LIM Transient Explorer
... depends on position in orbit Longer arrow – lower angle Unit coloured orange may be out of action due to stray light when too low ...
... depends on position in orbit Longer arrow – lower angle Unit coloured orange may be out of action due to stray light when too low ...
Early-type dwarf galaxies in clusters - ARI
... boxiness or a bar, or a central irregularity (Binggeli & Cameron,Côté et al., 2007), their nuclei (e.g. Lotz et al., 2004), and 1991). Later, weak spiral structure was identified in a dE for their globular cluster systems (e.g. Peng et al., 2006, 2008). the first time (Jerjen et al., 2000), with s ...
... boxiness or a bar, or a central irregularity (Binggeli & Cameron,Côté et al., 2007), their nuclei (e.g. Lotz et al., 2004), and 1991). Later, weak spiral structure was identified in a dE for their globular cluster systems (e.g. Peng et al., 2006, 2008). the first time (Jerjen et al., 2000), with s ...
Magnetized Gravitational Collapse & Star Formation
... which is Salpeter IMF at intermedia te masses (peak at 2 a 4 /3G 3 / 2 B0 0.5 M sun ; steeper at high stellar masses because of radiation pressure on dust grains). NB: SFE = 1/3 when F = 1 (cf. Lada & Lada 2003). ...
... which is Salpeter IMF at intermedia te masses (peak at 2 a 4 /3G 3 / 2 B0 0.5 M sun ; steeper at high stellar masses because of radiation pressure on dust grains). NB: SFE = 1/3 when F = 1 (cf. Lada & Lada 2003). ...
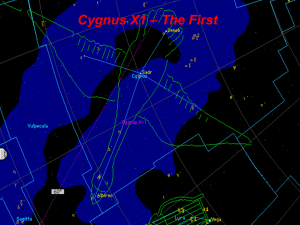
Cygnus X-1
... hundredth of a second bursts. It is also been proven that Cygnus X-1 is smaller than the Earth. Strangely enough, Cygnus X-1 has a companion star called HDE 226868. HDE 226868 is a supergiant with a temperature around 31,000 K. After extremely close observations of HDE 226868, it appears that its sp ...
... hundredth of a second bursts. It is also been proven that Cygnus X-1 is smaller than the Earth. Strangely enough, Cygnus X-1 has a companion star called HDE 226868. HDE 226868 is a supergiant with a temperature around 31,000 K. After extremely close observations of HDE 226868, it appears that its sp ...
... 1. Define the terms “black body” and “black body radiation”. 2. What are the postulates of Planck’s quantum theory? 3. State the hypothesis of Planck theory. 4. What is meant by photon? Give any two properties. 5. Define Stefen- Boltzmen law. 6. Define wien’s displacement law. Give its limitations. ...
June - Magic Valley Astronomical Society
... 6/3 Saturn (angular size 18.4", magnitude 0.0) is at opposition at 7:00; Mercury is 0.73° north of the Moon, the Moon is at perigee, subtending 33' 5" from a distance of 361,140 kilometers (224,402 miles), at 10:56 6/4 The Moon is 8.8° south of the bright open cluster M45 (the Pleiades) at 3:00; Jup ...
... 6/3 Saturn (angular size 18.4", magnitude 0.0) is at opposition at 7:00; Mercury is 0.73° north of the Moon, the Moon is at perigee, subtending 33' 5" from a distance of 361,140 kilometers (224,402 miles), at 10:56 6/4 The Moon is 8.8° south of the bright open cluster M45 (the Pleiades) at 3:00; Jup ...
$doc.title
... Cygnus X-1 at 15 GHz: a central source with a small but clear elongation. Is this morphological analogy enough to interpret the structure in the EVN map as a one-sided jet? In the case of Cygnus X-1 the interpretation of the small jet-like elongation has proved to be correct: a later observation of ...
... Cygnus X-1 at 15 GHz: a central source with a small but clear elongation. Is this morphological analogy enough to interpret the structure in the EVN map as a one-sided jet? In the case of Cygnus X-1 the interpretation of the small jet-like elongation has proved to be correct: a later observation of ...
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Carbon dioxide
... bending mode when CO2 is mixed with methanol, ethanol, propanol, butanol, diethylether and acetone. In the stretching mode region, the shape of the band is not altered too much as can be seen on Fig. 3 (middle panel), even when the substructure appears in the 15.2 µm band. The temperature at which t ...
... bending mode when CO2 is mixed with methanol, ethanol, propanol, butanol, diethylether and acetone. In the stretching mode region, the shape of the band is not altered too much as can be seen on Fig. 3 (middle panel), even when the substructure appears in the 15.2 µm band. The temperature at which t ...
A classification approach to solving the cosmic reionization puzzle
... peaks in flux that are labeled in the image, are higher for lower fesc values, and an effect on the slope in the beginning of the spectra is also visible. The astronomical explanation of this is a process in which the ionizing radiation produced within galaxies is affected by the surrounding gas. As t ...
... peaks in flux that are labeled in the image, are higher for lower fesc values, and an effect on the slope in the beginning of the spectra is also visible. The astronomical explanation of this is a process in which the ionizing radiation produced within galaxies is affected by the surrounding gas. As t ...
The myopia in the Hubble space telescope
... Foucault and Hartmann tests, the configuration with a hyberboloidal surface would produce spherical aberration, making high precision testing difficult. So the main problem in testing a hyperboloid surface is the spherical aberration. It has been common for about thirty years ago, to construct an op ...
... Foucault and Hartmann tests, the configuration with a hyberboloidal surface would produce spherical aberration, making high precision testing difficult. So the main problem in testing a hyperboloid surface is the spherical aberration. It has been common for about thirty years ago, to construct an op ...
1 - Piscataway High School
... forcing them to expand dramatically (■ Figure 14-2). Stars like the sun become giant stars of 10 to 100 solar radii, and the most massive stars become supergiants some 1000 times larger than the sun. This explains the large diameters and low densities of the giant and supergiant stars. In Chapter 12 ...
... forcing them to expand dramatically (■ Figure 14-2). Stars like the sun become giant stars of 10 to 100 solar radii, and the most massive stars become supergiants some 1000 times larger than the sun. This explains the large diameters and low densities of the giant and supergiant stars. In Chapter 12 ...
Can We Successfully Apply A Solar Thin-Flux
... No significant change in spot pattern for < 10 . At 10 an almost immediate transition to polar spots occurs. For higher than 25 : bimodal spot patterns: polar spots and medium-latitude spots. ...
... No significant change in spot pattern for < 10 . At 10 an almost immediate transition to polar spots occurs. For higher than 25 : bimodal spot patterns: polar spots and medium-latitude spots. ...
optical properties of dielectric mirrors, produced by large area glass
... represents color from green to red, while b* represents colors from yellow to blue. For a*=b*=0 means that all colors are present with the same level, so the overall color is white, or neutral. ...
... represents color from green to red, while b* represents colors from yellow to blue. For a*=b*=0 means that all colors are present with the same level, so the overall color is white, or neutral. ...
Do We Know of Any Maunder Minimum Stars?
... stars, S = 0.1451. Zhang et al. (1994) applied this value to an analysis of the effects of stellar activity on brightness and concluded that the Sun was 0.2 − 0.6% dimmer during the Maunder Minimum. However, most Maunder minimum candidates were identified before the advent of accurate parallaxes fro ...
... stars, S = 0.1451. Zhang et al. (1994) applied this value to an analysis of the effects of stellar activity on brightness and concluded that the Sun was 0.2 − 0.6% dimmer during the Maunder Minimum. However, most Maunder minimum candidates were identified before the advent of accurate parallaxes fro ...
Spectrophotometric follow-up of GU Mus, the (X
... The lightcurves in B, V and R bands are shown in Fig. 1a,b,c. Light fluctuations are seen in each lightcurve, with amplitudes up to 0.2 mag. These light variations are erratic in the early decline, and later they appear as small light oscillations with typical timescales of about 10 days (see also F ...
... The lightcurves in B, V and R bands are shown in Fig. 1a,b,c. Light fluctuations are seen in each lightcurve, with amplitudes up to 0.2 mag. These light variations are erratic in the early decline, and later they appear as small light oscillations with typical timescales of about 10 days (see also F ...
The Life of the Sun
... Astronomy, that our Sun is actually in the process of a cooling period that has to do with how the Magnetic Field is evolving over time. There’s lots of long term and short term changes in the Sun’s behavior. We think that there is currently a short term slight cooling phase going on but that’s supe ...
... Astronomy, that our Sun is actually in the process of a cooling period that has to do with how the Magnetic Field is evolving over time. There’s lots of long term and short term changes in the Sun’s behavior. We think that there is currently a short term slight cooling phase going on but that’s supe ...
Relativity, Space-Time And Cosmology
... the concept of two events occurring at the same time in different places is not absolute, but depends on the state of motion of the observer. Not content with this momentous achievements, Einstein argued that the Special Theory of Relativity itself was inapplicable under certain conditions, for exam ...
... the concept of two events occurring at the same time in different places is not absolute, but depends on the state of motion of the observer. Not content with this momentous achievements, Einstein argued that the Special Theory of Relativity itself was inapplicable under certain conditions, for exam ...
Observation of two-photon emission from semiconductors
... GaInP/AlGaInP two-photon emission, limited only by the detector’s temporal resolution. Two-photon transitions are much weaker than the related firstorder processes, so observations of multiphoton spontaneous decays have so far been restricted to a few atomic transition cases. In these instances the ...
... GaInP/AlGaInP two-photon emission, limited only by the detector’s temporal resolution. Two-photon transitions are much weaker than the related firstorder processes, so observations of multiphoton spontaneous decays have so far been restricted to a few atomic transition cases. In these instances the ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.