the red supergiant content of m31
... effective temperatures that increases with higher luminosities, with one sequence consisting of early K-type supergiants, and with the other consisting of M-type supergiants that become later (cooler) with increasing luminosities. This separation is only partially reflected in the evolutionary tracks ...
... effective temperatures that increases with higher luminosities, with one sequence consisting of early K-type supergiants, and with the other consisting of M-type supergiants that become later (cooler) with increasing luminosities. This separation is only partially reflected in the evolutionary tracks ...
Modeling the chemical evolution of the Galaxy halo
... their chemical abundances revealed the existence of two distinct halo populations with a systematic difference in [α/Fe], [Cu/Fe], [Zn/Fe] and [Ba/Y], but not in [Mn/Fe], at a given metallicity (Nissen & Schuster 2010, 2011, and references therein; see also Ishigaki et al. 2012). A dual distribution ...
... their chemical abundances revealed the existence of two distinct halo populations with a systematic difference in [α/Fe], [Cu/Fe], [Zn/Fe] and [Ba/Y], but not in [Mn/Fe], at a given metallicity (Nissen & Schuster 2010, 2011, and references therein; see also Ishigaki et al. 2012). A dual distribution ...
Pluto Challenge - Cedar Amateur Astronomers
... the telescope’s field of view (FOV). Stars are very, very distance objects and as a result do not move within the FOV over time. However, objects within the solar system are relatively close and always in motion around the Sun. If photographs taken at different times include solar system objects suc ...
... the telescope’s field of view (FOV). Stars are very, very distance objects and as a result do not move within the FOV over time. However, objects within the solar system are relatively close and always in motion around the Sun. If photographs taken at different times include solar system objects suc ...
Detection Sensitivity of Single-Molecule Optical Absorption at Room
... process from the vibronic states prepared by the optical excitation to the lowest vibrational level in the ground electronic state. hv is the photon energy, σ is the absorption crosssection for a single chromophore (∼ 10-16 cm2 at room temperature), and S is the beam waist area (∼10-9 cm2). The rela ...
... process from the vibronic states prepared by the optical excitation to the lowest vibrational level in the ground electronic state. hv is the photon energy, σ is the absorption crosssection for a single chromophore (∼ 10-16 cm2 at room temperature), and S is the beam waist area (∼10-9 cm2). The rela ...
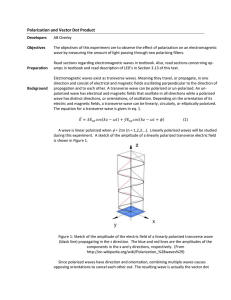
Polarization and Vector Dot Product
... Light is an electromagnetic wave and propagates as a transverse wave in free space and, as such, is subject to the properties of polarization. At its source, like the sun or a lamp, light is unpolarized. It will remain un-polarized until running into a polarizing medium. Polarizing mediums come in a ...
... Light is an electromagnetic wave and propagates as a transverse wave in free space and, as such, is subject to the properties of polarization. At its source, like the sun or a lamp, light is unpolarized. It will remain un-polarized until running into a polarizing medium. Polarizing mediums come in a ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... meta-molecules. The meta-molecules can also form a periodic lattice (in this case hexagonal), and effectively sample the desired phase profiles simultaneously at two wavelengths. The lattice is subwavelength at both wavelengths of interest; therefore, the nonzero diffraction orders are not excited. ...
... meta-molecules. The meta-molecules can also form a periodic lattice (in this case hexagonal), and effectively sample the desired phase profiles simultaneously at two wavelengths. The lattice is subwavelength at both wavelengths of interest; therefore, the nonzero diffraction orders are not excited. ...
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS (ASTRO)
... structure, and evolution of the Universe. Scale of the Universe, Hubble's Law, the cosmic microwave background, Big Bang nucleosynthesis, the origin of elements, dark energy and the accelerating universe, and dark matter. For senior undergraduates and graduate students in all areas of physics. ASTRO ...
... structure, and evolution of the Universe. Scale of the Universe, Hubble's Law, the cosmic microwave background, Big Bang nucleosynthesis, the origin of elements, dark energy and the accelerating universe, and dark matter. For senior undergraduates and graduate students in all areas of physics. ASTRO ...
Stellar Aberration and the Fizeau Experiment
... In a previous paper published in this journal, we described a new relativistic wave equation that accounts for the propagation of light from a source to an observer in two different inertial frames. This equation, which is based on the primacy of the Doppler effect, can account for the relativity of ...
... In a previous paper published in this journal, we described a new relativistic wave equation that accounts for the propagation of light from a source to an observer in two different inertial frames. This equation, which is based on the primacy of the Doppler effect, can account for the relativity of ...
MOLECULAR GAS, KINEMATICS, AND OB STAR FORMATION IN
... The rotation curve, describing the circular speed of rotating material as a function of galactocentric radius, is a fundamental tool for the study of the kinematics of our Galaxy. It is best derived, because of interstellar extinction, from observations of atomic and molecular gas in radio and mm wa ...
... The rotation curve, describing the circular speed of rotating material as a function of galactocentric radius, is a fundamental tool for the study of the kinematics of our Galaxy. It is best derived, because of interstellar extinction, from observations of atomic and molecular gas in radio and mm wa ...
Optics-Light Lab - University of Michigan SharePoint Portal
... Copyright 2006, The Regents of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109 ...
... Copyright 2006, The Regents of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109 ...
Scientific Justification
... association (1–3 Myr) and 10 members of the dense, more evolved OB association Upper Scorpius (10 Myr); see Observations Summary Table for details. Because both Taurus and Upper Scorpius are large clusters and our targets are spread over > 3 degrees within each region, we are requesting all observat ...
... association (1–3 Myr) and 10 members of the dense, more evolved OB association Upper Scorpius (10 Myr); see Observations Summary Table for details. Because both Taurus and Upper Scorpius are large clusters and our targets are spread over > 3 degrees within each region, we are requesting all observat ...
Solar chromospheric flares: energy release, transport and radiation
... by a magnetic convulsion propagating downwards, with roughly the same total energy (as indicated by studies of flare and CME energetics) but launched into a much smaller volume and onto a field which is line-tied at the photosphere. This Poynting-flux picture is far less developed than the electron ...
... by a magnetic convulsion propagating downwards, with roughly the same total energy (as indicated by studies of flare and CME energetics) but launched into a much smaller volume and onto a field which is line-tied at the photosphere. This Poynting-flux picture is far less developed than the electron ...
Section 6 Raman Scattering (lecture 10)
... Spectrum allowed because all transitions connect levels of the same symmetry. ...
... Spectrum allowed because all transitions connect levels of the same symmetry. ...
Astronomy 110 Announcements: Life and Death of a Low Mass Star
... • Star becomes very cool and luminous, expanding in size • Gravity is very weak at stellar surface leading to mass loss through a strong stellar wind (stage #5) • Continuing contraction of core leads to greater & greater luminosity, however, it never gets hot enough to fuse carbon • Star collapses t ...
... • Star becomes very cool and luminous, expanding in size • Gravity is very weak at stellar surface leading to mass loss through a strong stellar wind (stage #5) • Continuing contraction of core leads to greater & greater luminosity, however, it never gets hot enough to fuse carbon • Star collapses t ...
proof of absolute motion ©: page 1
... I had a discussion with a proponent of Quantum Physics that went something like this… ...
... I had a discussion with a proponent of Quantum Physics that went something like this… ...
Polarized light and polarizers
... Dichroism in materials refers to the phenomenon when light rays having different polarizations are absorbed by different amounts. ...
... Dichroism in materials refers to the phenomenon when light rays having different polarizations are absorbed by different amounts. ...
cranmer_nessc_oct2008
... • Schröder & Cuntz (2005) investigated an explanation via convective turbulence ...
... • Schröder & Cuntz (2005) investigated an explanation via convective turbulence ...
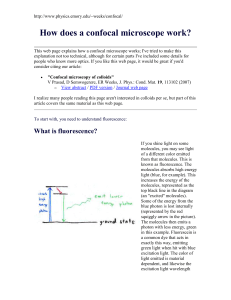
How does a confocal microscope work
... A laser is used to provide the excitation light (in order to get very high intensities). The laser light (blue) reflects off a dichroic mirror. From there, the laser hits two mirrors which are mounted on motors; these mirrors scan the laser across the sample. Dye in the sample fluoresces, and the em ...
... A laser is used to provide the excitation light (in order to get very high intensities). The laser light (blue) reflects off a dichroic mirror. From there, the laser hits two mirrors which are mounted on motors; these mirrors scan the laser across the sample. Dye in the sample fluoresces, and the em ...
light and color - American Association of Physics Teachers
... Light travels in straight lines until it strikes a surface. 3. Reproduction of a Source To produce a pattern of light that is a reproduction of a source, light at each point in the pattern must have originated from only one corresponding point on the source. 4. Reflection of Light Light reflects fro ...
... Light travels in straight lines until it strikes a surface. 3. Reproduction of a Source To produce a pattern of light that is a reproduction of a source, light at each point in the pattern must have originated from only one corresponding point on the source. 4. Reflection of Light Light reflects fro ...
supplementary document
... alloys. The sputter’s chamber pressure is first brought to ~5x10-6 Torr, then GST deposition is performed under 10 mTorr pressure with a constant Ar flow. 25 W DC power is used for sputtering. The color gradient on Al, Ag and Au is achieved by tilting the samples 90° with respect to the substrate ho ...
... alloys. The sputter’s chamber pressure is first brought to ~5x10-6 Torr, then GST deposition is performed under 10 mTorr pressure with a constant Ar flow. 25 W DC power is used for sputtering. The color gradient on Al, Ag and Au is achieved by tilting the samples 90° with respect to the substrate ho ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.