hours, at ...
Images
... time, t. The DF specifies the density of stars at each location in this phase space, i.e. the relative number at each location, r, with each velocity, v, within a small range dx dy dz dvx dvy dvz at time t. (i) The velocity part of the DF at the center of a galaxy would be a spherically symmetric fu ...
... time, t. The DF specifies the density of stars at each location in this phase space, i.e. the relative number at each location, r, with each velocity, v, within a small range dx dy dz dvx dvy dvz at time t. (i) The velocity part of the DF at the center of a galaxy would be a spherically symmetric fu ...
Homework #8 1. Problem 10.21 2. The Origin of the Main Sequence
... For each part below you will likely need to use the results of the previous parts and ρ ∝ M/R3 from above. Remember that we are primarily interested in the scalings (or proportionality) between different physical properties of stars (M, L, ...), so for the most part you do not need to keep constant ...
... For each part below you will likely need to use the results of the previous parts and ρ ∝ M/R3 from above. Remember that we are primarily interested in the scalings (or proportionality) between different physical properties of stars (M, L, ...), so for the most part you do not need to keep constant ...
Looking back in time to the big bang theory
... Element can be used as part of teaching this topic or as a consolidation. Learners should be introduced to at least one alternative theory to the Big Bang and reasons why the evidence supports the Big Bang rather than these other theories. Common difficulties and misconceptions include learners thin ...
... Element can be used as part of teaching this topic or as a consolidation. Learners should be introduced to at least one alternative theory to the Big Bang and reasons why the evidence supports the Big Bang rather than these other theories. Common difficulties and misconceptions include learners thin ...
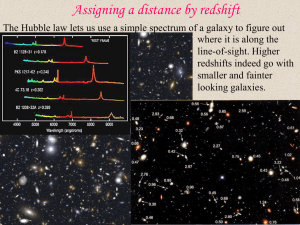
Redshift takes us from 2-D to 3-D
... would eventually end on a star. Even if it were very far away and faint, that would be made up for by having more of them in a smaller patch of sky. The sky should have the same brightness as the Sun (or at least an M star!). This resolved by the fact that the Universe started a finite amount of tim ...
... would eventually end on a star. Even if it were very far away and faint, that would be made up for by having more of them in a smaller patch of sky. The sky should have the same brightness as the Sun (or at least an M star!). This resolved by the fact that the Universe started a finite amount of tim ...
(Relative) Distances from the HST Snapshot Database
... Canonical models predict that the HeII convective region approaches the stellar surface in the ZAHB structures at T=23.000. In addition, mass loss, which is a competing process to diffusion increases with effective temperature. As a result, radiative levitation is less and less effective in the temp ...
... Canonical models predict that the HeII convective region approaches the stellar surface in the ZAHB structures at T=23.000. In addition, mass loss, which is a competing process to diffusion increases with effective temperature. As a result, radiative levitation is less and less effective in the temp ...
The Universe - the Scientia Review
... Galactic interaction occurs when one galaxy is distorted by another. It appears by a variety of processes, including satellite interaction, galactic collision, and galactic cannibalism. Satellite interaction, which is found in smaller galaxies orbiting larger counterparts, can affect both the satell ...
... Galactic interaction occurs when one galaxy is distorted by another. It appears by a variety of processes, including satellite interaction, galactic collision, and galactic cannibalism. Satellite interaction, which is found in smaller galaxies orbiting larger counterparts, can affect both the satell ...
Science 9 Unit 5: Space Name - Science 9
... Telescopes enable astronomers to see further into space and identify distant stars. The problem they still have is how far are they from the Earth? The answer to this question lies in two methods. Triangulation and Parallax are two ways to measure distances indirectly, on the ground, or in space. ...
... Telescopes enable astronomers to see further into space and identify distant stars. The problem they still have is how far are they from the Earth? The answer to this question lies in two methods. Triangulation and Parallax are two ways to measure distances indirectly, on the ground, or in space. ...
Phys 100 – Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for
... 39. The energy a white dwarf emits into space is a. replaced by fusion of hydrogen atoms into helium. b. replaced by fusion of helium atoms into carbon. * c. not replaced. 40. A Type I supernova is believed to occur when a. the core of a massive star collapses. b. carbon detonation occurs. * c. a wh ...
... 39. The energy a white dwarf emits into space is a. replaced by fusion of hydrogen atoms into helium. b. replaced by fusion of helium atoms into carbon. * c. not replaced. 40. A Type I supernova is believed to occur when a. the core of a massive star collapses. b. carbon detonation occurs. * c. a wh ...
Galaxies
... visual appearance does not allow us to place them into any of the other categories just discussed. Irregulars tend to be rich in interstellar matter and young, blue stars, but they lack any regular structure such as well-defined spiral arms or central bulges. They are conventionally divided into two ...
... visual appearance does not allow us to place them into any of the other categories just discussed. Irregulars tend to be rich in interstellar matter and young, blue stars, but they lack any regular structure such as well-defined spiral arms or central bulges. They are conventionally divided into two ...
Zealey Phys-in-Cont
... The wave description of light is most useful in describing the way in which electromagnetic disturbances propagate and interact. It can explain the phenomena of reflection, refraction, diffraction and interference. Electromagnetic waves are not usually infinite in length. They have a beginning and e ...
... The wave description of light is most useful in describing the way in which electromagnetic disturbances propagate and interact. It can explain the phenomena of reflection, refraction, diffraction and interference. Electromagnetic waves are not usually infinite in length. They have a beginning and e ...
Star in a Box
... – The temperature and density are sufficient to allow nuclear fusion to occur. – Stars are primarily composed of hydrogen, with small amounts of helium. – They are so hot that the electrons are stripped from the atomic nuclei. – This ionised gas is called a plasma. ...
... – The temperature and density are sufficient to allow nuclear fusion to occur. – Stars are primarily composed of hydrogen, with small amounts of helium. – They are so hot that the electrons are stripped from the atomic nuclei. – This ionised gas is called a plasma. ...
The_Origin_of_the_Universe
... separates light into its component colors Since stars are primarily hydrogen and helium, the lines we usually see are in the orange, yellow, green and blue areas ...
... separates light into its component colors Since stars are primarily hydrogen and helium, the lines we usually see are in the orange, yellow, green and blue areas ...
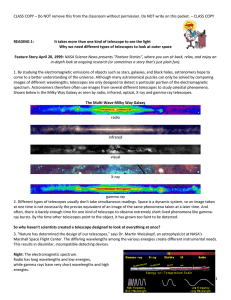
unit a activity 4d - telescopes - student readings-klh.ss
... Feature Story April 20, 1999: NASA Science News presents "Feature Stories", where you can sit back, relax, and enjoy an in-depth look at ongoing research (or sometimes a story that's just plain fun). 1. By studying the electromagnetic emissions of objects such as stars, galaxies, and black holes, as ...
... Feature Story April 20, 1999: NASA Science News presents "Feature Stories", where you can sit back, relax, and enjoy an in-depth look at ongoing research (or sometimes a story that's just plain fun). 1. By studying the electromagnetic emissions of objects such as stars, galaxies, and black holes, as ...
Document
... rough estimate of its surface temperature.(1A) To get a more accurate result, one needs to measure the distribution of the emission intensity in wavelength the spectrum, and one can compare the emission spectrum of an extrasolar planet to those of the objects heated up to known temperatures in the ...
... rough estimate of its surface temperature.(1A) To get a more accurate result, one needs to measure the distribution of the emission intensity in wavelength the spectrum, and one can compare the emission spectrum of an extrasolar planet to those of the objects heated up to known temperatures in the ...
1. Modern Optics: Introduction - University of Toronto Physics
... Prisms disperse white light into its various colors. ...
... Prisms disperse white light into its various colors. ...
Chapter 1 - Liceo Crespi
... Unlike a wave on a string or a sound wave, electromagnetic waves do not require a medium in which to propagate. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum or through substances (depending on the absorption properties of the substance). ...
... Unlike a wave on a string or a sound wave, electromagnetic waves do not require a medium in which to propagate. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum or through substances (depending on the absorption properties of the substance). ...
Greenhouse Effect - Southwest High School
... Radiation is absorbed from the sun by the earth in the form of visible light. Eventually the heat is re-emitted by the earth in the form of infrared radiation. Certain gases in the atmosphere have the property of absorbing infrared radiation. Oxygen and nitrogen the major gases in the atmosphere do ...
... Radiation is absorbed from the sun by the earth in the form of visible light. Eventually the heat is re-emitted by the earth in the form of infrared radiation. Certain gases in the atmosphere have the property of absorbing infrared radiation. Oxygen and nitrogen the major gases in the atmosphere do ...
Indoor lab #1: The Hertzsprung-Russel Diagram and Selection Effects
... a) the average distance of all the stars in your table: b) the number of and average distance of the red giant stars (stars of type 1) c) the number of and average distance of the bluer main sequence stars (stars of type 2) d) the number of and average distance of the redder main sequence stars (sta ...
... a) the average distance of all the stars in your table: b) the number of and average distance of the red giant stars (stars of type 1) c) the number of and average distance of the bluer main sequence stars (stars of type 2) d) the number of and average distance of the redder main sequence stars (sta ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.