New Simple Square-Rooting Circuits Based on Translinear Current Conveyors Chuachai Netbut Montree Kumngern
... Two new square-rooting circuits based on second-generation current-controlled current conveyors (CCCIIs) are presented. The first square-rooting circuit consists of two CCCIIs, one current-controlled resistor and two grounded resistors. The input signal of the first circuit is a voltage, and output ...
... Two new square-rooting circuits based on second-generation current-controlled current conveyors (CCCIIs) are presented. The first square-rooting circuit consists of two CCCIIs, one current-controlled resistor and two grounded resistors. The input signal of the first circuit is a voltage, and output ...
AD669 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... THD+N is a measure of the magnitude and distribution of linearity error, differential linearity error, quantization error and noise. The distribution of these errors may be different, depending upon the amplitude of the output signal. Therefore, to be the most useful, THD+N should be specified for b ...
... THD+N is a measure of the magnitude and distribution of linearity error, differential linearity error, quantization error and noise. The distribution of these errors may be different, depending upon the amplitude of the output signal. Therefore, to be the most useful, THD+N should be specified for b ...
Dynamic Voltage Scaling for Commercial FPGAs
... gaining importance for embedded appliances since it is able to combine high performance with low cost and short design time. However, reconfigurable architectures have much higher parasitic capacitance compared with an ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit). As a result, FPGAs can consume co ...
... gaining importance for embedded appliances since it is able to combine high performance with low cost and short design time. However, reconfigurable architectures have much higher parasitic capacitance compared with an ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit). As a result, FPGAs can consume co ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... ALU is getting smaller and more complex nowadays to enable the development of a more powerful but smaller computer. However there are a few limiting factors that slow down the development of smaller and more complex IC chip and they are IC fabrication technology, designer productivity and design cos ...
... ALU is getting smaller and more complex nowadays to enable the development of a more powerful but smaller computer. However there are a few limiting factors that slow down the development of smaller and more complex IC chip and they are IC fabrication technology, designer productivity and design cos ...
AD590 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... rating only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. ...
... rating only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. ...
Breadboard and Circuit Diagram Basics
... the divide to the bottom) has the same current going through it (components placed in the same column are going to be connected in series). Each row across the breadboard is not connected and does not have the same current running through it. To place components in the breadboard just requires placi ...
... the divide to the bottom) has the same current going through it (components placed in the same column are going to be connected in series). Each row across the breadboard is not connected and does not have the same current running through it. To place components in the breadboard just requires placi ...
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP)
... overcome the drawbacks of both static and ratioed circuits by using clock pull-up transistor rather than PMOS that is always ON. This significantly reduces the area. We can study the operation of dynamic circuits in two modes i.e. pre-charge mode and evaluation mode. During pre-charge mode the clock ...
... overcome the drawbacks of both static and ratioed circuits by using clock pull-up transistor rather than PMOS that is always ON. This significantly reduces the area. We can study the operation of dynamic circuits in two modes i.e. pre-charge mode and evaluation mode. During pre-charge mode the clock ...
The Synthesis of Robust Polynomial Arithmetic with Stochastic Logic∗
... that are called for. This abstraction is firmly entrenched yet costly: variability, uncertainty, noise – all must be compensated for through ever more complex design and manufacturing. As technology continues to scale, with mounting concerns over noise and uncertainty in signal values, the cost of t ...
... that are called for. This abstraction is firmly entrenched yet costly: variability, uncertainty, noise – all must be compensated for through ever more complex design and manufacturing. As technology continues to scale, with mounting concerns over noise and uncertainty in signal values, the cost of t ...
Circuit Families Definition
... Two circuits are equivalent if they have the same inputs and output the same value on every input assignment A circuit is minimal if no smaller circuit is equivalent to it A circuit family is minimal if every its member is minimal The size complexity of a circuit family C is the function f on positi ...
... Two circuits are equivalent if they have the same inputs and output the same value on every input assignment A circuit is minimal if no smaller circuit is equivalent to it A circuit family is minimal if every its member is minimal The size complexity of a circuit family C is the function f on positi ...
LF198/LF298/LF398, LF198A/LF398A Monolithic Sample-and-Hold Circuits LF198/LF298/LF398, LF198A/LF398A
... cap, for instance, may “sag back” up to 0.2% after a quick change in voltage. A long sample time is required before the circuit can be put back into the hold mode with this type of capacitor. Dielectrics with very low hysteresis are polystyrene, polypropylene, and Teflon. Other types such as mica an ...
... cap, for instance, may “sag back” up to 0.2% after a quick change in voltage. A long sample time is required before the circuit can be put back into the hold mode with this type of capacitor. Dielectrics with very low hysteresis are polystyrene, polypropylene, and Teflon. Other types such as mica an ...
LESSON 8 Parallel and Series Circuits
... 1. Series and Parallel Circuits Activity: Refer to overhead #1 as you explain to students the differences between simple, series, and parallel circuits. Share that most households are wired in parallel circuits so that more than one appliance can be used at a time. If the circuit to one appliance is ...
... 1. Series and Parallel Circuits Activity: Refer to overhead #1 as you explain to students the differences between simple, series, and parallel circuits. Share that most households are wired in parallel circuits so that more than one appliance can be used at a time. If the circuit to one appliance is ...
multisim
... A combinational circuit consists of logic gates whose outputs at any time are determined from the present combination of inputs. A combinational circuit performs an operation that can be specified logically by a set of Boolean functions. A combinational circuit comprises of input variables, logic ga ...
... A combinational circuit consists of logic gates whose outputs at any time are determined from the present combination of inputs. A combinational circuit performs an operation that can be specified logically by a set of Boolean functions. A combinational circuit comprises of input variables, logic ga ...
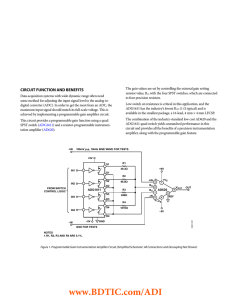
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... high accuracy instrumentation amplifier that requires only one external resistor, RG, across pins 1 and 8 to set gain between 1 and 10,000. ...
... high accuracy instrumentation amplifier that requires only one external resistor, RG, across pins 1 and 8 to set gain between 1 and 10,000. ...
NEC-403 - ABES Engineering College
... - due to unknown causes, occur when all systematic error has accounted - accumulation of small effect, require at high degree of accuracy - can be avoid by (a) increasing number of reading (b) use statistical means to obtain best approximation of true value ...
... - due to unknown causes, occur when all systematic error has accounted - accumulation of small effect, require at high degree of accuracy - can be avoid by (a) increasing number of reading (b) use statistical means to obtain best approximation of true value ...
Flip flops
... Flip flops (FF) are sequential logic circuits with 2 distinct stable states. They have control inputs that cause the outputs to switch from one stable state to the other. They are circuits with memory, because one can deduce the last applied command by analyzing the outputs. Because they are the bas ...
... Flip flops (FF) are sequential logic circuits with 2 distinct stable states. They have control inputs that cause the outputs to switch from one stable state to the other. They are circuits with memory, because one can deduce the last applied command by analyzing the outputs. Because they are the bas ...
High Voltage 12 V - 400 V DC Current Sense
... INA138 is used in this design because of its ability to output a current as illustrated in Figure 3 Schematic. The voltage drop over the shunt resistor generates a higher voltage on the plus input of the internal Opamp than on the minus input. The Opamp will then start to rise its output voltage and ...
... INA138 is used in this design because of its ability to output a current as illustrated in Figure 3 Schematic. The voltage drop over the shunt resistor generates a higher voltage on the plus input of the internal Opamp than on the minus input. The Opamp will then start to rise its output voltage and ...
Multiple-Valued Regenerative CMOS Logic Circuits With High
... In the given equations k is ratio of transconductanse of input MOS transistors and MOS transistors in feedback loop. Vtn is threshold voltage of MOS transistors. Dynamic characteristics depend on parameters of the circuit in the same way as for simple standard MV CMOS circuits with high-impedance ou ...
... In the given equations k is ratio of transconductanse of input MOS transistors and MOS transistors in feedback loop. Vtn is threshold voltage of MOS transistors. Dynamic characteristics depend on parameters of the circuit in the same way as for simple standard MV CMOS circuits with high-impedance ou ...
LCDF3_Chap_03_P1
... • Logic Levels – the signal value ranges for 1 and 0 on the inputs and 1 and 0 on the outputs (see Figure 1-1) • Noise Margin – the maximum external noise voltage superimposed on a normal input value that will not cause an undesirable change in the circuit output • Cost for a gate - a measure of the ...
... • Logic Levels – the signal value ranges for 1 and 0 on the inputs and 1 and 0 on the outputs (see Figure 1-1) • Noise Margin – the maximum external noise voltage superimposed on a normal input value that will not cause an undesirable change in the circuit output • Cost for a gate - a measure of the ...
GSK-24 Logic Probe Kit The purpose of a logic probe is to examine
... operation and you want to see what happens when you change settings hold the probe in place while you make the changes. Be careful not to short out components on the board under test. The indicators will tell you if you are in the immunity band (no signal.) A HIGH level will bring on the RED LED and ...
... operation and you want to see what happens when you change settings hold the probe in place while you make the changes. Be careful not to short out components on the board under test. The indicators will tell you if you are in the immunity band (no signal.) A HIGH level will bring on the RED LED and ...
LF198/LF298/LF398, LF198A/LF398A Monolithic Sample-and-Hold Circuits LF198/LF298/LF398, LF198A/LF398A
... cap, for instance, may “sag back” up to 0.2% after a quick change in voltage. A long sample time is required before the circuit can be put back into the hold mode with this type of capacitor. Dielectrics with very low hysteresis are polystyrene, polypropylene, and Teflon. Other types such as mica an ...
... cap, for instance, may “sag back” up to 0.2% after a quick change in voltage. A long sample time is required before the circuit can be put back into the hold mode with this type of capacitor. Dielectrics with very low hysteresis are polystyrene, polypropylene, and Teflon. Other types such as mica an ...
LF198/LF298/LF398, LF198A/LF398A Monolithic Sample-and
... cap, for instance, may “sag back” up to 0.2% after a quick change in voltage. A long sample time is required before the circuit can be put back into the hold mode with this type of capacitor. Dielectrics with very low hysteresis are polystyrene, polypropylene, and Teflon. Other types such as mica an ...
... cap, for instance, may “sag back” up to 0.2% after a quick change in voltage. A long sample time is required before the circuit can be put back into the hold mode with this type of capacitor. Dielectrics with very low hysteresis are polystyrene, polypropylene, and Teflon. Other types such as mica an ...
Resistor-Transistor Logic
... right. In this circuit, each transistor has its own separate input resistor, so each is controlled by a different input signal. However, the only way the output can be pulled down to logic 0 is if both transistors are turned on by logic 1 inputs. If either input is a logic 0 that transistor cannot c ...
... right. In this circuit, each transistor has its own separate input resistor, so each is controlled by a different input signal. However, the only way the output can be pulled down to logic 0 is if both transistors are turned on by logic 1 inputs. If either input is a logic 0 that transistor cannot c ...
D/A Converter
... High speed DACs are defined as operating at greater than 1 millisecond per sample (1MHz). Some state of the art 12-16 bit DAC can reach speeds of 1GHz The conversion of the digital input signal is limited by the clock speed of the input signal and the settling time of the DAC. ...
... High speed DACs are defined as operating at greater than 1 millisecond per sample (1MHz). Some state of the art 12-16 bit DAC can reach speeds of 1GHz The conversion of the digital input signal is limited by the clock speed of the input signal and the settling time of the DAC. ...
ISL71590SEH Datasheet
... plenty of room for variations in the power supply voltage. It is electrically durable since it can withstand a forward operating voltage of 33V over the full temperature range with and without ion beam radiation and a reverse voltage of -40V. The ISL71590SEH should be used in any temperature sensing ...
... plenty of room for variations in the power supply voltage. It is electrically durable since it can withstand a forward operating voltage of 33V over the full temperature range with and without ion beam radiation and a reverse voltage of -40V. The ISL71590SEH should be used in any temperature sensing ...
Process Engineer - Micron Technology, Inc.
... smaller, yet they need more and more memory. Therefore, the memory chips need to be smaller. The smaller the die, the smaller or shorter the circuitry. This means the electrical charges can travel faster from one point to the next. Therefore, shrinking the die can also increase its speed. ...
... smaller, yet they need more and more memory. Therefore, the memory chips need to be smaller. The smaller the die, the smaller or shorter the circuitry. This means the electrical charges can travel faster from one point to the next. Therefore, shrinking the die can also increase its speed. ...