Magnetic fields in O-, B- and A-type stars on the main sequence
... and when emerging at the surface would produce hot bright spots at the surface of massive stars. So far there are no direct observations of these fields because they lead to small-scaled structure of weak strengths. However, there is increasing evidence of indirect observations of such fields in hot s ...
... and when emerging at the surface would produce hot bright spots at the surface of massive stars. So far there are no direct observations of these fields because they lead to small-scaled structure of weak strengths. However, there is increasing evidence of indirect observations of such fields in hot s ...
Flow Cytometry and Sorting, Part 1
... The fluorescence emitted by each fluorochrome is usually detected in a unique fluorescence channel The specificity of detection is controlled by the wavelength selectivity of optical filters and mirrors ...
... The fluorescence emitted by each fluorochrome is usually detected in a unique fluorescence channel The specificity of detection is controlled by the wavelength selectivity of optical filters and mirrors ...
Research paper
... at all orientations from the dynamical ejection center shows similar behavior. The typical radial-velocity gradients range from less than 200 to over 2,000 km s−1 per parsec. In some, such as the 4000 -long streamer shown in lower-right of Figure 5, the line-brightness peaks near the high-velocity e ...
... at all orientations from the dynamical ejection center shows similar behavior. The typical radial-velocity gradients range from less than 200 to over 2,000 km s−1 per parsec. In some, such as the 4000 -long streamer shown in lower-right of Figure 5, the line-brightness peaks near the high-velocity e ...
Notes - Bill Wolf
... and luminosity to denote how much light the star is actually giving off. These two words have analogous magnitude scales. The magnitude scale that measures brightness is the one that Hipparchus thought up. We call it Apparent Magnitude, often denoted m. The scale corresponding to luminosity is calle ...
... and luminosity to denote how much light the star is actually giving off. These two words have analogous magnitude scales. The magnitude scale that measures brightness is the one that Hipparchus thought up. We call it Apparent Magnitude, often denoted m. The scale corresponding to luminosity is calle ...
CHARACTERIZING DUST ATTENUATION IN LOCAL STAR FORMING GALAXIES: UV AND... REDDENING ABSTRACT The dust attenuation for a sample of ∼10000 local (z ....
... The presence of dust in a galaxy causes its spectral energy distribution (SED) to experience reddening, a consequence of the highest attenuation occurring in the ultraviolet (UV) and decreasing towards longer wavelengths out to the infrared (IR) (see review by Draine et al. 2003). The nature of this ...
... The presence of dust in a galaxy causes its spectral energy distribution (SED) to experience reddening, a consequence of the highest attenuation occurring in the ultraviolet (UV) and decreasing towards longer wavelengths out to the infrared (IR) (see review by Draine et al. 2003). The nature of this ...
Astronomy Astrophysics First detection of the field star overdensity in the Perseus... &
... the two sets of physical parameters. This cleanest sample contains 8328 stars and is named CS-MB or CS-EC depending on whether their physical parameters were computed using the MB or EC method (see Fig. 1). This sample contains stars with more accurate SPP data, but has fewer statistics owing to the ...
... the two sets of physical parameters. This cleanest sample contains 8328 stars and is named CS-MB or CS-EC depending on whether their physical parameters were computed using the MB or EC method (see Fig. 1). This sample contains stars with more accurate SPP data, but has fewer statistics owing to the ...
Laser Refraction and Diffraction
... 2. Illuminate the glass plate with a laser beam at a predetermined incident angle. 3. Mark the following spots: ☉ The “spot of output” at the output of the laser. ☉ The “spot of incidence” on the glass plate. ☉ The “spot of refraction” on the other side of the glass plate. ☉ Any spot of the reflecte ...
... 2. Illuminate the glass plate with a laser beam at a predetermined incident angle. 3. Mark the following spots: ☉ The “spot of output” at the output of the laser. ☉ The “spot of incidence” on the glass plate. ☉ The “spot of refraction” on the other side of the glass plate. ☉ Any spot of the reflecte ...
Unit 1: The Foundations of Astronomy
... 1. Science builds upon itself over time. As new evidence arises and we acquire new understandings, old theories are revised or replaced by new ones. 2. Early astronomers tracked the motion of objects in the sky and used that information to describe the universe. 3. Mathematical tools and the use of ...
... 1. Science builds upon itself over time. As new evidence arises and we acquire new understandings, old theories are revised or replaced by new ones. 2. Early astronomers tracked the motion of objects in the sky and used that information to describe the universe. 3. Mathematical tools and the use of ...
paper - Lunar and Planetary Institute
... megapascal pressures to planetary magnetospheres, encompassing planetary mantles, surfaces, atmospheres, and ionospheres in between. The interplanetary environment includes magnetic and electrical fields, plasma, and dust. In order to understand planetary processes over these vast ranges, the proper ...
... megapascal pressures to planetary magnetospheres, encompassing planetary mantles, surfaces, atmospheres, and ionospheres in between. The interplanetary environment includes magnetic and electrical fields, plasma, and dust. In order to understand planetary processes over these vast ranges, the proper ...
Review !x
... Double Slit Intensity on a Distant Screen (8) ! We can see that the intensity varies from 0 to 4Imax ! Covering one slit, we get a constant intensity of Imax ! If we illuminate both slits with light that has random phases, we would observe a constant intensity of 2Imax ! Only when we illuminate bot ...
... Double Slit Intensity on a Distant Screen (8) ! We can see that the intensity varies from 0 to 4Imax ! Covering one slit, we get a constant intensity of Imax ! If we illuminate both slits with light that has random phases, we would observe a constant intensity of 2Imax ! Only when we illuminate bot ...
Lecture 5. Interstellar Dust and Extinction 1. Introduction 2. Extinction
... • The advent of photoelectric photometry (1940-1954) led to the discovery and quantification of interstellar reddening by precise comparison of stars of the same type • Interstellar reddening is ascribed to the continuous (with wavelength) absorption of small macroscopic particles, quantified by the ...
... • The advent of photoelectric photometry (1940-1954) led to the discovery and quantification of interstellar reddening by precise comparison of stars of the same type • Interstellar reddening is ascribed to the continuous (with wavelength) absorption of small macroscopic particles, quantified by the ...
Long-term photometry of the eclipsing dwarf nova V893 Scorpii
... ties – is spectroscopically similar to many other CVs of the same kind. Thorstensen (2003) measured trigonometrically a distance of 153+68 −35 pc. Mukai et al. (2009) observed V893 Sco in x-rays with the Suzaku satellite and found partial eclipses. Warner et al. (2003) report on the detection of qua ...
... ties – is spectroscopically similar to many other CVs of the same kind. Thorstensen (2003) measured trigonometrically a distance of 153+68 −35 pc. Mukai et al. (2009) observed V893 Sco in x-rays with the Suzaku satellite and found partial eclipses. Warner et al. (2003) report on the detection of qua ...
Experimental characterization of the optical fiber sensors Andrei Stancalie, Gelu Ilie
... The experimental spectra have been analyzed with respect to the changes in the full width at half maximum (FWHM), in the distance from the nearest lateral lobe, the signal to noise (S/N) ratio, and the amplitude of main lobe. The optical fiber sensors spectra have been characterized on-line, in tran ...
... The experimental spectra have been analyzed with respect to the changes in the full width at half maximum (FWHM), in the distance from the nearest lateral lobe, the signal to noise (S/N) ratio, and the amplitude of main lobe. The optical fiber sensors spectra have been characterized on-line, in tran ...
In the diagram below, the optical train of a set of binoculars is found
... axis that is centered between the mirrors at a small, arbitrary angle with respect to the axis so that it strikes one of the mirrors to the right or the left. (i) Carefully draw on the diagram the path subsequently followed by your chosen ray in the region between the mirrors, including additional r ...
... axis that is centered between the mirrors at a small, arbitrary angle with respect to the axis so that it strikes one of the mirrors to the right or the left. (i) Carefully draw on the diagram the path subsequently followed by your chosen ray in the region between the mirrors, including additional r ...
The formation of spiral galaxies - Case Western Reserve University
... diet-Salpeter IMF, understanding that this may not represent the exact M∗ /L for all galaxies in the THINGS survey. A Salpeter-like IMF is favoured in the spiral bulge models of Dutton et al. (2013) which serves as additional motivation for this choice of IMF. Furthermore, the choice of the diet-Sal ...
... diet-Salpeter IMF, understanding that this may not represent the exact M∗ /L for all galaxies in the THINGS survey. A Salpeter-like IMF is favoured in the spiral bulge models of Dutton et al. (2013) which serves as additional motivation for this choice of IMF. Furthermore, the choice of the diet-Sal ...
A Little Coherence in Photosynthetic Light Harvesting
... and Parson 2003, Scholes et al. 2011). These molecules, reaction center of photosystem II, something that is avoided known as chromophores, absorb certain wavelength bands by basically switching off the light-harvesting antenna in a of the incident light through their electronic wave function’s pro ...
... and Parson 2003, Scholes et al. 2011). These molecules, reaction center of photosystem II, something that is avoided known as chromophores, absorb certain wavelength bands by basically switching off the light-harvesting antenna in a of the incident light through their electronic wave function’s pro ...
The ultracompact nature of the black hole candidate X
... rate) and evidence against strong Hα emission from HST narrow-band photometry, they suggested the system might be a UCXB. They further inferred an orbital period of ∼ 25 min, from a correlation between quiescent X-ray luminosity and time-averaged mass transfer rate from the companion, and using calc ...
... rate) and evidence against strong Hα emission from HST narrow-band photometry, they suggested the system might be a UCXB. They further inferred an orbital period of ∼ 25 min, from a correlation between quiescent X-ray luminosity and time-averaged mass transfer rate from the companion, and using calc ...
Pre-main sequence evolution
... 1. Pre-main sequence evolution is driven by changes in temperature and density, which lead to changes in the dominant opacity contribution. => Stars alternate between convective and radiative phases. 2. The exact path of a PMS star in the Hertzsprung-Russel-Diagram, i.e. its luminosity-temperature e ...
... 1. Pre-main sequence evolution is driven by changes in temperature and density, which lead to changes in the dominant opacity contribution. => Stars alternate between convective and radiative phases. 2. The exact path of a PMS star in the Hertzsprung-Russel-Diagram, i.e. its luminosity-temperature e ...
Test Ch. 27 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes
... 25. In the last stage of stellar evolution following a supernova, stars too massive to form neutron stars may form a A. black dwarf. B. red supergiant. C. white dwarf. D. black hole. 26. In which stage of stellar evolution does combined hydrogen fusion and helium fusion cause a star’s outer shell to ...
... 25. In the last stage of stellar evolution following a supernova, stars too massive to form neutron stars may form a A. black dwarf. B. red supergiant. C. white dwarf. D. black hole. 26. In which stage of stellar evolution does combined hydrogen fusion and helium fusion cause a star’s outer shell to ...
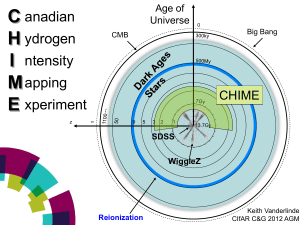
chime
... • every point in the northern celestial hemisphere • across an octave in frequency (400-800MHz) • for between 5 minutes and hours (depending on Decl.) • with s timing resolution & accuracy ...
... • every point in the northern celestial hemisphere • across an octave in frequency (400-800MHz) • for between 5 minutes and hours (depending on Decl.) • with s timing resolution & accuracy ...
Riccioli Measures the Stars: Observations of the
... the fixed stars must be 1520 millions of times as great as the earth, or nine millions of times as great as they supposed the sun to be. Now, one of the strong arguments against Ptolemy (and the one which has generally found its way into modern works) was the enormous motion which he supposed the s ...
... the fixed stars must be 1520 millions of times as great as the earth, or nine millions of times as great as they supposed the sun to be. Now, one of the strong arguments against Ptolemy (and the one which has generally found its way into modern works) was the enormous motion which he supposed the s ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.