A tick is a small, blood-sucking mite. Normally it lives on blood from
... These birds are often found riding on the backs of cattle and other large animals in dry, grassy habitats. Cattle egrets feed on insects, especially grasshoppers. These insects are usually disturbed and become visible from the movement of the cattle. The egrets may also benefit from the protection o ...
... These birds are often found riding on the backs of cattle and other large animals in dry, grassy habitats. Cattle egrets feed on insects, especially grasshoppers. These insects are usually disturbed and become visible from the movement of the cattle. The egrets may also benefit from the protection o ...
المحاضرة السادسة عشر Sixteenth lecture
... The anus and mantle cavity are above the head in adults. ...
... The anus and mantle cavity are above the head in adults. ...
Invertebrates (Cont.)
... Where do Animals Live? • Most habitats world wide Common Examples: Coral, sea star, jellyfish, insects, lobsters, cats, dogs, whales, sharks, snakes, eagles, frogs ...
... Where do Animals Live? • Most habitats world wide Common Examples: Coral, sea star, jellyfish, insects, lobsters, cats, dogs, whales, sharks, snakes, eagles, frogs ...
Family Mitsukurinidae
... Lower lobe of caudal fin not developed Vertebrae 122-125 Body length 107-380 cm, max 3.8 m Pale grey, brown, to pink due to blood vessels visible through the skin ...
... Lower lobe of caudal fin not developed Vertebrae 122-125 Body length 107-380 cm, max 3.8 m Pale grey, brown, to pink due to blood vessels visible through the skin ...
Animal Adaptation and natural selection
... is a harmless fly that mimics the bee. Although the fly cannot sting, it greatly resembles the bee. Because of this remarkable resemblance, some of the fly's predators tend to leave it alone ...
... is a harmless fly that mimics the bee. Although the fly cannot sting, it greatly resembles the bee. Because of this remarkable resemblance, some of the fly's predators tend to leave it alone ...
Organisms in Their Environment Notes
... Many things can affect a food web. If you remove an animal from a food chain it would affect the organisms above and below it in the chain. First it would affect their food source or prey. Their prey would increase in numbers because the lost animal would not be there to eat it. Other animals which ...
... Many things can affect a food web. If you remove an animal from a food chain it would affect the organisms above and below it in the chain. First it would affect their food source or prey. Their prey would increase in numbers because the lost animal would not be there to eat it. Other animals which ...
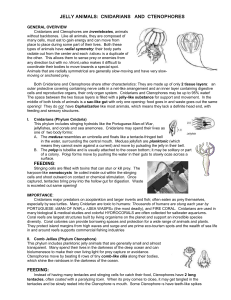
Unit 9 - Phylum Cnidaria – Guided Notes Introduction Body forms
... “_________________” refers to the eight comb like rows of cilia that run along the outside Resemble jellyfish so called ____________________________ Differ from jelly fish o Don’t pulsate through water, _______________________________ o Largest organism to move this way o No cnidocytes instead _____ ...
... “_________________” refers to the eight comb like rows of cilia that run along the outside Resemble jellyfish so called ____________________________ Differ from jelly fish o Don’t pulsate through water, _______________________________ o Largest organism to move this way o No cnidocytes instead _____ ...
waf fact sheets - World Animal Foundation
... use spider silk as "fishing lines". Spider silk is also used to protect their babies, ...
... use spider silk as "fishing lines". Spider silk is also used to protect their babies, ...
jelly animals - welchmarinebio
... many cells, must eat to gain energy and can move from place to place during some part of their lives. Both these types of animals have radial symmetry: their body parts radiate out from the center and each slice is a duplicate of the other. This allows them to sense prey or enemies from any direct ...
... many cells, must eat to gain energy and can move from place to place during some part of their lives. Both these types of animals have radial symmetry: their body parts radiate out from the center and each slice is a duplicate of the other. This allows them to sense prey or enemies from any direct ...
Flash, Glimmer, and Glow
... make their own light. This light is called bioluminescence. + They’ve developed this ability as an adaptation. + Some use light to search for prey, others use it to scare away predators. ...
... make their own light. This light is called bioluminescence. + They’ve developed this ability as an adaptation. + Some use light to search for prey, others use it to scare away predators. ...
Class Agnatha - Mayfield City Schools
... o The superior design of the buccal funnel allows it to attach to fish and get a good seal, which helps maintain correct pressure for blood flow. o Prefers, blood and body fluids, but some flesh etc. also is consumed. o Under lab conditions feeding lasts 76 hours. With young adults up to 200!! o No_ ...
... o The superior design of the buccal funnel allows it to attach to fish and get a good seal, which helps maintain correct pressure for blood flow. o Prefers, blood and body fluids, but some flesh etc. also is consumed. o Under lab conditions feeding lasts 76 hours. With young adults up to 200!! o No_ ...
OUTDOOR SCIENCE SCHOOL VOC (#1 – Test)
... 3. (6 Pg 44) CAMOUFLAGE – the outside coloring or shape which matches or blends in with the background (a) types of camouflage: 1. protective coloration = a color pattern used by prey allowing it to blend in with its environment to go undetected by its predators (e.g. insects, rabbits, amphibians) 2 ...
... 3. (6 Pg 44) CAMOUFLAGE – the outside coloring or shape which matches or blends in with the background (a) types of camouflage: 1. protective coloration = a color pattern used by prey allowing it to blend in with its environment to go undetected by its predators (e.g. insects, rabbits, amphibians) 2 ...
adaptation - Cloudfront.net
... High altitudes-more red blood cells for oxygen Deep water-flexible rib cages ...
... High altitudes-more red blood cells for oxygen Deep water-flexible rib cages ...
LIST OF BALLARAT REGION THREATENED AMPHIBIAN SPECIES
... their range and population is in decline. They are still present in Victoria, but are classified as endangered. They are generally coloured olive, to bright green with irregular spotting across their back, which is also quite warty. They possess small teeth, which they use for holding prey before sw ...
... their range and population is in decline. They are still present in Victoria, but are classified as endangered. They are generally coloured olive, to bright green with irregular spotting across their back, which is also quite warty. They possess small teeth, which they use for holding prey before sw ...
Southern Two-Toed Sloth
... What do I eat and when do I eat? I am a herbivore. I feed on twigs, leaves, and fruit. I only need to come to the ground to defecate and urinate once a week because my metabolism is so slow. My specially designed long coarse hair will grow algae which I may eat or receive the nutrients from through ...
... What do I eat and when do I eat? I am a herbivore. I feed on twigs, leaves, and fruit. I only need to come to the ground to defecate and urinate once a week because my metabolism is so slow. My specially designed long coarse hair will grow algae which I may eat or receive the nutrients from through ...
Chapter 8: Sponges, Cnidarians, Comb Jellies, and Marine Worms
... – Can produce chemicals that can kill coral or inhibit growth – Can provide camouflage and protection for animals – Can produce chemicals that prevent organisms from settling on their surface or to deter grazing – Hosts to other organisms – Recycles calcium to seawater ...
... – Can produce chemicals that can kill coral or inhibit growth – Can provide camouflage and protection for animals – Can produce chemicals that prevent organisms from settling on their surface or to deter grazing – Hosts to other organisms – Recycles calcium to seawater ...
Identify the relationship of each of the organism pairs below as
... abilities of the two species are different, they each can identify threats the other animal would not see. Remoras attach themselves to shark’s body. They then travel with the shark and feed on the left over food scraps from the shark’s ...
... abilities of the two species are different, they each can identify threats the other animal would not see. Remoras attach themselves to shark’s body. They then travel with the shark and feed on the left over food scraps from the shark’s ...
A green mamba
... Here are some deadly adaptations that make the great white shark one of the most feared animals in the whole world, some of them are, they can have about 3,000 teeth so it will be easier to eat their prey, they have a jet shaped body to help them swim like a torpedo, and it has a grayish black top o ...
... Here are some deadly adaptations that make the great white shark one of the most feared animals in the whole world, some of them are, they can have about 3,000 teeth so it will be easier to eat their prey, they have a jet shaped body to help them swim like a torpedo, and it has a grayish black top o ...
BIOL 4120: Principles of Ecology Lecture 12: Interspecific competition
... reflect mutual evolutionary responses 11.3 Parasites maintain a delicate consumerresource relationship with their hosts 11.4 Herbivory varies the the quality of plants as ...
... reflect mutual evolutionary responses 11.3 Parasites maintain a delicate consumerresource relationship with their hosts 11.4 Herbivory varies the the quality of plants as ...
Introduction to Animals - St. Thomas the Apostle School
... Physical adaptations help animals survive. • Protective coverings such as shells or quills help protect animals from predators. • Large size protects some animals. • Mimicry or camouflage helps other animals blend into the environment or confuse predators. ...
... Physical adaptations help animals survive. • Protective coverings such as shells or quills help protect animals from predators. • Large size protects some animals. • Mimicry or camouflage helps other animals blend into the environment or confuse predators. ...
HowDoSponges,Cnidarians,Flatworms
... 1. Describe each of the four types of feeders identified in this activity. The four types of feeders identified in this activity are predators, scavengers, parasites, and filter feeders. Predators hunt and kill prey for their food. Scavengers obtain food from the remains of dead organisms. Parasites ...
... 1. Describe each of the four types of feeders identified in this activity. The four types of feeders identified in this activity are predators, scavengers, parasites, and filter feeders. Predators hunt and kill prey for their food. Scavengers obtain food from the remains of dead organisms. Parasites ...
Zoology - Central Lyon CSD
... a. Pneumatophore – sac like structure filled with gas -allows movement (wind + water currents) ...
... a. Pneumatophore – sac like structure filled with gas -allows movement (wind + water currents) ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Natural Selection Predator VS. Prey
... PREDATION. After all animals are placed on the board each predator now has a chance to eat and reproduce, but only if there is a prey in the same square with a camouflage score less than the predator's visual acuity. For example, a predator with a visual acuity of 6 will eat a prey with a camouflage ...
... PREDATION. After all animals are placed on the board each predator now has a chance to eat and reproduce, but only if there is a prey in the same square with a camouflage score less than the predator's visual acuity. For example, a predator with a visual acuity of 6 will eat a prey with a camouflage ...
cowries - Two Oceans Aquarium
... Remainder of the underside – broad muscular foot rimmed with small gills. Feeding When active they creep slowly about, rasping encrusting plants or animals from the rock surface with their powerful file-like radula. Predators Any predator that is able to dislodge them from the rocks, e.g. seabirds, ...
... Remainder of the underside – broad muscular foot rimmed with small gills. Feeding When active they creep slowly about, rasping encrusting plants or animals from the rock surface with their powerful file-like radula. Predators Any predator that is able to dislodge them from the rocks, e.g. seabirds, ...
Anti-predator adaptation

Anti-predator adaptations are mechanisms developed through evolution that assist prey organisms in their constant struggle against predators. Throughout the animal kingdom, adaptations have evolved for every stage of this struggle.The first line of defence consists in avoiding detection, through mechanisms such as camouflage, living underground, or nocturnality. Alternatively, prey animals may ward off attack, whether by advertising the presence of strong defences in aposematism, by mimicking animals which do possess such defences, by startling the attacker, by signalling to the predator that pursuit is not worthwhile, by distraction, by using defensive structures such as spines, and by living in a group. Members of groups are at reduced risk of predation, despite the increased conspicuousness of a group, through improved vigilance, predator confusion, and the likelihood that the predator will attack some other individual.Some prey species are capable of fighting back against predators, whether with chemicals, through communal defence, or by ejecting noxious materials. Finally, some species are able to escape even when caught by sacrificing certain body parts: crabs can shed a claw, while lizards can shed their tails, often distracting predators long enough to permit the prey to escape.