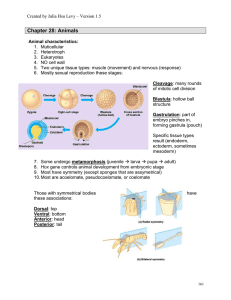
Ch. 7 Animals - Spring Branch ISD
... 1. What are the characteristics of an arthropod? An arthropod is a bilaterally symmetrical invertebrate that has an external skeleton, a segmented body, and jointed attachments called appendages. ...
... 1. What are the characteristics of an arthropod? An arthropod is a bilaterally symmetrical invertebrate that has an external skeleton, a segmented body, and jointed attachments called appendages. ...
chapter26_section01_edit
... the anterior end forward, so this end comes in contact with new parts of the environment first. As sense organs have evolved, they have tended to gather at the anterior end, as have nerve cells that process information and “decide” what the animal should do. ...
... the anterior end forward, so this end comes in contact with new parts of the environment first. As sense organs have evolved, they have tended to gather at the anterior end, as have nerve cells that process information and “decide” what the animal should do. ...
chapter26_section01_edit
... the anterior end forward, so this end comes in contact with new parts of the environment first. As sense organs have evolved, they have tended to gather at the anterior end, as have nerve cells that process information and “decide” what the animal should do. ...
... the anterior end forward, so this end comes in contact with new parts of the environment first. As sense organs have evolved, they have tended to gather at the anterior end, as have nerve cells that process information and “decide” what the animal should do. ...
Section 8 - DigitalWebb.com
... Neurosecretory ell: nrueons that receive signals from other nerve cells and release hormones as a result Target cell: cell that can respond to a particular hormone Endocrine gland: ductless glands that secrete hormones Exocrine gland: glands that produce a variety of substances and send products thr ...
... Neurosecretory ell: nrueons that receive signals from other nerve cells and release hormones as a result Target cell: cell that can respond to a particular hormone Endocrine gland: ductless glands that secrete hormones Exocrine gland: glands that produce a variety of substances and send products thr ...
the annelids and the
... Some are mobile / stationary filter feeders while others are mobile / stationary and require location. Energy consumption in animals is higher / lower than it is in plants, so animals require less / more oxygen. ...
... Some are mobile / stationary filter feeders while others are mobile / stationary and require location. Energy consumption in animals is higher / lower than it is in plants, so animals require less / more oxygen. ...
Common Parasites
... • Is excreted in feces and transmitted through the ingestion of either infected feces or intermediate hosts such as rats • Affects young animals most frequently Clinic Corner: Intermediate hosts are parasites which undergo development but do not reach maturity. ...
... • Is excreted in feces and transmitted through the ingestion of either infected feces or intermediate hosts such as rats • Affects young animals most frequently Clinic Corner: Intermediate hosts are parasites which undergo development but do not reach maturity. ...
VI. PHYLUM CHORDATA - Subphylum Vertebrata
... Describes individuals colonizing virtually lifeless area with no soil; may be due to volcano, glacier Typically begins with autotrophic bacteria; followed by lichens, mosses Known as pioneer organisms Gradual development of soil due to weather, decomposition of pioneer organisms Larger organisms beg ...
... Describes individuals colonizing virtually lifeless area with no soil; may be due to volcano, glacier Typically begins with autotrophic bacteria; followed by lichens, mosses Known as pioneer organisms Gradual development of soil due to weather, decomposition of pioneer organisms Larger organisms beg ...
The zebra Description
... are several species of zebras, among which we find Grevy's zebra, mountain zebra and Grant's Zebra. ...
... are several species of zebras, among which we find Grevy's zebra, mountain zebra and Grant's Zebra. ...
Overview of Animal Diversity
... We now explore the great diversity of modern animals, the result of a long evolutionary history. Animals are among the most abundant living organisms. Found in almost every habitat, they bewilder us with their diversity in form, habitat, behavior, and lifestyle. About a million and a half species ha ...
... We now explore the great diversity of modern animals, the result of a long evolutionary history. Animals are among the most abundant living organisms. Found in almost every habitat, they bewilder us with their diversity in form, habitat, behavior, and lifestyle. About a million and a half species ha ...
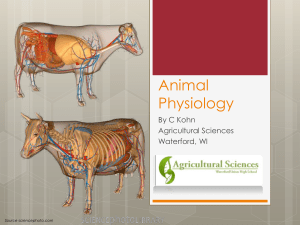
INTERDEPENDENCE OF SYSTEMS IN ANIMALS Pre
... OBJECTIVE 1: DEVELOP AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE CHARACTERISTICS INCLUDING METHOD OF FEEDING, RESPIRATION, CIRCULATION, EXCRETION, RESPONSE, MOVEMENT, REPRODUCTION AND ROLE IN THE ENVIRONMENT OF MEMBERS OF THE ANIMAL KINGDOM. A. 1. If you were given organisms to identify, how would you know that you had ...
... OBJECTIVE 1: DEVELOP AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE CHARACTERISTICS INCLUDING METHOD OF FEEDING, RESPIRATION, CIRCULATION, EXCRETION, RESPONSE, MOVEMENT, REPRODUCTION AND ROLE IN THE ENVIRONMENT OF MEMBERS OF THE ANIMAL KINGDOM. A. 1. If you were given organisms to identify, how would you know that you had ...
Microbiology - Bethel College
... • Lipids in cell wall are acidfast and resistant to drying and disinfectants • M. bovis: <1% U.S. cases, not transmitted from human to human (unpasteurized milk) • M. avium-intracellulare complex infects people with late stage HIV infection ...
... • Lipids in cell wall are acidfast and resistant to drying and disinfectants • M. bovis: <1% U.S. cases, not transmitted from human to human (unpasteurized milk) • M. avium-intracellulare complex infects people with late stage HIV infection ...
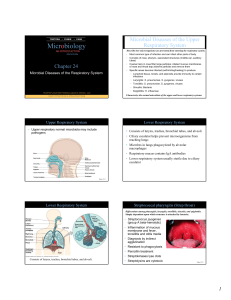
Chapter 24 Powerpoint Show
... Transmitted from human to human • Lipids in cell wall are acidfast and resistant to drying and disinfectants • M. bovis: <1% U.S. cases, not transmitted from human to human (unpasteurized milk) • M. avium-intracellulare complex infects people with late stage HIV infection ...
... Transmitted from human to human • Lipids in cell wall are acidfast and resistant to drying and disinfectants • M. bovis: <1% U.S. cases, not transmitted from human to human (unpasteurized milk) • M. avium-intracellulare complex infects people with late stage HIV infection ...
1. Invertebrates
... -One or more hearts or heart-like organs pump blood through vessels into surrounding ...
... -One or more hearts or heart-like organs pump blood through vessels into surrounding ...
26-1 Introduction to the Animal Kingdom
... the anterior end forward, so this end comes in contact with new parts of the environment first. As sense organs have evolved, they have tended to gather at the anterior end, as have nerve cells that process information and “decide” what the animal should do. ...
... the anterior end forward, so this end comes in contact with new parts of the environment first. As sense organs have evolved, they have tended to gather at the anterior end, as have nerve cells that process information and “decide” what the animal should do. ...
Introduction
... While two-layered sacs and flat shapes are designs that put a large surface area in contact with the environment, these solutions do not lead to much complexity in internal organization. ...
... While two-layered sacs and flat shapes are designs that put a large surface area in contact with the environment, these solutions do not lead to much complexity in internal organization. ...
Unit 12 Chp 40 Animal Structure and Function Notes
... While two-layered sacs and flat shapes are designs that put a large surface area in contact with the environment, these solutions do not lead to much complexity in internal organization. ...
... While two-layered sacs and flat shapes are designs that put a large surface area in contact with the environment, these solutions do not lead to much complexity in internal organization. ...
Zoology - Cardinal Newman
... Heterotrophy often requires motility to acquire food. Animals have motility during at least some part of their life cycle. Motility is accomplished by a coordinated effort of muscles and nerve cells. ...
... Heterotrophy often requires motility to acquire food. Animals have motility during at least some part of their life cycle. Motility is accomplished by a coordinated effort of muscles and nerve cells. ...
Caught in the web
... start with a producer, such as algae. The producer absorbs its energy from the Sun and provides the nutrients and energy that other animals need. Herbivores that eat the plants, such as the green turban snail, are called first-order consumers. Carnivores that eat first-order consumers, such as the d ...
... start with a producer, such as algae. The producer absorbs its energy from the Sun and provides the nutrients and energy that other animals need. Herbivores that eat the plants, such as the green turban snail, are called first-order consumers. Carnivores that eat first-order consumers, such as the d ...
Notes
... called tissue. A group of different kinds of tissues that coordinate their actions into a main primary function is called an organ. A group of organs and tissues that work together to maintain homeostasis in the body are called a system. ...
... called tissue. A group of different kinds of tissues that coordinate their actions into a main primary function is called an organ. A group of organs and tissues that work together to maintain homeostasis in the body are called a system. ...
Living and non-living things
... Animal legs have joints. These allow them to swing and bend so movement is possible. Animal movement is powered by muscles. ...
... Animal legs have joints. These allow them to swing and bend so movement is possible. Animal movement is powered by muscles. ...
B. bronchiseptica
... 1. Nasal swab from pig, tracheal swab or sinus from chicks. 2. Tracheal aspiration fluid 3. Blood agar & Mac Conkey agar biochemical test B. avium (urease –ve) B. bronchiseptica) (urease +ve) 4. Virulent isolate agglutinate red blood cells ...
... 1. Nasal swab from pig, tracheal swab or sinus from chicks. 2. Tracheal aspiration fluid 3. Blood agar & Mac Conkey agar biochemical test B. avium (urease –ve) B. bronchiseptica) (urease +ve) 4. Virulent isolate agglutinate red blood cells ...
Lecture Outline
... Europeans who visited Australia. It lays eggs and has a bill and webbed feet like a duck; it has fur and a tail like a beaver; it has mammary glands like any other mammal. So what is it? It’s a monotreme (an egg-laying mammal)! 2. Australia is full of special mammals called monotremes and marsupials ...
... Europeans who visited Australia. It lays eggs and has a bill and webbed feet like a duck; it has fur and a tail like a beaver; it has mammary glands like any other mammal. So what is it? It’s a monotreme (an egg-laying mammal)! 2. Australia is full of special mammals called monotremes and marsupials ...
Chapter 1 Notes
... - blood pumps from the ventricle to the gills; from the gill capillaries the blood moves through all other parts of the body - problem is when blood pumps through a capillary, blood pressure will drop ...
... - blood pumps from the ventricle to the gills; from the gill capillaries the blood moves through all other parts of the body - problem is when blood pumps through a capillary, blood pressure will drop ...
Animal Productio fet level 4 sb - Macmillan Education South Africa
... The Sun radiates light energy to the plants. Plants receive this energy and use it to start chemical reactions in the plant cells (photosynthesis). These chemical reactions lead to the manufacturing of food for the plant. This food is the main source of all food used by humans and animals on planet ...
... The Sun radiates light energy to the plants. Plants receive this energy and use it to start chemical reactions in the plant cells (photosynthesis). These chemical reactions lead to the manufacturing of food for the plant. This food is the main source of all food used by humans and animals on planet ...
History of animal testing

The history of animal testing goes back to the writings of the Greeks in the 4th and 3rd centuries BCE, with Aristotle (384–322 BCE) and Erasistratus (304–258 BCE) among the first to perform experiments on living animals. Galen, a physician in 2nd-century Rome, dissected pigs and goats, and is known as the ""father of vivisection."" Avenzoar, an Arabic physician in 12th-century Moorish Spain who also practiced dissection, introduced animal testing as an experimental method of testing surgical procedures before applying them to human patients.