Chapter 17
... 1. In 1960 an unusual star-like object—3C 273—was discovered that emitted intense radio waves. The object appeared to be very small, it had a small jet protruding from it, and the radio waves were emanating from the jet and the main body of the object. 2. The spectra of 3C 273 and 3C 48 (the second ...
... 1. In 1960 an unusual star-like object—3C 273—was discovered that emitted intense radio waves. The object appeared to be very small, it had a small jet protruding from it, and the radio waves were emanating from the jet and the main body of the object. 2. The spectra of 3C 273 and 3C 48 (the second ...
Introduction to Astrophysics Tutorial 4: Supernovae
... (but before actually reaching it), its C is ignited. Because of the high degeneracy (i.e. pressure weakly depends on temperature), the fusion process is a runaway one, burning the entire white dwarf, and producing a spectacular explosion. This process implies that all explosions of this type are ver ...
... (but before actually reaching it), its C is ignited. Because of the high degeneracy (i.e. pressure weakly depends on temperature), the fusion process is a runaway one, burning the entire white dwarf, and producing a spectacular explosion. This process implies that all explosions of this type are ver ...
Name:_____________________________________ ... Astro 1 (Levine) F2015 Kepler, Gravity, Light
... for D mxM is 5 and distance is 3 Mass is smaller than for A and distance is large, must be less than A (Force is proportional to 5/9 <1) ...
... for D mxM is 5 and distance is 3 Mass is smaller than for A and distance is large, must be less than A (Force is proportional to 5/9 <1) ...
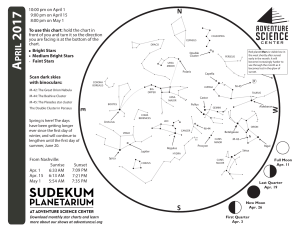
1704 chart front - Adventure Science Center
... sky, Sirius, in Canis Major the Big Dog. Follow the belt stars to the right to find orange star Aldebaran, the eye of Taurus the Bull. Still further beyond Aldebaran, you may find another orange-red dot, the red planet Mars. Mars will be much fainter. If you can’t find it, try scanning with binoculars. ...
... sky, Sirius, in Canis Major the Big Dog. Follow the belt stars to the right to find orange star Aldebaran, the eye of Taurus the Bull. Still further beyond Aldebaran, you may find another orange-red dot, the red planet Mars. Mars will be much fainter. If you can’t find it, try scanning with binoculars. ...
Stellar structure
... For a sufficiently large value of M/R (e.g. take one solar mass and one solar radius) T is large enough (> 107 K) that nuclear reactions will take place (high density also satisfied because also M/R3 very large) -- nuclear reactions establish a pressure/temperature gradient that supports the star a ...
... For a sufficiently large value of M/R (e.g. take one solar mass and one solar radius) T is large enough (> 107 K) that nuclear reactions will take place (high density also satisfied because also M/R3 very large) -- nuclear reactions establish a pressure/temperature gradient that supports the star a ...
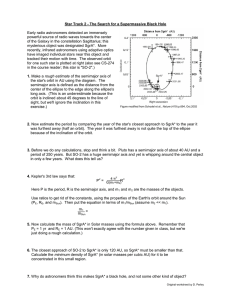
Star Track 2 - The Search for a Supermassive Black... Early radio astronomers detected an immensely
... Star Track 2 - The Search for a Supermassive Black Hole Early radio astronomers detected an immensely powerful source of radio waves towards the center of the Galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius; this mysterious object was designated SgrA*. More recently, infrared astronomers using adaptive opti ...
... Star Track 2 - The Search for a Supermassive Black Hole Early radio astronomers detected an immensely powerful source of radio waves towards the center of the Galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius; this mysterious object was designated SgrA*. More recently, infrared astronomers using adaptive opti ...
EEn.1.1.1 Explain the Earth`s motion through space, including
... more smaller ones while fusion is the fusing of two or more smaller atoms into a larger one. ...
... more smaller ones while fusion is the fusing of two or more smaller atoms into a larger one. ...
transparencies - Rencontres de Blois
... Or, is MOND a summary of how DM behaves? Ubiquitous appearance of cH 0 -- acceleration at which discrepancy appears in galaxies. -- normalization of TF -- normalization of FJ -- internal acceleration of spheroidal systems (sub-gal.) ...
... Or, is MOND a summary of how DM behaves? Ubiquitous appearance of cH 0 -- acceleration at which discrepancy appears in galaxies. -- normalization of TF -- normalization of FJ -- internal acceleration of spheroidal systems (sub-gal.) ...
Meet the Jovians` Hot Siblings DONT ERASE
... Jovians. Hundreds of these strange new planets have been found around stars the same size or smaller than our own we call the sun. The majority of these planets have been filed under the category of “Hot jupiters”. ...
... Jovians. Hundreds of these strange new planets have been found around stars the same size or smaller than our own we call the sun. The majority of these planets have been filed under the category of “Hot jupiters”. ...
PH607lec11
... Another question is why, if all galaxies are mergers of smaller ones, many of them don't look it. Beautiful spiral galaxies, for instance, appear neat and symmetrical, not as though they were formed from violent collisions of multiple smaller galaxies. Merging galaxies look like train wrecks. Maybe ...
... Another question is why, if all galaxies are mergers of smaller ones, many of them don't look it. Beautiful spiral galaxies, for instance, appear neat and symmetrical, not as though they were formed from violent collisions of multiple smaller galaxies. Merging galaxies look like train wrecks. Maybe ...
Stellar Evolution Diagram Answer Key:
... This is a cloud of dust and gas that can last for millions of years. A nebula consists commonly of about 70% Hydrogen, 28% Helium, and about 2% of other heavier elements. Nebulas rarely start to clump together on their own- often they require an outside force to nudge them into coalescing. Such a fo ...
... This is a cloud of dust and gas that can last for millions of years. A nebula consists commonly of about 70% Hydrogen, 28% Helium, and about 2% of other heavier elements. Nebulas rarely start to clump together on their own- often they require an outside force to nudge them into coalescing. Such a fo ...
PH607 – Galaxies
... Another question is why, if all galaxies are mergers of smaller ones, many of them don't look it. Beautiful spiral galaxies, for instance, appear neat and symmetrical, not as though they were formed from violent collisions of multiple smaller galaxies. Merging galaxies look like train wrecks. Maybe ...
... Another question is why, if all galaxies are mergers of smaller ones, many of them don't look it. Beautiful spiral galaxies, for instance, appear neat and symmetrical, not as though they were formed from violent collisions of multiple smaller galaxies. Merging galaxies look like train wrecks. Maybe ...
The Birth, Life, and Death of Stars
... Most of its life, the Sun will burn H into He in its core (Main Sequence Star) Once H is exhausted, core contracts and heats (Gravitational → Thermal) Core must heat up to 100 MK to burn He; H shell to only 10 MK As H burns, envelope expands, cools, and leaves the main sequence ... Eventually core t ...
... Most of its life, the Sun will burn H into He in its core (Main Sequence Star) Once H is exhausted, core contracts and heats (Gravitational → Thermal) Core must heat up to 100 MK to burn He; H shell to only 10 MK As H burns, envelope expands, cools, and leaves the main sequence ... Eventually core t ...
Astronomy II (ASTR-1020) — Homework 1
... 8. A force of 100 newtons is applied to a body which causes it to accelerate at 20 m/s2 . What must be the mass of the body? a) 100 gm ...
... 8. A force of 100 newtons is applied to a body which causes it to accelerate at 20 m/s2 . What must be the mass of the body? a) 100 gm ...
Images
... time, t. The DF specifies the density of stars at each location in this phase space, i.e. the relative number at each location, r, with each velocity, v, within a small range dx dy dz dvx dvy dvz at time t. (i) The velocity part of the DF at the center of a galaxy would be a spherically symmetric fu ...
... time, t. The DF specifies the density of stars at each location in this phase space, i.e. the relative number at each location, r, with each velocity, v, within a small range dx dy dz dvx dvy dvz at time t. (i) The velocity part of the DF at the center of a galaxy would be a spherically symmetric fu ...
Answer all questions in Section A and two and only two questions in
... one, magnetic braking is thought to be the dominant spindown mechanism. Can magnetic braking of this pulsar be powering the surrounding pulsar wind nebula, which is observed to have an X-ray luminosity of ...
... one, magnetic braking is thought to be the dominant spindown mechanism. Can magnetic braking of this pulsar be powering the surrounding pulsar wind nebula, which is observed to have an X-ray luminosity of ...
Day 1: How to Describe the Sky The Motions of the Stars
... • Yes, due to the rotation of the Earth. Many stars rise and set at different times of night. Some are circumpolar, some we don’t see at all. • ... your latitude on Earth? • Yes. Your latitude affects your horizon and zenith. • ... your longitude on Earth? ...
... • Yes, due to the rotation of the Earth. Many stars rise and set at different times of night. Some are circumpolar, some we don’t see at all. • ... your latitude on Earth? • Yes. Your latitude affects your horizon and zenith. • ... your longitude on Earth? ...
April 2015 - Hermanus Astronomy Centre
... Mars years - producing global snapshots of each, as well as their ratio. The maps reveal seasonal changes and microclimates, even though modern Mars is essentially a desert. The team was especially interested in regions near the north and south poles because the polar ice caps are the planet’s large ...
... Mars years - producing global snapshots of each, as well as their ratio. The maps reveal seasonal changes and microclimates, even though modern Mars is essentially a desert. The team was especially interested in regions near the north and south poles because the polar ice caps are the planet’s large ...
Star formation and Evolution
... hydrogen into helium. Because stars shine by those nuclear reactions, they have a finite life span. The theory of stellar evolution describes how stars form and change during that life span. Stars are formed when part of a interstellar gas cloud contracts under its own gravitational force; as it col ...
... hydrogen into helium. Because stars shine by those nuclear reactions, they have a finite life span. The theory of stellar evolution describes how stars form and change during that life span. Stars are formed when part of a interstellar gas cloud contracts under its own gravitational force; as it col ...
T - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... • Event horizon is 3 km or 1/200,000 of Sun’s radius • Luminosity can be 30,000 time the Sun’s luminosity ...
... • Event horizon is 3 km or 1/200,000 of Sun’s radius • Luminosity can be 30,000 time the Sun’s luminosity ...
Chapter 29: Life in the Universe
... Life on Earth is based on organic molecules: carbon-based molecules with hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, or a few other elements. Organic molecules have been found in clouds of interstellar gas and dust! Starting from these organic molecules, chemists formed amino acids in a simple apparatus that mimics ...
... Life on Earth is based on organic molecules: carbon-based molecules with hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, or a few other elements. Organic molecules have been found in clouds of interstellar gas and dust! Starting from these organic molecules, chemists formed amino acids in a simple apparatus that mimics ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.