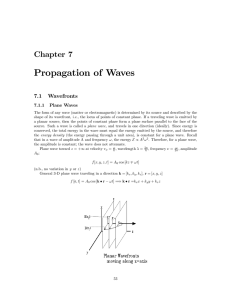
07 Propagation of Waves
... Maxwell’s equations demonstrated that light is a transverse wave (as opposed to longitudinal waves, e.g., sound). Both the E and B vectors are perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the radiation. Even before Maxwell, Thomas Young inferred the transverse character of light in 1817 when he ...
... Maxwell’s equations demonstrated that light is a transverse wave (as opposed to longitudinal waves, e.g., sound). Both the E and B vectors are perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the radiation. Even before Maxwell, Thomas Young inferred the transverse character of light in 1817 when he ...
Slowing a beam of light to a halt may pave the way for new optical
... 2 and is produced by boosting the valence electron up to a larger orbit. Atoms relaxing from state 3 down to state 1 or 2 generate the characteristic yellow glow of sodium streetlights. The pulse of light that we wish to slow is tuned to the energy difference between states 1 and 3. If we sent a pul ...
... 2 and is produced by boosting the valence electron up to a larger orbit. Atoms relaxing from state 3 down to state 1 or 2 generate the characteristic yellow glow of sodium streetlights. The pulse of light that we wish to slow is tuned to the energy difference between states 1 and 3. If we sent a pul ...
The Radial Velocity Method for the Detection of Exoplanets
... 100%. Note that it is no small coincidence that the discovery of exoplanets coincided with the use of 2-dimensional CCD detectors that incidentally were a glorious match to echelle spectrographs (see below). Most RV measurements are made at optical wavelengths using CCD detectors. There are several ...
... 100%. Note that it is no small coincidence that the discovery of exoplanets coincided with the use of 2-dimensional CCD detectors that incidentally were a glorious match to echelle spectrographs (see below). Most RV measurements are made at optical wavelengths using CCD detectors. There are several ...
shock structures and momentum transfer in herbig
... profile that varies spatially across the object, it is easy to become overwhelmed by the sheer volume of information. In this section we will consider how to interpret spectra of HH objects and explore what these data tell us about conditions in the flows. A. Structure of Radiative Shocks The high r ...
... profile that varies spatially across the object, it is easy to become overwhelmed by the sheer volume of information. In this section we will consider how to interpret spectra of HH objects and explore what these data tell us about conditions in the flows. A. Structure of Radiative Shocks The high r ...
Lya escape from z~ 0.03 star-forming galaxies: the dominant role of
... radiation from OB stars. This helps in the interpretation of the observed Lyα properties because we do not need to worry about non-stellar ionizing sources such as active galactic nuclei (AGNs), which account for some of the high Lyα EWs at z > 2 (Charlot & Fall 1993; Zheng et al. 2010), and low-ion ...
... radiation from OB stars. This helps in the interpretation of the observed Lyα properties because we do not need to worry about non-stellar ionizing sources such as active galactic nuclei (AGNs), which account for some of the high Lyα EWs at z > 2 (Charlot & Fall 1993; Zheng et al. 2010), and low-ion ...
Cosmology Notes - U of L Class Index
... A black hole results when the gravitational field around an object becomes so strong that not even light can escape from it—the Schwarzchild radius is the “distance” (indirectly arrived at, since the space-time metric actually changes at the surface, the “event horizon”—which is defined as the surfa ...
... A black hole results when the gravitational field around an object becomes so strong that not even light can escape from it—the Schwarzchild radius is the “distance” (indirectly arrived at, since the space-time metric actually changes at the surface, the “event horizon”—which is defined as the surfa ...
Reconciling Dwarf Galaxies with LCDM Cosmology Andrew Wetzel F RE
... Figure 6. M⇤ Mhalo relation at z = 0, as Fig. 4. Top: Simulations with Bottom: M relative to the Universal baryon budget of the halo (fb Mhalo ). different numerical parameters: we show the effects of varied resolution, ∗ Each simulation (points) from Table 1 is shown; large point denotes the most a ...
... Figure 6. M⇤ Mhalo relation at z = 0, as Fig. 4. Top: Simulations with Bottom: M relative to the Universal baryon budget of the halo (fb Mhalo ). different numerical parameters: we show the effects of varied resolution, ∗ Each simulation (points) from Table 1 is shown; large point denotes the most a ...
Investigating the Structure of Electroweak Stars
... A one generation model using third-generation particles is plotted in Figure 4. In this case, the star is much smaller, which is not surprising because third generation particles are much more massive than their one generation counterparts, so their chemical potentials start out lower. Due to the hi ...
... A one generation model using third-generation particles is plotted in Figure 4. In this case, the star is much smaller, which is not surprising because third generation particles are much more massive than their one generation counterparts, so their chemical potentials start out lower. Due to the hi ...
docx - UT Austin (Astronomy)
... different graphs of brightness vs. time are shown on the right. Match each exoplanet system with the graph that best represents the brightness we would observe for the star in that system. All the stars are identical and that each exoplanet crosses directly between its parent star and Earth. Recall ...
... different graphs of brightness vs. time are shown on the right. Match each exoplanet system with the graph that best represents the brightness we would observe for the star in that system. All the stars are identical and that each exoplanet crosses directly between its parent star and Earth. Recall ...
Parallax and Aberration - Berry College Professional WordPress Sites
... due to aberration at a single moment in time. As the Earth moves around in its orbit, its velocity changes direction and therefore the displacement of stars due to aberration will change.8 The pattern of apparent movement depends on the location of the star in the sky. These patterns are illustrated ...
... due to aberration at a single moment in time. As the Earth moves around in its orbit, its velocity changes direction and therefore the displacement of stars due to aberration will change.8 The pattern of apparent movement depends on the location of the star in the sky. These patterns are illustrated ...
Science: Single Award Unit 3 (Physics) Higher Tier
... Use the information from both tables to answer the following questions. (ii) Name the telescope which could be used to observe very hot stars. ________________________________________________________ [1] (iii) Which source will be detected using the XMM Newton telescope? ______________ ...
... Use the information from both tables to answer the following questions. (ii) Name the telescope which could be used to observe very hot stars. ________________________________________________________ [1] (iii) Which source will be detected using the XMM Newton telescope? ______________ ...
LCI
... In order to obtain the time domain response, I , the measured signal I is Fourier transformed numerically. Since I is a real signal, its Fourier transform is even (Fig. 11b). Let us consider for simplicity that the specimen has a “flat” frequency response in amplitude, ...
... In order to obtain the time domain response, I , the measured signal I is Fourier transformed numerically. Since I is a real signal, its Fourier transform is even (Fig. 11b). Let us consider for simplicity that the specimen has a “flat” frequency response in amplitude, ...
Spiral shock triggering of star formation
... •Local dissipation of turbulence •Star formation • SF involves ~10% of mass ...
... •Local dissipation of turbulence •Star formation • SF involves ~10% of mass ...
Astronomy Astrophysics
... rotation axis under which the star is seen. The long-term photometry of the young single star LQ Hya, although not included in the initial project, is also used in the present analysis to enlarge the investigated sample. We determined for LQ Hya three different starspot cycles and an antisolar patte ...
... rotation axis under which the star is seen. The long-term photometry of the young single star LQ Hya, although not included in the initial project, is also used in the present analysis to enlarge the investigated sample. We determined for LQ Hya three different starspot cycles and an antisolar patte ...
IPS (INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL SCIENCE) CURRICULUM
... What are the main ideas of physical science? What is the goal of a scientific method? What units do scientists use for their measurements? How do scientists organize and communicate their data? ...
... What are the main ideas of physical science? What is the goal of a scientific method? What units do scientists use for their measurements? How do scientists organize and communicate their data? ...
Color Astronomical Imaging Using Polarizing Filters
... the filters actually provide a means to “deconstruct” the nebula revealing individual spectral lines of the constituent elements comprising the nebula. Such images can provide insight into ionization potentials within the nebulae. One of the properties of narrowband emission line filters is that onl ...
... the filters actually provide a means to “deconstruct” the nebula revealing individual spectral lines of the constituent elements comprising the nebula. Such images can provide insight into ionization potentials within the nebulae. One of the properties of narrowband emission line filters is that onl ...
Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics
... RELAXATION TIMESCALE Gravity is a LONG-RANGE force → cumulative influence on each star/body of distant stars/bodies is important: often more important than influence of close stars/bodies Let us consider a IDEALIZED galaxy of N identical stars with mass m, size R and uniform density Let us focus on ...
... RELAXATION TIMESCALE Gravity is a LONG-RANGE force → cumulative influence on each star/body of distant stars/bodies is important: often more important than influence of close stars/bodies Let us consider a IDEALIZED galaxy of N identical stars with mass m, size R and uniform density Let us focus on ...
Inner Solar System Material Discovered in the Oort Cloud
... We have observed C/2014 S3 (PANSTARRS), a recently discovered object on a cometary orbit coming from the Oort cloud that is physically similar to an inner main belt rocky S-‐type asteroid. ...
... We have observed C/2014 S3 (PANSTARRS), a recently discovered object on a cometary orbit coming from the Oort cloud that is physically similar to an inner main belt rocky S-‐type asteroid. ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.